Bonytail
Bonytail fish have a limited migratory pattern, moving to spawn in shallow areas of rivers during the breeding season.
Discover the fascinating world of Bonytail fish, commonly found in the US. These fish have a unique limited migration pattern and can live for decades. Learn more about their reproduction behavior and the elusive documentation of their age. #BonytailFish #USFisheries #RiverLife
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: Bonytail
Habitat: Bonytail fish can be found in deep, fast-flowing rivers with clean, clear water.
Color: Bonytail fish have a dark olive-green to bronze back and sides, with a pale belly.
The Fascinating Bonytail Fish: A Jewel of the Colorado River Basin
The Colorado River basin in the southwestern United States is home to a diverse array of aquatic life. From delicate mayflies to powerful salmon, this river system supports a rich ecosystem that is vital to the region. One of the most remarkable residents of this basin is the Bonytail fish, scientifically known as Gila elegans. With its unique appearance and intriguing behaviors, this fish has captured the attention of scientists and anglers alike Bonytail. In this article, we will dive deep into the world of the Bonytail fish and uncover its fascinating features.About the Bonytail Fish
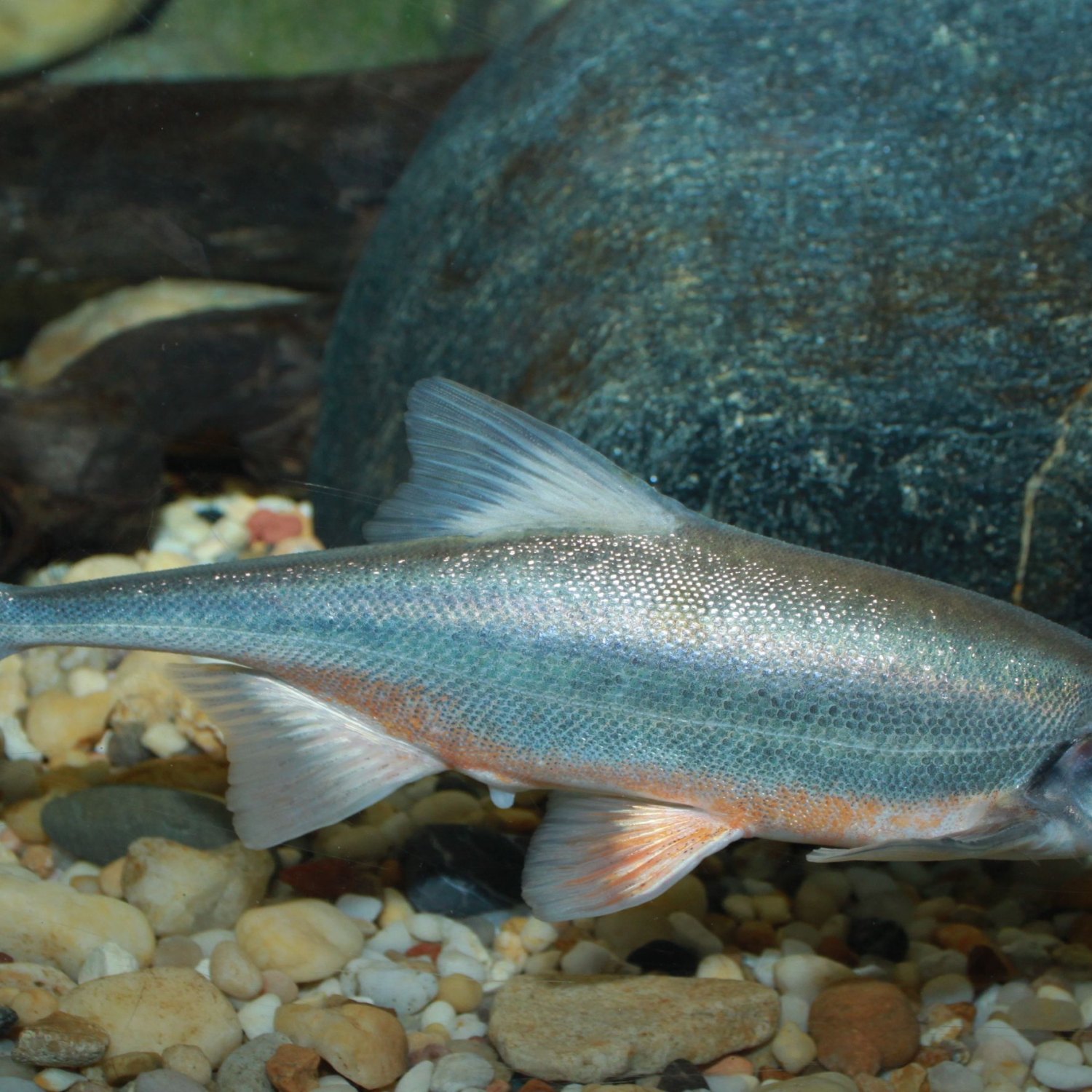
The Bonytail fish, as the name suggests, has a bony body that is well-suited for its life in fast-flowing rivers. This fish has a dark olive-green to bronze back and sides, with a pale belly. Its body shape is streamlined, with a large, triangular caudal fin that helps it navigate the swift currents of its habitat. The Bonytail fish can grow up to 24 inches in length, with adult fish typically reaching a size of 18 to 24 inches. Although the age of Bonytail fish is not well-documented, they can live up to several decades.Habitat and Feeding Habits
Bonytail fish can be found in deep, fast-flowing rivers with clean, clear water. They thrive in rocky areas with swift currents, where they can easily find their preferred food sources. As opportunistic predators, Bonytail fish feed on a variety of prey, including insects, crustaceans, and small fish Brill. They have adapted to their fast-moving environment, using their streamlined body and sharp senses to ambush their prey or actively search for food.Geographic Distribution and Migration Patterns
The Bonytail fish is native to the Colorado River basin, which spans seven US states: Wyoming, Colorado, Utah, New Mexico, Nevada, Arizona, and California. This river basin is known for its complexity, with a diverse range of habitats and unique species. The Bonytail fish is one of the many jewels of this basin, and its presence is crucial to the ecosystem's balance.During the breeding season, which typically occurs between March and June, Bonytail fish migrate to shallow areas of rivers to spawn. This vital behavior ensures the continuation of the species and is a natural marvel to behold. However, the migratory pattern of Bonytail fish is limited, unlike other migratory fish species. They only move to spawn and do not make widespread movements throughout their life.
Reproduction and Behavior
Bonytail fish reproduce through external fertilization, a process in which females release eggs and males release sperm simultaneously. These fish are known to spawn multiple times during the breeding season, ensuring a better chance of successful fertilization. During the breeding season, Bonytail fish also exhibit courtship behaviors, with the males and females swimming together and performing a distinctive dance. This dance is essential in stimulating the release of sperm and eggs, leading to successful reproduction.The Importance of Conservation
As with many other aquatic species, the Bonytail fish faces numerous conservation challenges. Due to changes in its habitat, such as dam construction and water diversions, Bonytail populations have declined significantly. Additionally, pollution and overfishing have also contributed to the decline of this species. In fact, the Bonytail fish is considered an endangered species by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List. This critical status highlights the urgent need for conservation efforts to protect and preserve this unique fish.The Role of Human Interaction
Human actions play a significant role in the survival of the Bonytail fish. The construction of dams and water diversions, while integral for agricultural and urban development, has negatively impacted this fish's habitat. These structures can disrupt the natural movement and migration patterns of the Bonytail fish, affecting their ability to spawn successfully. Additionally, pollution from industries and agricultural run-off threatens the water quality that is essential for the survival of this species. It is crucial for humans to understand the impact of their actions and work towards co-existing with the natural environment.How Can We Help?
Awareness and knowledge are key in protecting and conserving the Bonytail fish. As an endangered species, every effort counts in ensuring the survival of this unique fish in its natural habitat. Individuals can support the conservation of Bonytail fish by avoiding pollution and being mindful of their water usage. Participating in clean-up efforts and supporting organizations that work towards the preservation of this species are also impactful ways to make a positive impact.The Final Word
The Bonytail fish is one of the many marvels of the Colorado River basin, and its survival is vital for the health of the ecosystem. With its unique appearance, intriguing behaviors, and crucial role in the river system, the Bonytail fish deserves recognition and conservation efforts. By understanding the importance of this species and taking steps towards its protection, we can ensure its survival and continue to admire this jewel of the Colorado River basin.

Bonytail
Fish Details Bonytail - Scientific Name: Gila elegans
- Category: Fish B
- Scientific Name: Gila elegans
- Common Name: Bonytail
- Habitat: Bonytail fish can be found in deep, fast-flowing rivers with clean, clear water.
- Feeding Habitat: Bonytail fish inhabit rocky areas with swift currents, where they feed on insects, crustaceans, and small fish.
- Feeding Method: Bonytail fish are opportunistic predators and feed by ambushing their prey or by actively searching for food.
- Geographic Distribution: Bonytail fish are native to the Colorado River basin in the southwestern United States.
- Country Of Origin: United States
- Color: Bonytail fish have a dark olive-green to bronze back and sides, with a pale belly.
- Body Shape: Bonytail fish have a streamlined body with a large, triangular caudal fin.
- Length: Bonytail fish can grow up to 24 inches in length.
- Adult Size: Adult Bonytail fish typically reach a size of 18 to 24 inches.
- Age: The age of Bonytail fish is typically not well-documented, but they can live up to several decades.
- Reproduction: Bonytail fish reproduce through external fertilization, with females releasing eggs and males releasing sperm simultaneously.
- Reproduction Behavior: During the breeding season, Bonytail fish migrate to shallow areas of rivers to spawn.
- Migration Pattern: Bonytail fish have a limited migratory pattern, moving to spawn in shallow areas of rivers during the breeding season.

Bonytail
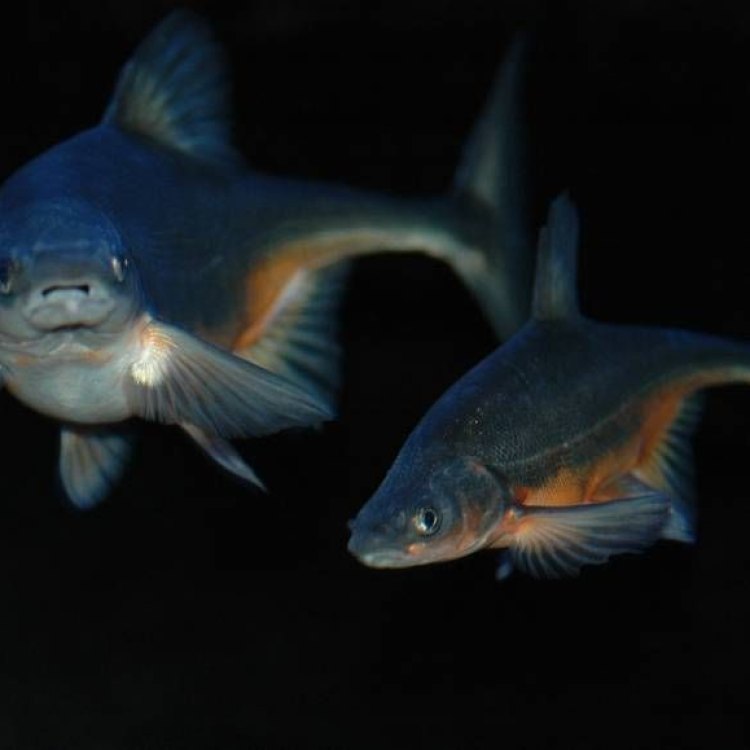
- Social Group: Bonytail fish are typically solitary and do not form large schools.
- Behavior: Bonytail fish are generally shy and elusive, seeking cover in submerged vegetation or rock crevices.
- Diet: The diet of Bonytail fish consists mainly of small fish, crustaceans, and insects.
- Predators: Common predators of Bonytail fish include larger predatory fish, such as bass and catfish.
- Prey: Bonytail fish primarily feed on small fish, crustaceans, and insects.
- Environmental Threats: Habitat destruction, water pollution, and the introduction of non-native species are major environmental threats to Bonytail fish.
- Conservation Status: The Bonytail fish is listed as critically endangered due to habitat loss and reduced water flow in its native range.
- Special Features: Bonytail fish have a bony ridge along their caudal peduncle, giving them their name.
- Interesting Facts: Bonytail fish are one of the rarest fishes in North America, with only a few thousand individuals remaining in the wild.
- Reproduction Period: Bonytail fish typically spawn between April and June.
- Nesting Habit: Bonytail fish do not build nests, but rather scatter their eggs over the river substrate.
- Lifespan: The lifespan of Bonytail fish is not well-documented, but they can potentially live for several decades.
- Habitat Threats: Habitat destruction, water diversion, and the construction of dams are major threats to the habitat of Bonytail fish.
- Population Trends: The population of Bonytail fish has declined significantly over the past century.
- Habitats Affected: Bonytail fish are dependent on clean, clear rivers with swift currents, but these habitats have been greatly impacted by human activities.

Gila elegans
The Mysterious and Endangered Bonytail Fish - A Threatened Species of North America
In the vast rivers and streams of North America, there is a rare and elusive fish that goes by the name Bonytail. This distinctive fish, with its unique features and fragile existence, is facing a catastrophic decline in its population. It is a species that represents not only the diverse aquatic life of North America but also the ecological impact of human activities on our natural world.The Bonytail fish (scientific name - Gila elegans), also known as the Colorado Squawfish, is a freshwater fish that belongs to the family Cyprinidae RadioDouRosul.com. It is one of the most critically endangered fish species in North America, listed as such by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). With only a few thousand individuals left in the wild, efforts are being made to protect this remarkable fish before it becomes an unfortunate memory.
Social Behavior:
The Bonytail fish, unlike other common fish species, is a solitary creature. It does not form large schools or groups, making it challenging to spot in the wild. They prefer to stay hidden and are notoriously shy and elusive. This behavior makes them even more vulnerable to environmental threats, as their solitary lifestyle makes it difficult for them to find mates and reproduce.
Diet and Prey:
Bonytail fish are primarily carnivorous, and their diet consists mainly of small fish, crustaceans, and insects. They are opportunistic feeders and will often feed on whatever is available in their habitat. Their sharp teeth and swift movements make them efficient predators, preying on small fish, crustaceans, and insects in the water Bichir.
Predators:
However, despite their predatory nature, the Bonytail fish are not immune to threats from larger predatory fish such as bass and catfish. These fish pose a significant danger to the Bonytail population, especially as their numbers continue to dwindle.
Environmental Threats:
The Bonytail fish's biggest threat is the degradation of their habitat. Human activities such as water pollution, habitat destruction, and the introduction of non-native fish species have significantly impacted their population. The construction of dams, water diversion for agricultural and urban developments, and the alteration of rivers and streams' natural flow patterns have all contributed to the decline of this species.
Conservation Status:
The Bonytail fish is listed as critically endangered by the IUCN, and its conservation status is in grave danger. The decline in population can be attributed to the loss of their natural habitat and reduced water flow in their native range. The construction of dams has also impacted their reproductive behavior, altering their natural spawning patterns.
Special Features:
The Bonytail fish has distinctive physical features that make it stand out from other fish species. One of its most unique features is the bony ridge along its caudal peduncle, giving it its name. This bony structure is beneficial in providing protection, allowing the fish to swim swiftly through the swift currents of their habitat.
Interesting Facts:
The Bonytail fish is considered a living fossil due to its ancient lineage. It is believed to have evolved over 5 million years ago and is one of the last remaining species in the genus Gila. Despite its long existence, it is now one of the rarest fish species in North America, with only a few thousand individuals left in the wild.
Reproduction and Nesting:
Bonytail fish typically spawn between April to June, which coincides with the spring flooding of rivers and streams. However, the construction of dams has disrupted their natural spawning patterns, making it difficult for them to reproduce. Unlike other fish that build nests, Bonytail fish scatter their eggs over the river substrate, which hatches after a week or so.
Lifespan:
The average lifespan of Bonytail fish is not well-documented, but they can potentially live for several decades if they have a healthy environment to thrive in. Unfortunately, given their declining numbers and the numerous environmental threats, their lifespan is likely to be cut short.
Habitat Threats and Population Trends:
The Bonytail fish is dependent on clean, clear, and swift river currents for its survival. However, with increasing human activities, these habitats are under threat. Water diversion for agriculture, urbanization, and the construction of dams have significantly impacted their habitat, making it unsuitable for their survival. As a result, the Bonytail fish population has declined significantly over the past century, with a 98% decline in their numbers.
Habitats Affected:
The Bonytail fish is endemic to the Colorado River Basin, and their habitat includes the Colorado River and its tributaries. However, the construction of dams, water diversion, and habitat destruction have greatly impacted these rivers and streams, rendering them dangerous for the survival of Bonytail fish.
In conclusion, the Bonytail fish is a rare and fascinating species that is facing a dire situation. It reminds us of the impact human activities can have on our environment and the dire consequences of not taking necessary conservation measures. With continued efforts and awareness, we can save this unique and critically endangered fish species from extinction and preserve the ecological balance of North America's rivers and streams. Let us make a conscious effort to protect our natural world and all the diverse creatures that call it home.

The Fascinating Bonytail Fish: A Jewel of the Colorado River Basin
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.