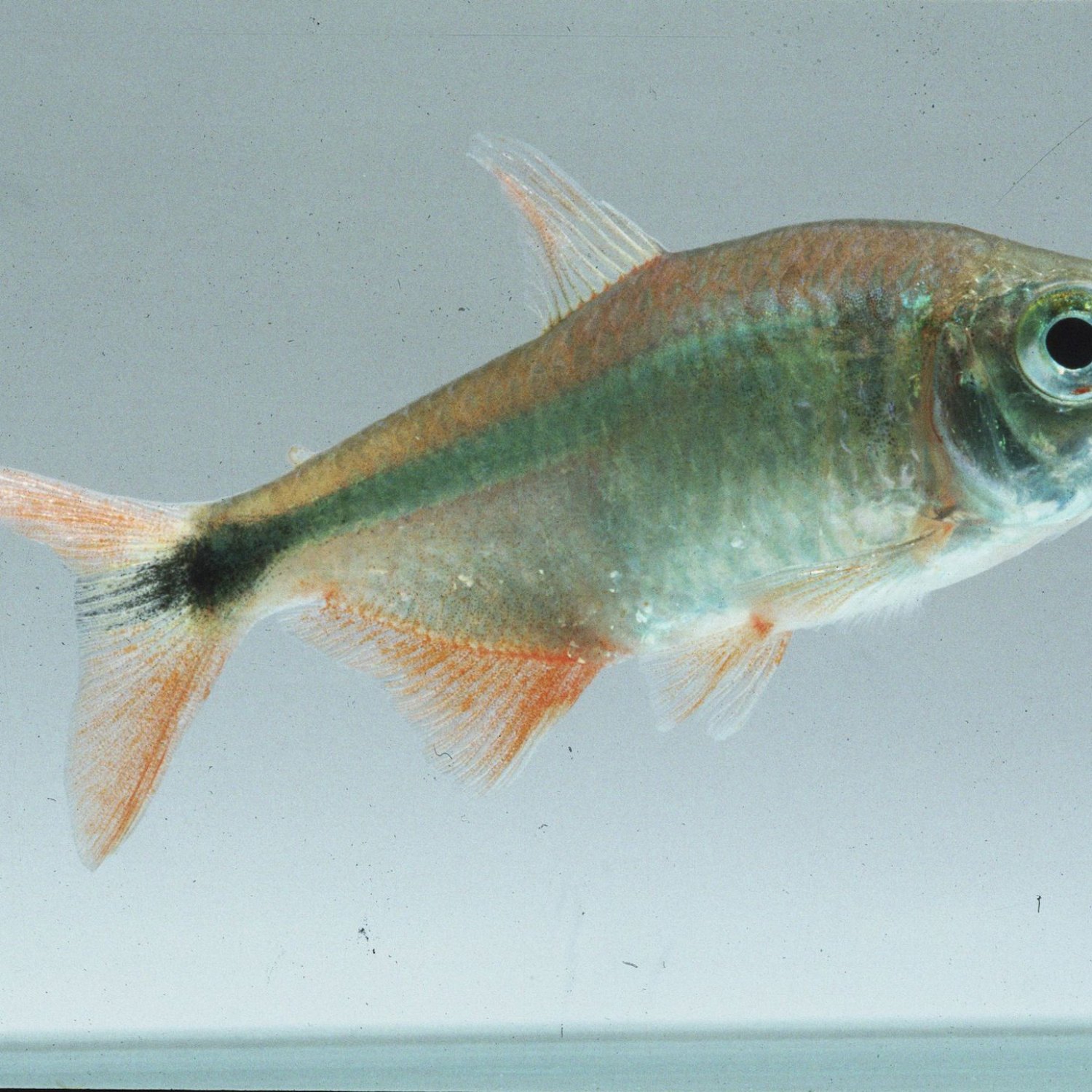
Dogteeth Tetra
Non-migratory
The Dogteeth Tetra is a non-migratory fish species native to Brazil. Despite its name, it does not have literal dog teeth but instead sports sharp triangular teeth. Its reproduction behavior and age are still unknown, making it a mysterious yet fascinating addition to any aquarium. #DogteethTetra #BrazilianFish #AquariumFish
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: Dogteeth Tetra
Habitat: Freshwater rivers and streams
Color: Silver with black stripes
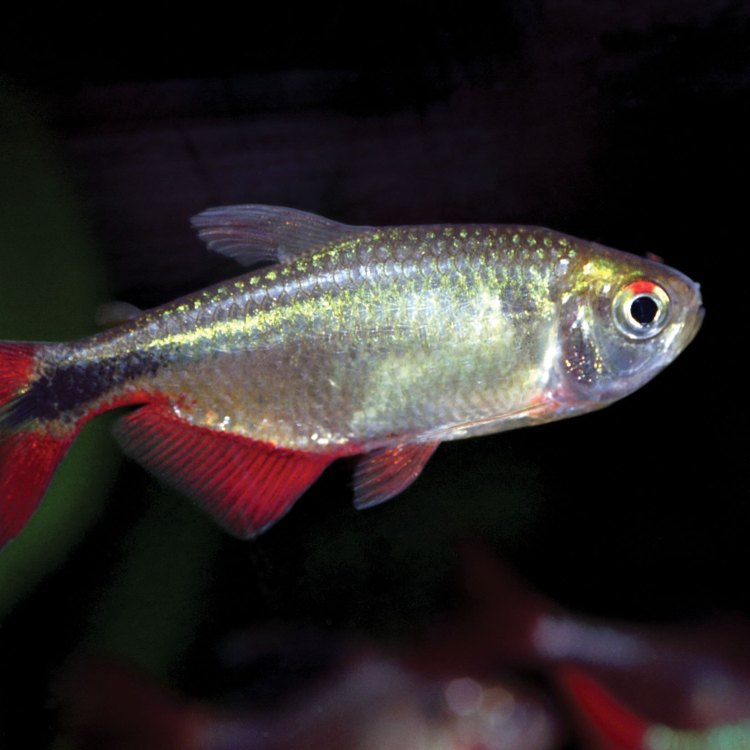
The Ferocious Predator of South America: The Dogteeth Tetra
If you're a fan of unique, exotic fish, then the Dogteeth Tetra should definitely be on your radar. This fierce and fascinating creature is native to the rivers and streams of South America, specifically Brazil. With its streamlined and elongated body shape, silver with black stripes coloring, and impressive size of up to 30 cm (12 inches), the Dogteeth Tetra is a sought-after addition to any freshwater aquarium. But what makes this fish so special? Let's dive deeper into the world of the Dogteeth Tetra and discover its unique characteristics and behavior Dogteeth Tetra.Habitat and Feeding Habits
The Dogteeth Tetra is found in freshwater rivers and streams, particularly in the Amazon and Orinoco River basins. As a surface dwelling fish, it prefers to reside in areas with plenty of vegetation and rocks, as well as slower-moving water. This allows for easier hunting and hiding from predators.As a carnivorous species, the Dogteeth Tetra feeds on smaller fish, crustaceans, and insects. However, what sets this fish apart is its unique feeding method. Using its sharp, elongated teeth, it can obtain its prey by slicing through it. This technique gives this species its common name, as its teeth resemble that of a dog. Their impressive sharp teeth and carnivorous nature make them a formidable predator in their natural habitat.
Geographic Distribution and Country of Origin
As mentioned before, the Dogteeth Tetra can be found in the Amazon and Orinoco River basins, as well as other rivers and streams throughout Brazil Dwarf Loach. They are also known to inhabit neighboring countries such as Venezuela, Colombia, and Peru.Their popularity in the aquarium trade has led to human-introduced populations in other parts of the world such as Malaysia, Cambodia, and the United States. However, their native home remains in South America, where they play a significant role in the ecosystem as a top predator.
Appearance and Size
One of the striking characteristics of the Dogteeth Tetra is its silver color with black stripes, making it a visually stunning fish to observe. Its elongated and streamlined body shape is perfect for swift movements and hunting its prey. On average, these fish can grow up to 20-30 cm (8-12 inches) in length, but some have been known to reach a whopping 30 cm (12 inches) in captivity.As with most fish species, the males are slightly larger and more colorful than the females. However, it can be challenging to differentiate between the two sexes, even for experienced fishkeepers.
Life Span and Reproduction
The average life span of the Dogteeth Tetra is unknown, primarily due to limited research on this species. However, there have been reports of these fish living up to 5-7 years in captivity.As for their reproductive behavior, not much is known about it. It is believed that they reproduce sexually, with females laying eggs that are fertilized by the males. However, specific details on their breeding patterns and behaviors are still a mystery.
Migration and Behavior
The Dogteeth Tetra is a non-migratory fish species, meaning they do not migrate to different areas throughout their lifetime. They are social creatures and are typically found in schools of 6-10 individuals. However, their behavior can change when it comes to food, as they become fiercely competitive and solitary while hunting.In their natural habitat, the Dogteeth Tetra may also exhibit aggressive behavior towards other fish species, making them unsuitable tankmates for smaller and less aggressive fish.
Aquarium Care and Maintenance
Keeping a Dogteeth Tetra in your aquarium can be a rewarding and exciting experience. However, it's essential to ensure you're prepared to meet its specific care needs.First and foremost, these fish require a suitable tank size and plenty of hiding places and plants. The ideal tank size for a group of Dogteeth Tetras would be at least 100 gallons. This allows for plenty of swimming space and reduces any potential aggression between tankmates.
Water quality is also crucial for the well-being of these fish. Ideally, the temperature should be kept between 24-29°C (75-85°F), with a pH range of 5.5-7.5. It's essential to perform regular water changes and use a good filter to maintain clean and healthy water conditions.
When it comes to feeding, the Dogteeth Tetra is not a picky eater. They will readily accept a variety of live and frozen meaty foods such as bloodworms, brine shrimp, and small fish. It's essential to provide a varied diet to ensure they receive all the necessary nutrients for optimal health.
In Conclusion
The Dogteeth Tetra is undoubtedly a unique and fascinating fish species. Its ferocious appearance and sharp teeth make it stand out from other freshwater fish, making it a popular choice for aquarium enthusiasts. However, their specific care needs and potential aggression may make them more suitable for experienced fishkeepers. Nevertheless, if you are up for the challenge, adding a few Dogteeth Tetras to your aquarium will undoubtedly bring some excitement to your underwater world.
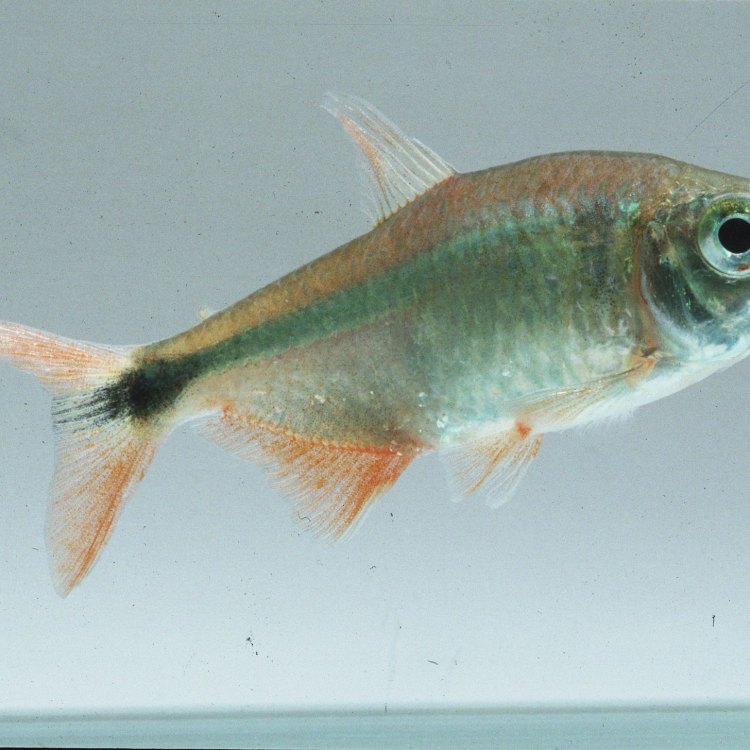

Dogteeth Tetra
Fish Details Dogteeth Tetra - Scientific Name: Hydrolycus scomberoides
- Category: Fish D
- Scientific Name: Hydrolycus scomberoides
- Common Name: Dogteeth Tetra
- Habitat: Freshwater rivers and streams
- Feeding Habitat: Surface waters
- Feeding Method: Carnivorous
- Geographic Distribution: South America
- Country Of Origin: Brazil
- Color: Silver with black stripes
- Body Shape: Streamlined and elongated
- Length: Up to 30 cm (12 inches)
- Adult Size: 20-30 cm (8-12 inches)
- Age: Unknown
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproduction Behavior: Unknown
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory

Dogteeth Tetra
- Social Group: Solitary
- Behavior: Aggressive
- Diet: Fish, crustaceans, and insects
- Predators: Unknown
- Prey: Fish, crustaceans, and insects
- Environmental Threats: Habitat destruction, pollution
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Special Features: Large fangs, sharp teeth
- Interesting Facts: The Dogteeth Tetra gets its name from its large fangs that resemble dog teeth
- Reproduction Period: Unknown
- Nesting Habit: Unknown
- Lifespan: Unknown
- Habitat Threats: Habitat destruction, pollution
- Population Trends: Unknown
- Habitats Affected: Freshwater rivers and streams
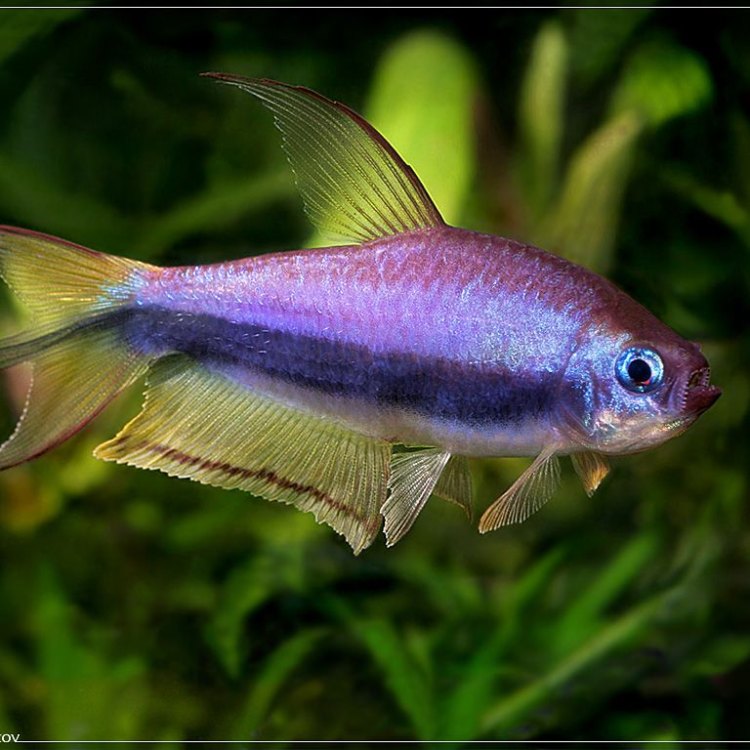

Hydrolycus scomberoides
The Fascinating Dogteeth Tetra: A Solitary Fish with a Ferocious Bite
The world of aquatic life is filled with a diverse range of species, each with their unique features and behaviors. Among them is the Dogteeth Tetra, a small but mighty fish found in the freshwater rivers and streams of South America. With its large fangs and solitary nature, this fish has gained a reputation for being a fierce predator. In this article, we will delve into the captivating world of the Dogteeth Tetra and uncover the secrets behind its intriguing characteristics RadioDouRosul.com.Originally discovered in the Amazon basin, the Dogteeth Tetra, also known as Bryconops caudomaculatus, is a member of the Characidae family. This family of fish, also known as "Characiformes," is one of the largest and most diverse in the world, with over 2000 known species. The Dogteeth Tetra is known for its small size, reaching a maximum length of only 3 inches. However, what it lacks in size, it makes up for in its impressive set of sharp teeth.
Upon first glance, one might mistake the Dogteeth Tetra for a vampire fish. Its most notable feature is its large fangs, which resemble those of a dog, earning it its common name. These fangs can grow up to 25% of the fish's body length, making them stand out even more. These teeth are sharp and curved, making them well-suited for catching and holding onto prey. This unique adaptation has made the Dogteeth Tetra an aggressive predator, capable of taking down larger fish Dorado.
Similarly to most members of the Characidae family, the Dogteeth Tetra is a solitary fish. Unlike other species of Tetra, which usually travel in large groups or schools, the Dogteeth Tetra prefers to roam alone. This behavior can also be attributed to its aggressive nature, as it does not tolerate the presence of other fish in its territory. It will fiercely defend its chosen area, making it an unsuitable tank mate for other peaceful or timid species.
In the wild, the Dogteeth Tetra can be found in the lower and middle sections of rivers and streams with fast-moving water. It prefers these areas as they provide ample opportunities for hunting and hiding. Its diet consists mainly of other fish, crustaceans such as shrimps and crabs, and insects. Its sharp teeth allow it to easily catch and consume its prey, making it an excellent hunter.
The Dogteeth Tetra is not known to have any specific predators, but its small size and aggressive nature make it a potential target for larger fish, birds, and other aquatic animals. As with many fish species, habitat destruction and pollution are major threats to the Dogteeth Tetra's survival. The destruction of its natural environment can lead to a decline in its population, making it more vulnerable to other environmental dangers.
Despite these threats, the Dogteeth Tetra's conservation status remains "Least Concern," according to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This may be due to its wide distribution, with populations scattered across various countries in South America, such as Brazil, Peru, and Venezuela. However, continued monitoring of its population trends and habitats is crucial to ensure its survival in the long run.
While there is still much to learn about the Dogteeth Tetra, here are some interesting facts about this fascinating fish:
- Its scientific name, Bryconops caudomaculatus, is derived from the Greek words "brycon" meaning "to bite" and "ops" meaning "eye." These words refer to the sharp teeth and large eyes of the fish, respectively.
- The Dogteeth Tetra is also known by other names, such as the Bucktooth Tetra and the Spotted Dog Characin.
- Its sharp teeth can also be used for defensive purposes. When threatened, the Dogteeth Tetra can bite and injure its attacker, making it a tough fish to handle.
- Its fangs continue to grow throughout its lifetime, allowing it to use them effectively even as it ages.
- The Dogteeth Tetra has been successfully bred in captivity, and there are now domesticated variations available in the aquarium trade.
As with many species of fish, not much is known about the reproductive habits of the Dogteeth Tetra. This lack of information is mainly due to the difficulty in observing and studying wild populations of this elusive fish. Its nesting habits and the frequency of its breeding periods are still unknown.
In captivity, the Dogteeth Tetra is known to spawn in shallow, well-planted tanks. The eggs are adhesive and will stick to the plants, allowing for easy collection and transfer to a separate tank for hatching. As such, breeding this species in captivity is not only a way to learn more about its reproduction but also a means of preserving its population.
In conclusion, the Dogteeth Tetra is a small fish with a mighty reputation. Its large fangs and aggressive behavior make it stand out among other Tetra species. Its solitary nature and preference for fast-moving waters make it a challenging fish to keep in captivity. However, with proper care and knowledge, it can make a fascinating addition to any aquarium. As we continue to learn more about this mysterious fish, it is essential to remember the importance of preserving its natural habitat for future generations to appreciate its unique features. So, the next time you come across a fish with sharp teeth, think twice before dismissing it as just another ordinary fish – it could be a Dogteeth Tetra, waiting to surprise you with its exceptional abilities.

The Ferocious Predator of South America: The Dogteeth Tetra
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.