
Brotula
Brotula does not have a notable migration pattern.
Brotula, also known as ikan lokal in Indonesia, is a popular fish found in the United States, Caribbean, and South America. This fish can live up to 10 years and does not migrate, making it a reliable catch for local fishermen. Despite its widespread presence, little is known about its reproduction behavior, adding to the mystery of this fascinating fish. #Brotula #FishesofIndonesia #MysteryFish
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: Brotula
Habitat: Brotula can be found in deep waters, often at depths between 300 and 1000 meters.
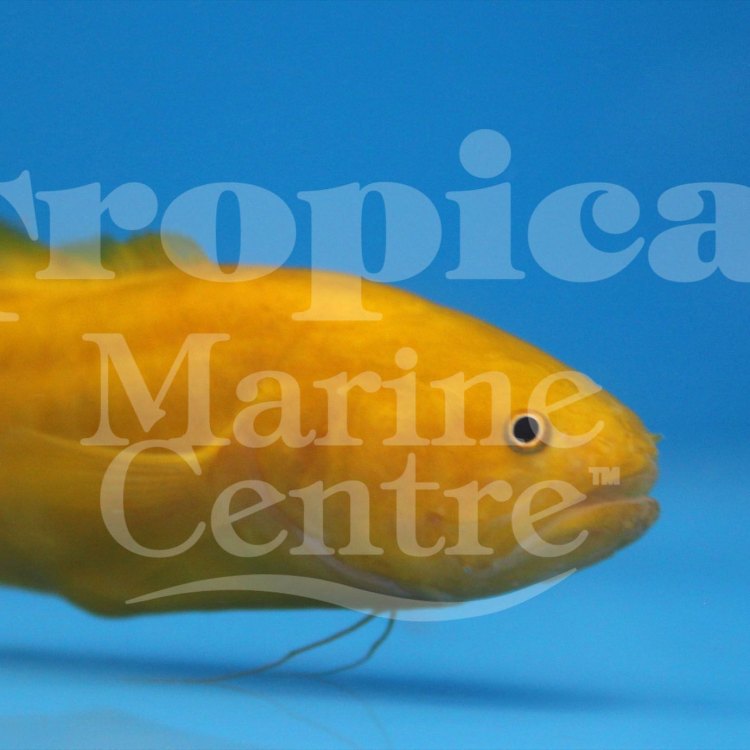
Color: Brotula has a dark brown to blackish body with a lighter colored belly.
The Fascinating World of Brotula: Discovering the Deep-Sea Denizen
Deep in the dark, mysterious depths of the ocean lies a creature known as Brotula, a fish that captivates with its unique appearance and behavior. Often overlooked by its more famous ocean-dwelling counterparts, Brotula is a fascinating species that calls the Atlantic Ocean its home. In this article, we will take a closer look at the remarkable features of this creature and delve into its intriguing world.Scientifically known as Brotula, this fish also goes by the same name in the common language Brotula. Its name derives from the Latin word "brota," meaning sprout or shoot. This name is a nod to its characteristic long and cylindrical body shape, similar to a shoot or sprout. However, there is more to this fascinating creature than just its appearance.
Brotula is primarily found in deep waters, often at depths between 300 and 1000 meters. This means that it is not a commonly seen fish, as it prefers to showcase its beauty in the depths of the ocean far away from the surface. However, it occasionally makes its appearance near the shore during breeding season to lay eggs.
The feeding habitat of Brotula is near the bottom of the ocean, where it can easily find its prey. It has a varied diet and feeds on small fish and invertebrates, making it an opportunistic feeder. Brotula is a voracious predator, using its strong jaws and sharp teeth to capture and swallow its prey whole Blind Goby. It is a stealthy hunter, lurking in the dark depths waiting for the perfect opportunity to strike.
Brotula's geographic distribution is limited to the western Atlantic waters, from Massachusetts to South America. It can also be found in the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea. Its country of origin includes the United States, Caribbean islands, and South America, where it is native. However, it has also been reported in other parts of the world, such as the Mediterranean Sea, as an invasive species.
The color of Brotula varies from dark brown to blackish, with a lighter colored belly. This coloration serves as a camouflage in the dark ocean depths, allowing it to blend in with its surroundings and ambush its prey. Its body shape is long and cylindrical, with a slightly flattened head. One of its most striking features is its large mouth, which is filled with sharp teeth.
Brotula is a relatively large fish, growing up to 70 centimeters in length. It reaches its adult size at around 3 years of age and can live up to 10 years. This makes it a long-lived species, with a lifespan similar to other deep-sea dwellers. However, not much is known about the reproduction behavior of Brotula, although it is known to be oviparous, meaning it reproduces by laying eggs.
One of the most fascinating aspects of Brotula is its mysterious reproduction behavior. As it lives in the deep sea, not much is known about how it mates and lays its eggs. However, it is believed that Brotula follows a specific courtship ritual, similar to other fish species. This involves the male and female fish swimming together in a circular motion, releasing a mixture of sperm and eggs into the water.
Brotula does not have a notable migration pattern, likely due to its preferred deep-sea habitat. However, it is known to move from deeper to shallower waters during the breeding season. Apart from this, it remains relatively sedentary, with little migratory movements.
In recent years, Brotula has become a popular species for deep-sea fishing enthusiasts, prized for its unique appearance and challenging catch. It is also sometimes caught by commercial fishing vessels, although its meat is not as highly valued as other species. However, due to its slow reproductive rate and limited distribution, there has been concern about overfishing and its impact on the Brotula population.
Furthermore, Brotula is facing other threats, including habitat destruction and pollution. As a deep-sea species, it is highly susceptible to the effects of climate change and ocean pollution, which can have a detrimental impact on its survival. Therefore, conservation efforts have been initiated to protect this unique species and its habitat.
In conclusion, Brotula is an intriguing denizen of the deep sea, with its striking appearance, fascinating behavior, and mysterious lifestyle. It is a species that continues to surprise and captivate marine biologists and researchers, with many aspects of its life still shrouded in mystery. As we continue to explore and understand the ocean depths, we can only hope to unravel more of the secrets of this remarkable creature. Let us appreciate the beauty and wonder of Brotula and work towards preserving its existence for future generations to appreciate.

Brotula
Fish Details Brotula - Scientific Name: Brotula
- Category: Fish B
- Scientific Name: Brotula
- Common Name: Brotula
- Habitat: Brotula can be found in deep waters, often at depths between 300 and 1000 meters.
- Feeding Habitat: Brotula is commonly found near the bottom of the ocean and feeds on a variety of small fish and invertebrates.
- Feeding Method: Brotula uses its strong jaws and sharp teeth to capture and swallow its prey whole.
- Geographic Distribution: Brotula is found in the Atlantic Ocean, specifically in the waters of the western Atlantic from Massachusetts to South America, including the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea.
- Country Of Origin: Brotula is native to the United States, the Caribbean, and South America.
- Color: Brotula has a dark brown to blackish body with a lighter colored belly.
- Body Shape: Brotula has a long and cylindrical body with a slightly flattened head. It has a large mouth with sharp teeth.
- Length: Brotula can grow up to 70 centimeters in length.
- Adult Size: Brotula reaches its adult size at around 3 years of age.
- Age: Brotula can live up to 10 years.
- Reproduction: Brotula is oviparous, which means it reproduces by laying eggs.
- Reproduction Behavior: Not much is known about the reproduction behavior of Brotula.
- Migration Pattern: Brotula does not have a notable migration pattern.

Brotula
- Social Group: Brotula is a solitary fish and does not form social groups.
- Behavior: Brotula is a nocturnal fish, meaning it is most active during the night. It spends its days hiding in crevices or burrows.
- Diet: Brotula is a carnivorous fish that primarily feeds on small fish and invertebrates.
- Predators: Brotula is preyed upon by larger fish and marine mammals.
- Prey: Brotula feeds on small fish and invertebrates.
- Environmental Threats: Brotula is not currently facing any significant environmental threats.
- Conservation Status: The conservation status of Brotula is currently unknown.
- Special Features: Brotula has a well-developed swim bladder, which allows it to control its buoyancy and maintain its position in the water column.
- Interesting Facts: Brotula is known for its ability to produce a loud and distinctive sound by grinding its pharyngeal teeth.
- Reproduction Period: The reproduction period of Brotula is not well-documented.
- Nesting Habit: The nesting habits of Brotula are currently unknown.
- Lifespan: Brotula can live up to 10 years.
- Habitat Threats: Brotula is generally not threatened by habitat destruction or degradation.
- Population Trends: The population trends of Brotula are currently unknown.
- Habitats Affected: Brotula does not significantly affect any specific habitats.

Brotula
The Incredible World of Brotula: A Fascinating Deep-Sea Fish
Deep in the dark, mysterious depths of the ocean, there is a fish that often goes unnoticed, but its unique features and behaviors make it stand out among many other marine species. This fish is known as Brotula, and it belongs to the family Ophidiidae, commonly known as cusk-eels. Brotula, also known as "spotted cusk-eel," is a fascinating creature that is found in the deep-sea waters around the world. In this article, we will explore the intriguing world of Brotula and discover what makes it such a special and distinct fish RadioDouRosul.com.Brotula is a solitary fish and does not form social groups. It is known to be a solitary predator, meaning it prefers to hunt and live alone. This solitary nature may help them to avoid competition for resources and reduce the risk of getting attacked by predators. When it comes to behavior, Brotula is a nocturnal fish, meaning it is most active during the night. During the day, they seek shelter in crevices or burrows, where they feel safe and hidden from predators. This behavior is crucial for their survival as they are relatively small and vulnerable.
As a carnivorous fish, Brotula's diet mainly consists of small fish and invertebrates. Their sharp teeth and powerful jaws allow them to hunt and feed on their prey with ease. They are also known to have a varied diet, which includes crustaceans, mollusks, and other small marine creatures Burbot. This carnivorous behavior also helps keep the population of their prey in balance, ensuring the overall health of the marine ecosystem.
Unfortunately, like every other species in the ocean, Brotula also has its share of predators. Larger fish and marine mammals, such as whales, seals, and dolphins, are known to prey upon Brotula. Due to their solitary nature, Brotula does not have any defense mechanisms to protect themselves from predators. They rely on their speed and agility to escape and hide in crevices or burrows when threatened.
On the other hand, Brotula is also a predator itself, and its prey mostly consists of small fish and invertebrates. This predator-prey relationship is essential for maintaining the ecological balance in the ocean. Brotula's population is an important part of the food chain, and any significant decline in their numbers can have a ripple effect on the entire ecosystem.
Despite living in the deep ocean, Brotula is not currently facing any significant environmental threats. Its solitary nature and deep-sea habitat make it less susceptible to human activities such as overfishing and pollution. However, with the increasing impact of human activities on the ocean, Brotula's habitat and food sources may become affected in the future.
The conservation status of Brotula is currently unknown. As deep-sea creatures, they are not studied extensively, and limited information is available about their population and distribution. More research is required to understand and monitor their population trends and assess any potential risks to their survival.
One of the most unique features of Brotula is its well-developed swim bladder, also known as "gas bladder." This gas-filled organ helps the fish to control its buoyancy and maintain its position in the water column. By regulating the amount of gas inside the bladder, Brotula can easily move up and down in the water, without using much energy. This feature is crucial for their survival, as it allows them to navigate the deep-sea currents and reach their prey efficiently.
In addition to its well-developed swim bladder, Brotula is also known for its ability to produce a loud and distinctive sound. This is achieved by grinding its pharyngeal teeth, which creates vibrations that can be detected by other fish in the area. This sound is often used for communication and is a characteristic feature of Brotula, making it easily identifiable.
The reproduction period of Brotula is not well-documented, yet it is believed to be similar to other cusk-eels. Most species of this family are known to reproduce through external fertilization, where the female releases eggs into the water, and the male fertilizes them externally. However, further research is required to understand Brotula's reproductive habits fully.
Currently, the nesting habits of Brotula are also unknown. It is unclear if they prefer to lay their eggs in specific locations or if they build nests to protect them. Studying their nesting behavior can provide valuable insights into their reproductive cycle and help with their conservation efforts.
Brotula has an average lifespan of around 10 years. However, as deep-sea creatures, their exact lifespan is difficult to determine. Factors such as water temperature, food availability, and competition for resources can impact their lifespan.
Fortunately, Brotula is generally not threatened by habitat destruction or degradation. Their deep-sea habitat is relatively stable, and they are not significantly impacted by human activities. However, as mentioned earlier, with the increasing threat of pollution and overfishing, the stability of their habitat may be at risk in the future.
The population trends of Brotula are currently unknown, and limited information is available about their numbers and distribution. As a species that lives in the deep-sea, they are not easily observable or accessible for research. However, with the advancements in technology and underwater exploration, we can hope to learn more about their population and conservation needs in the future.
Lastly, Brotula does not significantly affect any specific habitats. As a solitary fish, their impact on other species or habitats is minimal. However, as a vital part of the deep-sea ecosystem, their role in maintaining the balance cannot be ignored. Any significant decline in their population can have serious implications for the ocean's health and biodiversity.
In conclusion, Brotula is an incredible deep-sea fish with several unique features and behaviors. Its solitary nature, well-developed swim bladder, and distinctive ability to produce sounds make it an intriguing and fascinating creature. While currently not facing any significant environmental threats, more research is required to understand and monitor their population and distribution. As we continue to explore and learn about the mysterious world of the deep-sea, we must also ensure the protection and conservation of these fascinating creatures for future generations to appreciate and admire.
The Fascinating World of Brotula: Discovering the Deep-Sea Denizen
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.












