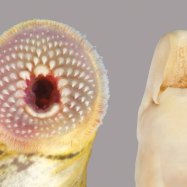
Arrowtooth Eel
Arrowtooth eels have a migratory pattern, moving to deeper waters during the day and shallower waters at night.
Discover the elusive Arrowtooth Eel, a popular Fish A species found in the United States and Canada. Known for their unique migratory pattern and short lifespan of 5 to 12 years, these eels are a fascinating sight in shallow waters at night. #ArrowtoothEel #FishA #MigrationPattern
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: Arrowtooth Eel
Habitat: Arrowtooth eels are found at depths of 800 to 6,500 feet, primarily in the eastern North Pacific Ocean.
Color: Arrowtooth eels are usually dark brown or black in color, with a pale underbelly.
The Mysterious Arrowtooth Eel: A Deep-Sea Predator of the Pacific Ocean
The depths of the ocean are full of fascinating creatures that most of us have never seen or even heard of. One such creature is the Arrowtooth Eel, also known as Synaphobranchus kaupii, a deep-sea predator found in the eastern North Pacific Ocean. This elusive eel has intrigued scientists and ocean enthusiasts for years, with its unique characteristics and mysterious behavior. In this article, we will dive into the world of the Arrowtooth Eel, exploring everything from its habitat and feeding habits to its reproduction and migration patterns Arrowtooth Eel.The Arrowtooth Eel, as its name suggests, has a distinctive arrow-shaped tooth at the front of its mouth. This tooth is used for capturing and holding onto its prey, which mainly consists of benthic organisms found on or near the ocean floor. Arrowtooth eels have been observed feeding on a variety of creatures, including mollusks, crustaceans, and smaller fish. Their long, slender bodies and sharp teeth make them efficient and deadly predators in the deep sea.
This species of eel is primarily found in the eastern North Pacific Ocean, from Alaska to California, at depths ranging from 800 to 6,500 feet. They prefer to live in areas with soft, sandy bottoms, where they can easily burrow and hunt for food. However, they have also been found in areas with rocky substrates, showcasing their ability to adapt to different habitats.
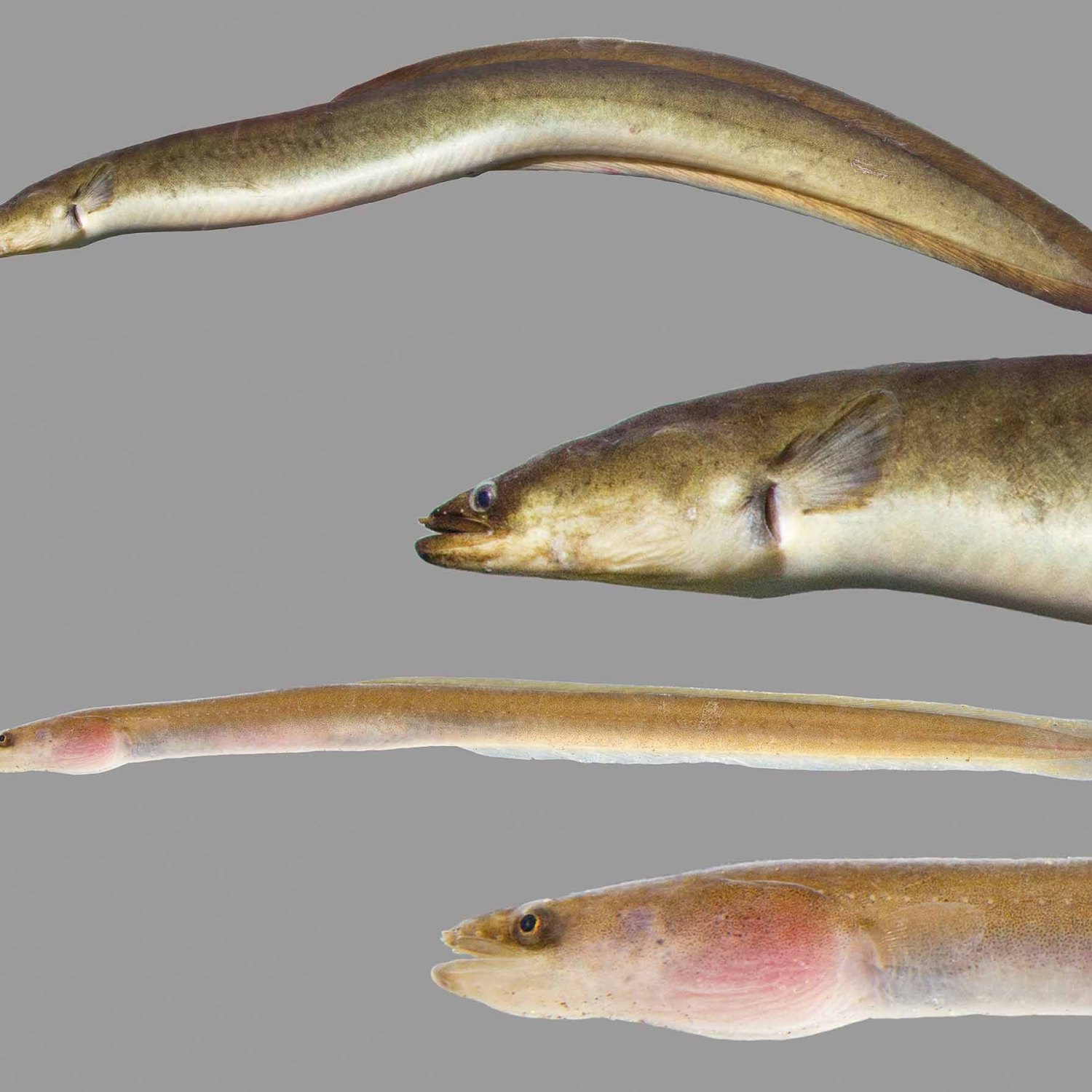
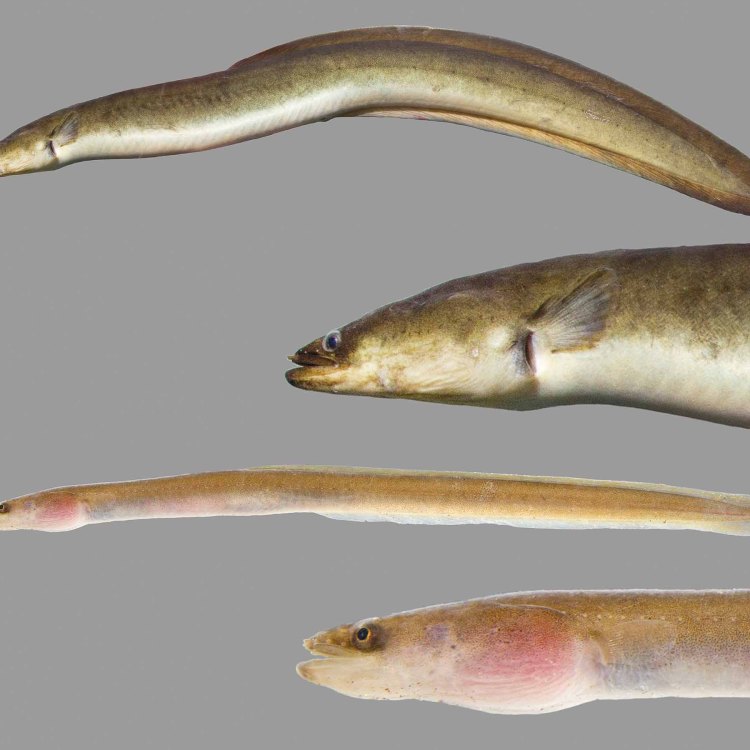
The coloration of Arrowtooth Eels is dark brown or black, with a pale underbelly. This coloration allows them to blend in with their surroundings and remain hidden from potential predators Alaska Blackfish. Their elongated and cylindrical bodies, with a pointed snout and a long tail, also contribute to their stealthy appearance. They can reach lengths of up to 3.3 feet, making them one of the longest eel species in the North Pacific Ocean.
Arrowtooth eels reach their adult size at around 2 to 3 years of age and have a lifespan of about 5 to 12 years. However, their reproductive behavior is not well known. It is believed that they reproduce through external fertilization, where the female releases eggs and the male fertilizes them externally. The spawning behavior of Arrowtooth eels is still a mystery, and further research is needed to fully understand their reproductive habits.
One of the most intriguing aspects of Arrowtooth eels is their migration pattern. These eels have been observed moving to deeper waters during the day and shallower waters at night. Scientists speculate that this behavior is linked to avoiding predators and seeking out food sources. This migratory pattern also highlights their ability to thrive in various ocean depths, making them a truly versatile and resilient species.
Despite its name, the Arrowtooth Eel is not a true eel. It belongs to the family Synaphobranchidae, which is a group of eel-like fishes found in the deep sea. This family also includes other unique species such as the Pelican eel and the Gulper eel. The name Synaphobranchus kaupii was given by French naturalist Charles-Etienne Bonaparte in honor of German naturalist Johann Jakob Kaup, who first described this species in 1860.
Arrowtooth Eels play a vital role in the deep-sea ecosystem of the Pacific Ocean. As predators, they help regulate the populations of their prey, ensuring a balance is maintained. They also serve as an important food source for larger predators, such as sharks and marine mammals. However, as with many deep-sea species, not much is known about their population size and trend.
The need for further research and conservation efforts for the Arrowtooth Eel emphasizes the importance of understanding and protecting our oceans' deep-sea ecosystems. These creatures, although rarely seen, play a crucial role in the marine environment and are indicators of the overall health of our oceans.
In the past, deep-sea creatures like the Arrowtooth Eel have been overlooked due to the difficulty and expense of studying them in their natural habitat. However, with advancements in technology and underwater exploration, we are discovering more about these mysterious creatures than ever before. From deep-sea robots to remote-operated vehicles, scientists can now explore the depths of the ocean and document its inhabitants without disturbing their natural behaviors.
As we continue to uncover the secrets of the deep sea, we must also keep in mind the potential impacts of human activities on these delicate ecosystems. The eastern North Pacific Ocean, where the Arrowtooth Eel is found, is a prime fishing ground. The use of bottom trawling, a method of fishing that involves dragging a net along the ocean floor, can potentially disrupt the eel's habitat and lead to bycatch, where non-target species are inadvertently caught and harmed.
Furthermore, the effects of climate change on deep-sea creatures like the Arrowtooth Eel are still not fully understood. As the ocean's temperature and chemistry changes, these creatures may face challenges in adapting to their new environments. It is crucial to continue monitoring their populations and behaviors to assess the impacts of climate change on their survival.
In conclusion, the Arrowtooth Eel is an intriguing and enigmatic creature of the deep sea. With its sharp teeth, migratory patterns, and mysterious reproductive behavior, it continues to pique the interest of scientists and ocean enthusiasts alike. As we learn more about this fascinating species, we must also recognize the importance of preserving its habitat and the entire deep-sea ecosystem. With ongoing research and conservation efforts, we can ensure that the Arrowtooth Eel and other deep-sea creatures continue to thrive in their natural home, the Pacific Ocean.

Arrowtooth Eel
Fish Details Arrowtooth Eel - Scientific Name: Synaphobranchus kaupii
- Category: Fish A
- Scientific Name: Synaphobranchus kaupii
- Common Name: Arrowtooth Eel
- Habitat: Arrowtooth eels are found at depths of 800 to 6,500 feet, primarily in the eastern North Pacific Ocean.
- Feeding Habitat: Arrowtooth eels are benthic predators, meaning they feed on organisms found on or near the ocean floor.
- Feeding Method: Arrowtooth eels use their long, slender bodies and sharp teeth to capture and eat their prey.
- Geographic Distribution: Arrowtooth eels are primarily found in the eastern North Pacific Ocean, from Alaska to California.
- Country Of Origin: United States and Canada
- Color: Arrowtooth eels are usually dark brown or black in color, with a pale underbelly.
- Body Shape: Arrowtooth eels have elongated and cylindrical bodies, with a pointed snout and a long tail.
- Length: Arrowtooth eels can reach lengths of up to 3.3 feet.
- Adult Size: Arrowtooth eels reach their adult size at around 2 to 3 years of age.
- Age: Arrowtooth eels have a lifespan of about 5 to 12 years.
- Reproduction: Arrowtooth eels reproduce through external fertilization, where the female releases eggs and the male fertilizes them externally.
- Reproduction Behavior: The spawning behavior of Arrowtooth eels is not well known.
- Migration Pattern: Arrowtooth eels have a migratory pattern, moving to deeper waters during the day and shallower waters at night.

Arrowtooth Eel
- Social Group: Arrowtooth eels are solitary creatures and do not form social groups.
- Behavior: Arrowtooth eels are nocturnal, meaning they are most active at night.
- Diet: Arrowtooth eels feed on a variety of prey, including fish, squid, and crustaceans.
- Predators: Arrowtooth eels are preyed upon by larger fish and marine mammals.
- Prey: Arrowtooth eels are opportunistic predators and will eat any suitable prey they encounter.
- Environmental Threats: Arrowtooth eels face threats from bottom trawling and habitat destruction due to human activities.
- Conservation Status: Arrowtooth eels are not currently listed as a threatened species.
- Special Features: Arrowtooth eels have a slender body shape, sharp teeth, and a long, snake-like tail.
- Interesting Facts: Arrowtooth eels are commercially important as a food source, particularly in Asian cuisine.
- Reproduction Period: The reproduction period for Arrowtooth eels is not well defined.
- Nesting Habit: Arrowtooth eels do not construct nests.
- Lifespan: Arrowtooth eels have a lifespan of about 5 to 12 years.
- Habitat Threats: Arrowtooth eels are threatened by habitat destruction due to bottom trawling and other human activities.
- Population Trends: The population trends of Arrowtooth eels are not well studied.
- Habitats Affected: Arrowtooth eels primarily inhabit deep-sea habitats, which are vulnerable to human activities.

Synaphobranchus kaupii
The Fascinating World of the Arrowtooth Eel
When we think about the diversity of marine life, we often imagine colorful fish, majestic whales, and graceful dolphins. However, the ocean is also home to strange and mysterious creatures, such as the arrowtooth eel. This unique species, also known as the arrowtooth flounder, is a fascinating creature that deserves our attention and protection.In this article, we will delve into the world of the arrowtooth eel, exploring their behavior, diet, predators, threats, and special features RadioDouRosul.com. We will also learn about their reproduction, nesting habits, lifespan, and the scientific efforts in place to understand and protect them. So grab your snorkels and let's dive into the world of the arrowtooth eel.
Social Nature: Solitary Creatures
The arrowtooth eel, also known by its scientific name Synaphobranchus kaupii, is a solitary creature. This means that they do not form social groups or engage in any type of social behavior with other individuals of their species. They are primarily loners, therefore, their interactions with other eels are limited.Nocturnal Behavior: Creatures of the Night
As the sun sets and darkness descends, the arrowtooth eel comes to life. They are nocturnal creatures, which means they are most active at night. This behavior could be an adaptation to avoid predators, as many of their natural predators are diurnal (active during the day). This feeding pattern also allows them to take advantage of the cover of darkness to hunt for prey Angelfish.Diet: Versatile and Opportunistic Eaters
The arrowtooth eel is a versatile eater, and its diet consists of a variety of prey. They are opportunistic predators, meaning they will eat any suitable prey they encounter. This includes fish, squid, and crustaceans. Their sharp teeth and sleek body shape make them efficient predators, allowing them to catch and consume their prey easily.In particular, arrowtooth eels have a penchant for lanternfish, which are small, bioluminescent fish that can often be found in abundance in the deep sea. Eating these fish ultimately contributes to the balance of the ocean's food web, as they are an important food source for many marine animals.
Natural Predators: Surviving in a Dangerous World
As with any organism, the arrowtooth eel faces threats in its natural environment. They are preyed upon by larger fish, such as sharks and other eels, as well as marine mammals like seals and sea lions. Being solitary creatures, arrowtooth eels do not have the protection of a social group to ward off predators. The long, snake-like tail of the arrowtooth eel helps them to quickly escape from their predators by propelling them through the water.Environmental Threats: Human Activities Impacting the Arrowtooth Eel
While natural predators pose a threat to the arrowtooth eel, they also face significant threats from human activities. Bottom trawling, a fishing method that drags large nets along the ocean floor, is a major threat to deep-sea habitats where arrowtooth eels reside. This destructive fishing practice not only impacts the eels but also causes grave harm to other marine species and their fragile habitats.Habitat destruction is another significant environmental threat to the arrowtooth eel. As human activities continue to encroach on deep-sea habitats, the eels lose their homes, food sources, and breeding grounds. This destruction could ultimately lead to a decline in the eel's population and disrupt the balance of the ocean's ecosystems.
Conservation Status: A Species of Least Concern
Despite the environmental threats they face, the arrowtooth eel is not currently considered a threatened species. They are listed as a species of least concern on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List. This status is due to their wide distribution and the fact that their population trends are not well studied.However, this does not mean that the arrowtooth eel is safe from harm. The lack of population studies and conservation efforts could put the eel at risk in the future. It is crucial to continue monitoring and researching this species to ensure their survival.
Special Features: A Striking Appearance
The arrowtooth eel has some unique features that make it stand out among other marine creatures. They have a slender body shape, which allows them to maneuver through the deep-sea environments with ease. They also have a long, snake-like tail that helps them move quickly and gracefully through the water.Their most striking feature, however, is their sharp teeth, which give the eel its name. They have a single fang-like tooth on the roof of their mouth and larger, backward-facing fang-like teeth in their lower jaw. These teeth are used to grasp and hold onto their prey, making them efficient hunters.
Interesting Facts: A Culinary Delicacy
Aside from their unique appearance and behavior, the arrowtooth eel also has economic significance. They are commercially important as a food source, particularly in Asian cuisine. In Japan, arrowtooth eels are considered a delicacy, and their meat is often used in traditional dishes such as unagi (grilled eel) and dojô nabe (eel hotpot).However, this commercial demand can also have a negative impact on the eel's population. Overfishing and unsustainable fishing practices can lead to a decline in the eel's population, and as with any species, this could have severe consequences for the ocean's ecosystem.
Reproduction and Nesting Habits: Still a Mystery
The reproduction and nesting habits of arrowtooth eels are not well defined. Scientists have little information about their breeding patterns, and due to their deep-sea habitat, it is challenging to study their reproductive behavior. What is known is that breeding takes place in the winter months, and their eggs and larvae float in the surface layers of the ocean.Lifespan: A Short Life Under the Sea
Arrowtooth eels have a relatively short lifespan compared to other marine species. They typically live for about 5 to 12 years. This short lifespan, combined with their slow reproductive rates, makes them vulnerable to environmental changes and overfishing.The Need for Conservation and Protection
Despite being listed as a species of least concern, it is evident that the arrowtooth eel faces numerous threats from human activities. Their deep-sea habitats are particularly vulnerable to bottom trawling and other human disturbances. It is essential to implement sustainable fishing practices and increase our understanding of this unique species to ensure their survival.The good news is that efforts are being made to protect the arrowtooth eel and its deep-sea habitat. Scientists are working to study and monitor the eel's population and behavior to inform conservation measures. Additionally, organizations and governments are implementing regulations and policies to regulate bottom trawling and other fishing practices to minimize their impact on the deep-sea ecosystem.
In Conclusion
The arrowtooth eel may not be the first species that comes to mind when we think of marine life, but they are a vital part of the ocean's delicate ecosystem. As we continue to explore and exploit the ocean's resources, it is crucial to remember that our actions have consequences for all of the creatures that call it home.Through increased scientific research and responsible management practices, we can ensure that the arrowtooth eel and other deep-sea species continue to thrive for generations to come. After all, the ocean is a vast and wondrous world that deserves our utmost respect and protection.

The Mysterious Arrowtooth Eel: A Deep-Sea Predator of the Pacific Ocean
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.