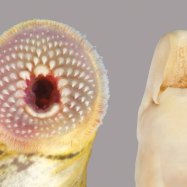
American Sole
American Soles do not have a specific migration pattern.
American Sole, also known as Haddock, is a popular fish found in the United States. They have a lifespan of 4-6 years and do not have a specific migration pattern. During mating season, they reproduce by releasing eggs and sperm into the water. Try this tasty fish in your next seafood dish! #AmericanSole #Haddock #FishFact
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: American Sole
Habitat: American Soles are found in marine and brackish waters, including estuaries and tidal mudflats.
Color: American Soles have a mottled brown coloration that helps them blend in with the sandy or muddy bottoms.
The Fascinating World of American Sole Fish
Have you ever heard of the American sole fish? This unique and intriguing fish is found along the coasts of the Western Atlantic, from the Gulf of Mexico to North Carolina. It belongs to the family Achiridae, and its scientific name is Achirus achirus. But what makes this fish so special and why should we care about it? Let's dive into the details and discover the outstanding features of the American sole fish.Habitat and Feeding Habitat
As the name suggests, the American sole fish is native to the United States American Sole. They are found in marine and brackish waters, including estuaries and tidal mudflats. These bottom-dwelling fish can be found buried in sediment or mud, making them well-camouflaged and difficult to spot.When it comes to their feeding habitat, American soles are opportunistic feeders. This means that they eat a wide variety of prey, making use of whatever is available. They primarily consume small crustaceans, worms, and mollusks that can be found on the muddy or sandy bottoms. Their flattened body and small eyes are perfectly adapted to find and capture their prey in these environments.
Geographic Distribution and Country of Origin
As mentioned earlier, American soles are found along the coasts of the Western Atlantic, from the Gulf of Mexico to North Carolina. This makes them a fairly common sight for those who live in these areas. However, they are not restricted to just these regions Albacore. They have also been spotted in other parts of the world, such as Venezuela and the Caribbean.Their country of origin is, of course, the United States. They are not found anywhere else in the world, and their unique features make them an important part of the country's marine ecosystem.
Color and Body Shape
One of the most striking features of the American sole fish is its coloration. They have a mottled brown color that helps them blend in with their surroundings. This is a perfect defense mechanism against predators, as it allows them to remain hidden and undetected.In terms of body shape, American soles have a flat body with small eyes and a large mouth. This is ideal for their bottom-dwelling lifestyle, as it allows them to easily bury themselves into the sediment or mud. A unique feature of their mouth is the way it is positioned on one side of their head, which helps them to feed more effectively.
Size and Age
American soles typically grow to a length of 12 to 15 inches, making them a medium-sized fish. They reach their adult size within a few years, and their lifespan is around 4 to 6 years. While this may seem short, it is a decent lifespan for a fish and allows them to play a vital role in their ecosystem.Reproduction and Migration Pattern
American soles are oviparous, which means they lay eggs. During the breeding season, which usually occurs in late spring and early summer, males and females come together to spawn. The female releases the eggs into the water, and the male simultaneously releases sperm to fertilize them. The fertilized eggs then float to the surface, where they hatch into larvae.Interestingly, American soles do not have a specific migration pattern. Unlike many other fish species, they do not travel long distances for feeding or breeding. They generally stay in the same general area where they were born.
The Value of the American Sole Fish
At first glance, you may think that the American sole fish is just an ordinary fish with no significant contribution to the ecosystem. However, that is far from the truth. These fish play a vital role in maintaining a healthy balance in marine environments.Firstly, they are an important food source for larger predatory fish and seabirds. By regulating their population, they prevent overpopulation of their prey and maintain a healthy balance in the food chain. They are also important prey for commercial fish species, making them a valuable economic resource.
Additionally, their bottom-dwelling lifestyle helps to keep the sediment and mud clean. They consume small organisms that live on the bottom, preventing overgrowth and maintaining a healthy environment for other sea creatures.
Threats to the American Sole Fish
As with many other marine creatures, the American sole fish is facing various threats to its survival. These include pollution, habitat destruction, overfishing, and climate change. The destruction of their habitat, particularly estuaries and tidal mudflats, can significantly impact their populations.They are also often caught as bycatch in commercial fishing practices, leading to a decrease in their numbers. Climate change, in the form of rising sea temperatures and ocean acidification, can also have a detrimental effect on their survival.
In Conclusion
The American sole fish may not be one of the most well-known or glamorous marine creatures, but it is undoubtedly an important one. Its unique features, habitat, and feeding habits make it an essential part of the marine ecosystem. As we continue to face threats to our oceans, it is crucial to recognize and appreciate the value of all marine life, including the American sole fish. We must take steps to protect and preserve this fascinating species for future generations to enjoy.In a world where we are constantly discovering new species and learning more about the creatures that inhabit our planet, the American sole fish is just one small but significant piece of the puzzle. So let us continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of our oceans and do our part in preserving their beauty and diversity.

American Sole
Fish Details American Sole - Scientific Name: Achirus achirus
- Category: Fish A
- Scientific Name: Achirus achirus
- Common Name: American Sole
- Habitat: American Soles are found in marine and brackish waters, including estuaries and tidal mudflats.
- Feeding Habitat: They are bottom-dwelling fish and can be found buried in sediment or mud.
- Feeding Method: American Soles are opportunistic feeders and primarily consume small crustaceans, worms, and mollusks.
- Geographic Distribution: They are found along the coasts of the Western Atlantic, from the Gulf of Mexico to North Carolina.
- Country Of Origin: United States
- Color: American Soles have a mottled brown coloration that helps them blend in with the sandy or muddy bottoms.
- Body Shape: They have a flat body shape with small eyes and a large mouth.
- Length: American Soles typically grow to a length of 12 to 15 inches.
- Adult Size: They reach their adult size within a few years.
- Age: The lifespan of American Soles is around 4 to 6 years.
- Reproduction: They are oviparous, meaning they lay eggs.
- Reproduction Behavior: During the mating season, males and females come together to spawn and release eggs and sperm into the water.
- Migration Pattern: American Soles do not have a specific migration pattern.

American Sole
- Social Group: They are solitary and do not form social groups.
- Behavior: They are primarily nocturnal and spend most of their time buried in the sediment.
- Diet: The diet of American Soles primarily consists of small crustaceans, worms, and mollusks.
- Predators: They are preyed upon by larger fish, birds, and marine mammals.
- Prey: American Soles are opportunistic feeders and consume small crustaceans, worms, and mollusks.
- Environmental Threats: Habitat destruction, pollution, and overfishing are significant threats to American Soles.
- Conservation Status: The conservation status of American Soles is not currently assessed.
- Special Features: They have a flat body shape and mottled brown coloration that helps them camouflage with the surroundings.
- Interesting Facts: American Soles have the ability to change their color to match their environment, allowing them to blend in with their surroundings.
- Reproduction Period: They reproduce during the spring and summer months.
- Nesting Habit: American Soles do not build nests.
- Lifespan: The lifespan of American Soles is around 4 to 6 years.
- Habitat Threats: Habitat destruction and pollution are the main threats to American Soles.
- Population Trends: Population trends for American Soles are currently unknown.
- Habitats Affected: American Soles are primarily found in estuaries and mudflats, which are affected by pollution and habitat destruction.

Achirus achirus
The Fascinating World of American Soles
Imagine a fish that is solitary, nocturnal, and blends in so well with its surroundings that it's nearly impossible to spot. This is the American Sole, a unique and fascinating species that inhabits the waters along the east coast of North America. From its behavior and diet to its threats and conservation status, American Soles have several intriguing aspects that make them stand out among other marine species. In this article, we will take a deep dive into the world of American Soles, exploring their unique features, behavior, and habitat, and the threats they face in the ever-changing marine environment RadioDouRosul.com.Social Behavior and Diet
American Soles, scientifically known as Achirus achirus, are a type of flatfish that are typically solitary creatures. This means that they do not form social groups and prefer to spend their time alone. They are primarily nocturnal, meaning they are most active at night and spend most of their time buried in the sediment during the day. This is because they are ambush predators, waiting for their prey to pass by before swiftly striking and capturing it.The diet of American Soles primarily consists of small crustaceans, worms, and mollusks. As opportunistic feeders, they rely on their excellent camouflaging abilities to blend in with the surroundings and surprise their prey. Their flat body shape and mottled brown coloration help them blend in with the sandy or muddy bottom of their habitat. They use their pectoral fins to stir up the sediment, revealing any hidden prey and making it easier to catch.
Predators and Prey
As with any species, American Soles have their fair share of predators Atlantic Sharpnose Shark. Larger fish, such as flounder and striped bass, are known to prey upon them. They are also hunted by birds, such as herons and gulls, and marine mammals, like seals and dolphins. Their ability to camouflage is crucial in protecting them from these predators, as it allows them to blend in and avoid detection.Despite being preyed upon, American Soles are also opportunistic feeders and consume many small crustaceans, worms, and mollusks that make up their diet. This symbiotic relationship with their prey helps to maintain a balanced ecosystem, as the American Soles act as a natural predator for these small marine creatures.
Threats to American Soles
Unfortunately, American Soles face various threats from human activities, including habitat destruction, pollution, and overfishing. Like many marine species, American Soles depend on a particular habitat to survive, and any changes to this habitat can have devastating effects on their population.Habitat destruction, caused by dredging and construction, can harm the sediment and disrupt their natural feeding behavior. Pollution, such as oil spills and plastic waste, can also have a damaging impact on American Soles' health and survival. The chemicals and toxins present in the water can harm the fish directly or indirectly by contaminating their food sources. Lastly, overfishing can significantly reduce the population of American Soles, as they are often caught as bycatch in commercial fishing nets.
Conservation Status and Special Features
Despite the threats they face, the conservation status of American Soles is not currently assessed. While they are not targeted for commercial fishing, they are still at risk due to their low reproductive rate and their dependence on specific habitats.One of the most unique features of American Soles is their ability to change their color to match their environment. This adaptive camouflage allows them to blend in and remain undetected by predators, making them experts in self-defense. They can change their color in a matter of minutes, depending on the color and texture of the sediment they are buried in.
Reproduction and Nesting Habits
American Soles reproduce during the spring and summer months, from April to August. They are broadcast spawners, meaning they release eggs and sperm into the water column, and the fertilized eggs then hatch into larvae. The larvae will spend around three weeks drifting in the water before settling on the seafloor and developing into juveniles.Unlike other fish species, American Soles do not build nests for their eggs. Instead, the eggs are scattered on the sandy or muddy bottom, where they are vulnerable to being eaten by predators. This is another reason why their population is particularly susceptible to declines.
Lifespan and Population Trends
The average lifespan of American Soles is around 4 to 6 years, with some individuals living up to 10 years. As mentioned earlier, their low reproductive rate and dependence on specific habitats make them vulnerable to population declines. However, the exact population trends for this species are currently unknown, as they have not been extensively studied.Impacted Habitats and Future Predictions
American Soles are primarily found in estuaries and mudflats, which are shallow, highly productive coastal areas. These habitats are essential for the survival of not only American Soles but also countless other marine species. However, these areas are also at risk from human activities, such as pollution and development, which can disturb the natural balance and harm the species that depend on them.Experts predict that if the threats to American Soles' habitats continue, their populations will decline, placing them at risk of extinction. This is why it is crucial to monitor their populations and address the root cause of these threats to ensure their survival and the health of their habitat.
Conclusion
The world of American Soles is a fascinating one, filled with unique features and behaviors that make them stand out in the marine world. Their solitary and nocturnal nature, coupled with their ability to blend in with their surroundings, makes them elusive and challenging to study. However, despite their elusive nature, they are a crucial part of their ecosystem, and any decline in their population can have damaging effects on the marine ecosystem.It is essential to continue researching and monitoring American Soles' populations, as well as addressing the threats they face to ensure their survival and the health of their habitat. By raising awareness and taking action to protect these solitary fish, we can ensure that they continue to thrive in the fascinating world they inhabit.

The Fascinating World of American Sole Fish
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.