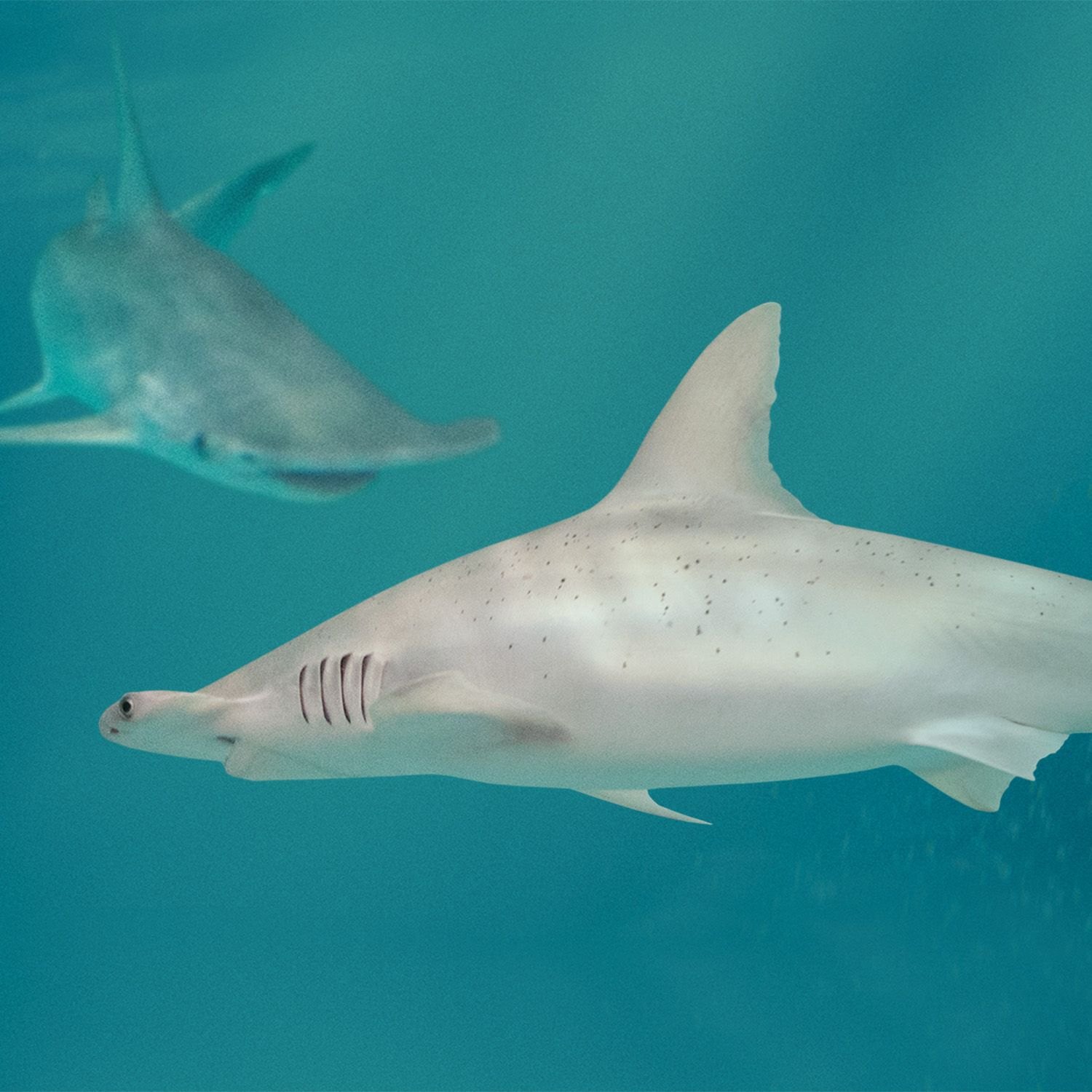

Bonnethead Shark
Some populations undertake seasonal migrations
Did you know that the Bonnethead Shark, also known as Fish B, can live up to 10-15 years? It's found in the coastal waters of the United States and some populations migrate seasonally. Mating happens year-round, with the peak during summer. Fascinating facts about this beautiful fish! #BonnetheadShark #FishB #USCoastalWaters #SeasonalMigration #MatingBehavior #FunFishFacts.
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: Bonnethead Shark
Habitat: Shallow coastal waters, including beaches, bays, estuaries, and mangrove habitats
Color: Gray or brown with a lighter underbelly
Bonnethead Shark: The Underestimated Giant of Coastal Waters
When we think of sharks, we often picture large and intimidating creatures with a ferocious appetite for anything that crosses their path. We imagine them lurking in the depths of the ocean, ready to attack at any given moment. However, not all sharks fit this stereotype. Meet the bonnethead shark (Sphyrna tiburo), a small but fascinating species that inhabits the shallow coastal waters of the western Atlantic Ocean Bonnethead Shark.With its unique physical features and feeding habits, the bonnethead shark is a highly adaptable and underrated marvel of nature. In this article, we will delve deeper into the world of this elusive creature and uncover what makes it stand out from the rest of its shark counterparts.
A Unique and Misunderstood Species
The bonnethead shark is commonly known as the "little hammerhead" due to its small, shovel-shaped head. However, don't be deceived by its diminutive size. This shark can reach up to 5 feet (1.5 meters) in length, making it the smallest of the hammerhead shark species.Despite its small size, the bonnethead shark has a broad geographical distribution, with sightings recorded from the coast of New England in the United States to southern Brazil. It prefers to inhabit shallow coastal waters, including beaches, bays, estuaries, and mangrove habitats. This makes it a popular species among recreational fishermen, yet its unique appearance and elusive nature often cause it to be mistaken for other shark species Bitterling.
One of the reasons for this confusion is that the bonnethead shark has a streamlined and slender body that is often gray or brown in color, with a lighter underbelly. This coloration helps it blend in with its surroundings, making it a cunning predator in its natural habitat.
An Unconventional Diet for a Shark
While most sharks are known for their ferocious appetite, the bonnethead shark has a different approach to its diet. Unlike its larger and more aggressive counterparts, this species feeds predominantly on small fish, shrimp, crabs, and mollusks. What makes it unique is that it is the only known shark species that is primarily herbivorous.The bonnethead shark has a highly adaptable digestive system, allowing it to metabolize and digest a high percentage of seagrass. It uses its flattened and serrated teeth to grind and extract the nutrients from seagrass beds, sandy or muddy bottoms, and even the shells of mollusks. This remarkable feeding habit has earned it the nickname "the lawnmower of the sea."
The Science Behind the Shovel-Shaped Head
The bonnethead shark's most distinctive feature is its shovel-shaped head. Its head is significantly broader and flatter than that of other shark species, making it an enigma to researchers and scientists. But recent studies have shed light on the science behind this peculiar feature.Studies have shown that the bonnethead shark's head shape is specifically designed to aid in its unique feeding habits. This shape allows the shark to maneuver efficiently in shallow waters and navigate through narrow spaces in the seagrass beds. The various sensors and electroreceptors on its head also help it locate prey and detect changes in water temperature and salinity levels.
The Life of a Bonnethead Shark
The bonnethead shark's lifespan is estimated to be around 10 to 15 years, with a maximum recorded age of 18 years. Its reproductive behavior is similar to that of other shark species, with males and females engaging in a courtship ritual before mating. Mating occurs year-round, with peak activity during the summer. Female bonnethead sharks give birth to live young after a gestation period of around five months.Another interesting aspect of the bonnethead shark's life is its migration patterns. While some populations are known to stay in one location, others undertake seasonal migrations, following the movement of their prey. This makes them a vital part of the ecosystem, as they help maintain the balance of the food chain.
A Species in Need of Conservation
Despite its adaptability and resilience, the bonnethead shark is facing numerous threats from human activities. The most significant threat is overfishing, with this species being caught as by-catch in commercial fishing for other species.The loss of habitat is also a major concern, as human development and pollution continue to degrade the coastal waters where the bonnethead shark thrives. The decline of seagrass beds, which are an essential part of this species' diet, also poses a threat to its survival.
To protect this misunderstood species, conservation efforts are being made worldwide. The United States has implemented regulations to protect the bonnethead shark, including catch limits and minimum size requirements for caught specimens. Additionally, efforts are being made to restore and conserve seagrass beds, which will have a positive impact on the bonnethead shark's population.
In Conclusion
The bonnethead shark may not fit the typical image of a "shark," but it is undoubtedly a fascinating and unique species. With its small size, herbivorous diet, and peculiar head shape, this shark defies stereotypes and proves that there is much more to these creatures than meets the eye.As we continue to learn more about the bonnethead shark and its role in the ocean ecosystem, it is crucial to protect and preserve this species. Through conservation efforts and raising awareness, we can ensure that this remarkable shark continues to thrive in its coastal habitat for years to come.
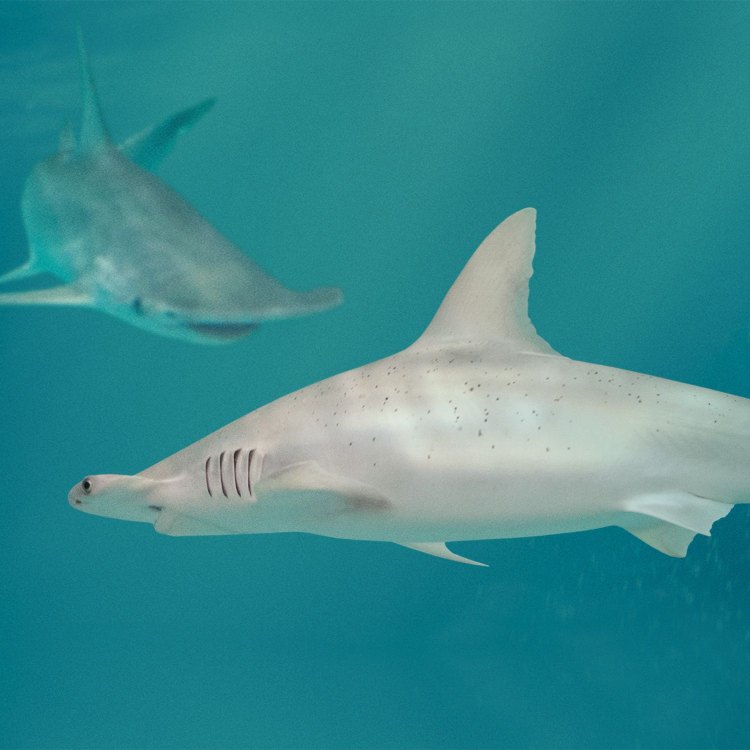

Bonnethead Shark
Fish Details Bonnethead Shark - Scientific Name: Sphyrna tiburo
- Category: Fish B
- Scientific Name: Sphyrna tiburo
- Common Name: Bonnethead Shark
- Habitat: Shallow coastal waters, including beaches, bays, estuaries, and mangrove habitats
- Feeding Habitat: Seagrass beds, sandy or muddy bottoms
- Feeding Method: Mainly feeds on small fish, shrimp, crabs, and mollusks
- Geographic Distribution: Coastal waters of the western Atlantic Ocean, from New England in the United States to southern Brazil
- Country Of Origin: United States
- Color: Gray or brown with a lighter underbelly
- Body Shape: Slender body with a broad, shovel-shaped head
- Length: Up to 5 feet (1.5 meters)
- Adult Size: Average adult size is around 3 to 4 feet (0.9 to 1.2 meters)
- Age: Maximum lifespan is estimated to be around 10 to 15 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproduction Behavior: Mating occurs year-round, with peak activity during the summer
- Migration Pattern: Some populations undertake seasonal migrations
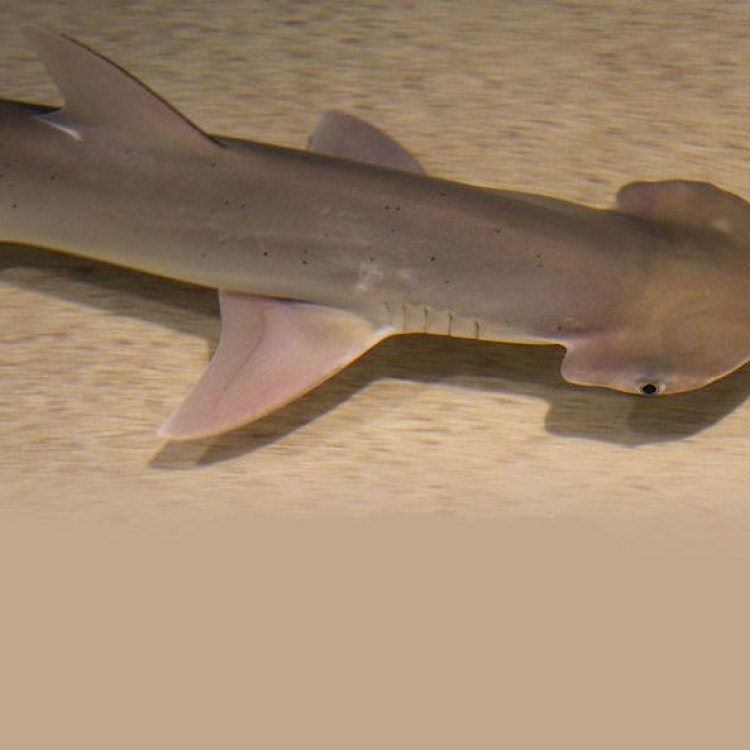

Bonnethead Shark
- Social Group: Solitary
- Behavior: Generally non-aggressive towards humans
- Diet: Carnivorous
- Predators: Larger sharks, dolphins, and larger predatory fish
- Prey: Small fish, shrimp, crabs, and mollusks
- Environmental Threats: Overfishing, habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Special Features: The head of the bonnethead shark is shaped like a shovel
- Interesting Facts: Bonnethead sharks are the only known omnivorous sharks, as they can digest and obtain nutrients from seagrass
- Reproduction Period: Year-round
- Nesting Habit: No specific nesting habits
- Lifespan: Around 10 to 15 years
- Habitat Threats: Habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change
- Population Trends: Population trends are currently stable
- Habitats Affected: Coastal marine habitats
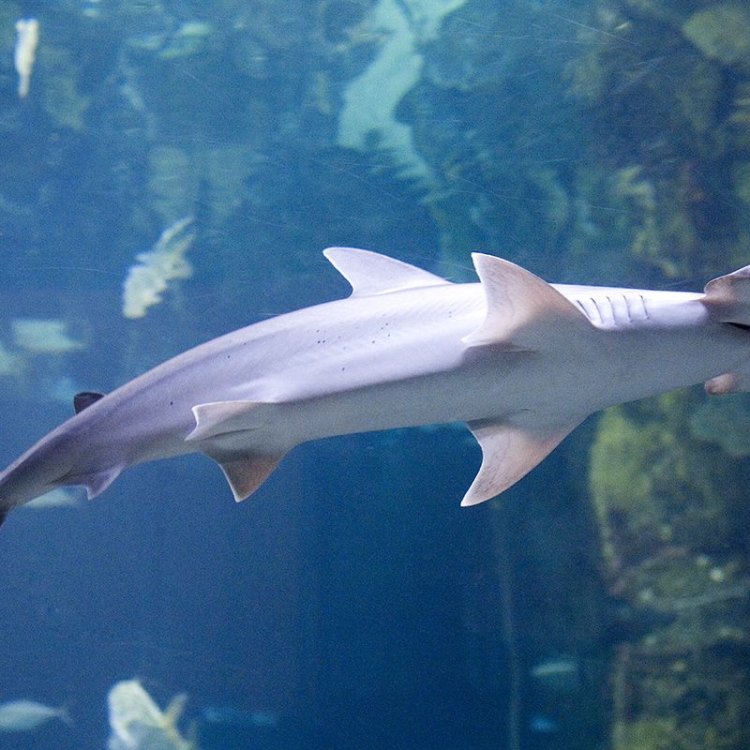
Sphyrna tiburo
The Bonnethead Shark: A Unique and Fascinating Creature of the Sea
From movies to toys, sharks have always been a subject of fascination and fear for many people. One particular species that stands out is the Bonnethead Shark, with its distinct head shape and intriguing behavioral and dietary habits. Despite its intimidating appearance, the Bonnethead Shark is often considered harmless to humans. But what makes this shark unique? In this article, we will explore the fascinating facts and features of the Bonnethead Shark, ranging from its diet to its conservation status RadioDouRosul.com.The Bonnethead Shark, scientific name Sphyrna tiburo, is a small species of hammerhead shark that can be found in the coastal waters of the Western Atlantic Ocean, from North Carolina to Brazil, including the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea. The shape of its head, which resembles a shovel, is the reason behind its name. Adults can reach a maximum length of 5 feet and weigh up to 24 pounds, making them one of the smallest species of hammerhead sharks. They are also easily recognizable due to their gray-brown color and small eyes.
One of the most interesting features of the Bonnethead Shark is its diet. They are known to be carnivorous, meaning they primarily feed on meat. However, their diet is not limited to just other fish; unlike most species of sharks that are strictly carnivorous, the Bonnethead Shark is the only known omnivorous shark. They have a unique digestive system that allows them to digest and obtain nutrients from seagrass. Their diet consists of small fish, shrimp, crabs, and mollusks, in addition to seagrass Blue Catfish. This makes them an essential part of the ecosystem, as they help maintain the seagrass beds, which provide vital habitats for many other marine species.
But despite being an important part of the marine ecosystem, Bonnethead Sharks are facing environmental threats that are putting their population at risk. Like many other shark species, overfishing is one of the biggest threats they face. They are often caught as bycatch in commercial fishing gear, leading to a decrease in their numbers. Habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change are also significant threats to the Bonnethead Shark. Their coastal marine habitats are constantly being destroyed, and pollution is causing harm to their habitats, making it harder for them to thrive. The effects of climate change, such as rising sea levels and rising ocean temperatures, can also have a negative impact on their habitats and food sources.
Despite these threats, the conservation status of the Bonnethead Shark is currently listed as "Least Concern" by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This means that their population is relatively stable and not in immediate danger of extinction. However, with the increase in environmental threats, conservation efforts must continue to ensure the survival of this unique species.
Apart from its interesting diet and conservation status, the Bonnethead Shark also has intriguing social and reproductive behaviors. Unlike many other shark species, Bonnetheads are solitary animals, meaning they prefer to live alone rather than in groups. They are generally non-aggressive towards humans, making them a safe species to observe and study in their natural habitat. But like any other animal, they can become defensive if they feel threatened, so caution must always be taken when encountering them in the wild.
In terms of reproduction, Bonnethead Sharks have a year-round breeding season. Female Bonnetheads give birth to live young, called pups, after a gestation period of about four months. Typically, they give birth to one to twelve pups at a time, which are approximately 8 to 13 inches in length. Interestingly, Bonnetheads do not have specific nesting habits like other shark species. Instead, they give birth in shallow waters near the coast, where their offspring can easily find food and shelter.
The Bonnethead Shark is estimated to have a lifespan of around 10 to 15 years in the wild. However, their lifespan can be affected by various factors such as pollution, habitat destruction, and overfishing.
In conclusion, the Bonnethead Shark is a unique and fascinating creature of the sea. With its shovel-shaped head, omnivorous diet, and generally non-threatening behavior, it is a remarkable species to behold. However, their existence is being threatened by human activities, and it is our responsibility to ensure their survival for the sake of the marine ecosystem. By understanding and appreciating these creatures, we can work towards preserving their habitats and ensuring their continued existence for generations to come.

Bonnethead Shark: The Underestimated Giant of Coastal Waters
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.












