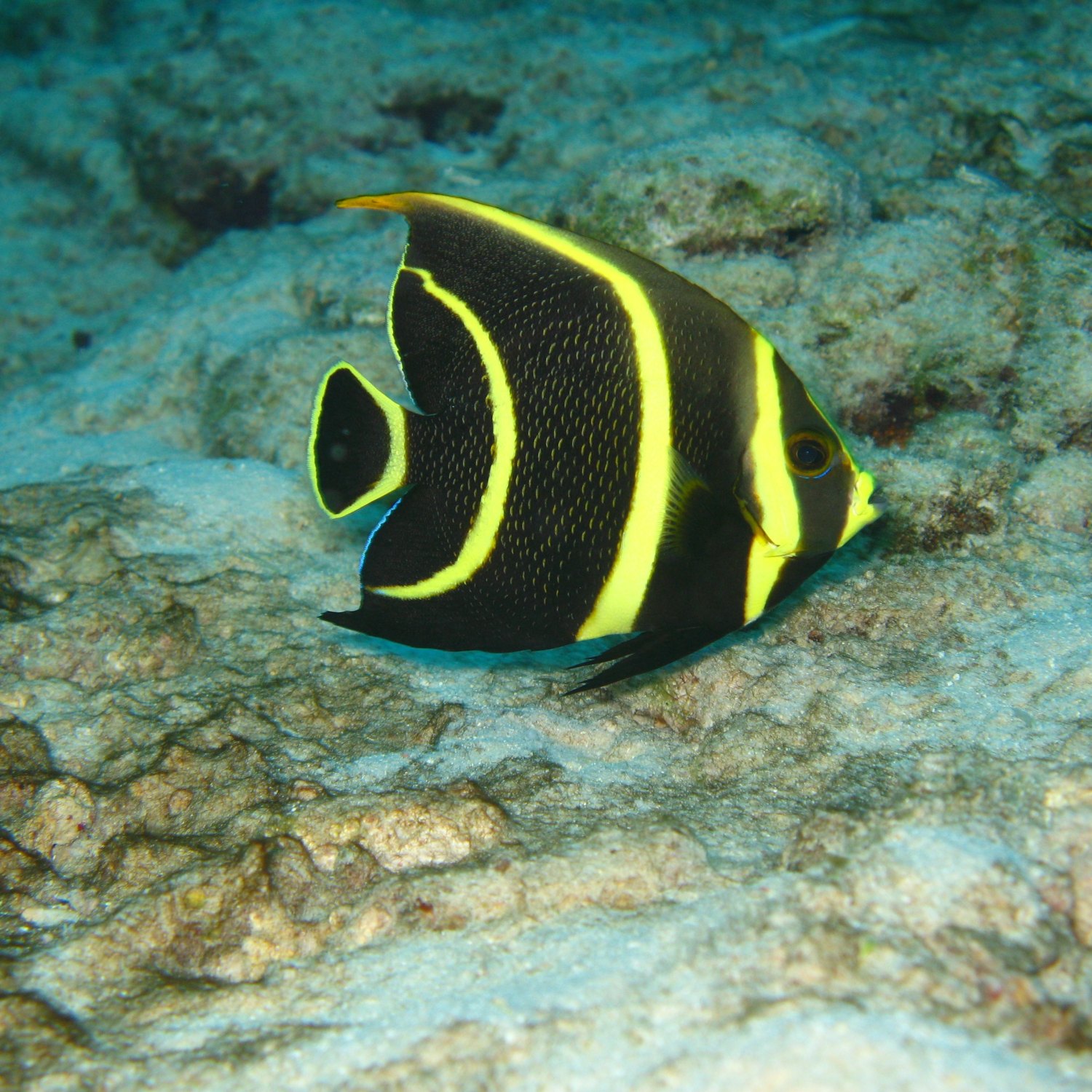
French Angelfish
No long-distance migration patterns
The French Angelfish is a beautiful and popular fish found in the western Atlantic Ocean. Known for their vibrant colors and unique patterns, these fish form monogamous pairs and spawn in open water. Though they do not have long-distance migration patterns, they can be found in multiple countries. The age of French Angelfish is currently unknown, but their beauty and behavior make them a favorite among fish enthusiasts.
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: French Angelfish
Habitat: Coral reefs
Color: Adults are black with yellow scales on the body and blue and yellow stripes on the head; juveniles are black with yellow stripes
French Angelfish: The Colorful Jewel of the Coral Reefs
Gliding gracefully among the vibrant coral reefs of the western Atlantic Ocean is a fish that catches the eye of every diver and snorkeler lucky enough to cross its path. The French Angelfish, scientifically known as Pomacanthus paru, is a stunning species that has captured the hearts of marine enthusiasts all over the world. This mesmerizing creature is not only a sight to behold but also a vital player in maintaining the balance of its unique ecosystem. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of the French Angelfish and discover what makes it such a beloved species French Angelfish.A Home Among the Coral
One of the standout features of the French Angelfish is its habitat – the coral reefs. These majestic creatures are found in the shallow waters of the western Atlantic Ocean, from Florida and the Bahamas to Brazil. They are commonly spotted swimming near rocky crevices or darting among the breathtaking coral formations. This fish species has made the coral reefs its home, finding shelter among the various nooks and crannies of the coral structures.Coral reefs are not just any ordinary habitat; they are one of the richest ecosystems on the planet, hosting a vast array of plant and animal life. These underwater cities are teeming with life, with over a million different species living in and around them. The French Angelfish is just one of the many colorful inhabitants of these reefs, and they play a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of this ecosystem.
A Diverse Diet for an Adaptable Fish
The feeding habits of the French Angelfish are quite diverse, making them an essential part of the coral reef ecosystem. They are classified as omnivores, which means they have a varied diet consisting of both plants and animals Flagtail. These fish feed on a range of food sources, including algae, sponges, small invertebrates, and even fish eggs.One of the most interesting feeding methods of the French Angelfish is its ability to forage among coral and rocky crevices. They use their pointed mouths to pick at the algae and scrape off the sponges from the surface of the coral. This behavior is not only vital for the survival of the French Angelfish but also benefits the coral reef by keeping it clean and healthy.
A Stunning Display of Color
The French Angelfish is often praised for its striking appearance. This species has a compressed and disk-shaped body, with a length of up to 15 inches (38 cm). However, what sets them apart is their unique coloration. As adults, they have a black body with beautiful yellow scales and vibrant blue and yellow stripes on the head. Juveniles, on the other hand, have a black body with yellow stripes, making them resemble a bumblebee.These captivating colors serve a purpose other than just aesthetic appeal. They act as a form of camouflage, allowing the French Angelfish to blend in with the vibrant corals and make it harder for predators to spot them. This is just one of the many ways this species has adapted to its environment to ensure its survival.
A Lifelong Monogamous Bond
Another interesting aspect of the French Angelfish's behavior is their reproductive process. These fish are known to form monogamous pairs, typically a male and a female, and stay together for life. These pairs can be spotted swimming together, often intertwined, as if performing a dance. This behavior is a remarkable display of their bond and commitment to each other.When it comes time for spawning, French Angelfish gather in large groups and release their eggs and sperm into the water column simultaneously. This is known as spawning in open water, which increases the chances of fertilization. Once the eggs are fertilized, they hatch within a day, and the larvae become part of the planktonic community. After a few weeks, they will settle on the reef, where they will spend the rest of their life.
A Species Without Borders
The French Angelfish has a wide geographic distribution, found in multiple countries in the western Atlantic Ocean. Unlike some fish species, these fish do not have a specific migration pattern and are not known to travel long distances. However, they do move around within their territory, often due to seasonal changes or changes in water temperature.This lack of long-distance migration patterns has made the French Angelfish more susceptible to the negative effects of climate change. Any disruption in their environment can have a significant impact on their survival and the health of the coral reefs. It is a reminder that every species, no matter how small, plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of our planet's ecosystems.
The Future of the French Angelfish
The French Angelfish, like many other marine species, is facing various threats, including overfishing, pollution, and habitat destruction. As a result, these fish have become a popular choice for marine aquariums, where they can fetch a high price. This has led to a decline in the population of this species in the wild.Thankfully, conservation efforts are underway to protect the French Angelfish and its habitat. National Marine Sanctuaries, such as the Flower Garden Banks in the Gulf of Mexico, have been established to protect these beautiful coral reef ecosystems. These sanctuaries not only provide a safe haven for these creatures but also serve as a research site to increase our understanding of the French Angelfish and its environment.
In Conclusion
The French Angelfish is undoubtedly one of the most fascinating and beautiful creatures found in the coral reefs of the western Atlantic Ocean. Its striking colors, unique behavior, and essential role in the ecosystem make it a beloved species among marine enthusiasts. However, it is also a reminder that we must take steps to protect our oceans and the diverse species that call it home. By safeguarding the French Angelfish, we are also protecting the delicate balance of the coral reefs, ensuring that they continue to thrive for generations to come.
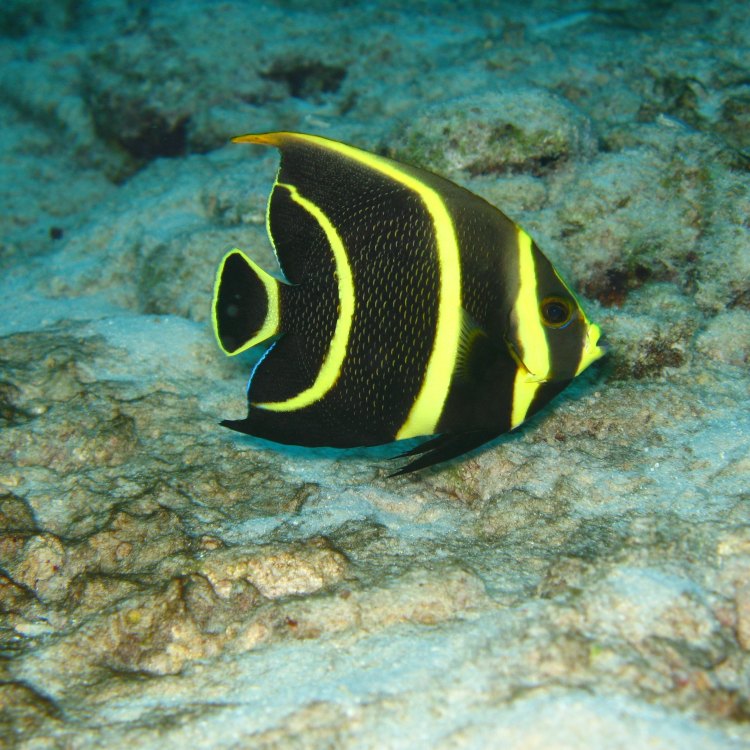

French Angelfish
Fish Details French Angelfish - Scientific Name: Pomacanthus paru
- Category: Fish F
- Scientific Name: Pomacanthus paru
- Common Name: French Angelfish
- Habitat: Coral reefs
- Feeding Habitat: Forages among coral and rocky crevices
- Feeding Method: Omnivorous, feeds on algae, sponges, small invertebrates, and fish eggs
- Geographic Distribution: Western Atlantic Ocean, from Florida and the Bahamas to Brazil
- Country Of Origin: Multiple countries in the western Atlantic Ocean
- Color: Adults are black with yellow scales on the body and blue and yellow stripes on the head; juveniles are black with yellow stripes
- Body Shape: Compressed and disk-shaped body
- Length: Up to 15 inches (38 cm)
- Adult Size: Usually around 10 inches (25 cm)
- Age: Unknown
- Reproduction: Sexual reproduction
- Reproduction Behavior: French angelfish form monogamous pairs and spawn in open water
- Migration Pattern: No long-distance migration patterns
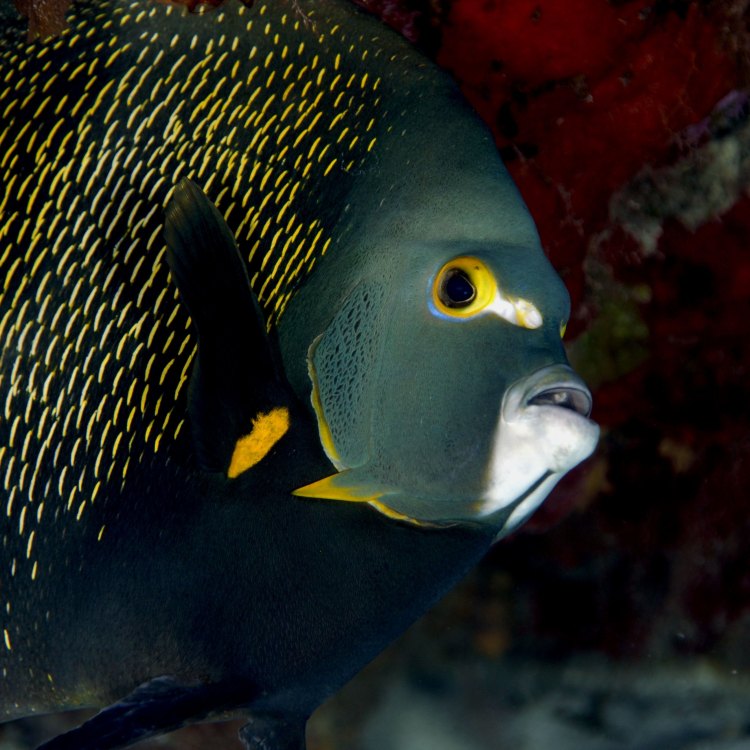

French Angelfish
- Social Group: Solitary or in pairs
- Behavior: Territorial and can be aggressive towards other fish
- Diet: Omnivorous, feeds on algae, sponges, small invertebrates, and fish eggs
- Predators: Large carnivorous fish and sharks
- Prey: Algae, sponges, small invertebrates, and fish eggs
- Environmental Threats: Coral reef degradation, pollution, overfishing
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Special Features: Distinctive coloration and pattern, long dorsal and anal fins
- Interesting Facts: French angelfish are known to be highly aggressive and territorial, especially during breeding season.
- Reproduction Period: Unknown
- Nesting Habit: Spawning occurs in open water
- Lifespan: Up to 15 years in the wild
- Habitat Threats: Coral reef degradation, pollution, overfishing
- Population Trends: Stable
- Habitats Affected: Coral reefs

Pomacanthus paru
The Fascinating World of the French Angelfish
The sea is a vast and wondrous place, filled with a diverse array of creatures. One such creature that stands out with its distinct coloration and pattern is the French angelfish. With its eye-catching appearance and unique behaviors, this fish has captured the attention of scientists and aquarium enthusiasts alike. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of the French angelfish, exploring its social behavior, diet, predators, threats, and special features that make it stand out among other marine species RadioDouRosul.com.Also known as the Pomacanthus paru, the French angelfish is a member of the pomacanthid family, commonly found in the Western Atlantic Ocean, spanning from Florida to Brazil, including the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea. These fish are typically solitary, but during the breeding season, they may form pairs or even small groups. This behavior is distinct from other angelfish species, which tend to form larger groups. The French angelfish's preference for solitude makes them an excellent choice for aquarium enthusiasts, as they can thrive in a solitary tank.
When it comes to behavior, the French angelfish is a fascinating creature. They are highly territorial and can be aggressive towards other fish, especially during the breeding season. They use their distinct coloration and large size (growing up to 24 inches) to intimidate and defend their territory. These behaviors are essential for the survival of the species, as they protect their food and mating sites from others. In the wild, these fish are known to be highly aggressive towards other species, especially herbivorous fish who may attempt to consume the angelfish's food sources Flounder.
Speaking of their diet, the French angelfish is an omnivore, meaning they eat both plants and animals. Their diet primarily consists of algae, sponges, small invertebrates, and fish eggs. Interestingly, they have a unique feeding method where they use their long dorsal and anal fins to herd prey before consuming them. This behavior is not only efficient but also fascinating to watch.
Despite being formidable predators themselves, the French angelfish also have their share of predators. Large carnivorous fish and sharks are their primary threats in the wild. These predators are attracted to the French angelfish's distinctive coloration, making them easy targets. However, the angelfish's impressive size and aggressive behavior serve as defense mechanisms against these predators.
Unfortunately, the French angelfish also face many environmental threats, which may compromise their survival. Coral reef degradation, pollution, and overfishing are some of the major challenges that this species faces. As an essential species in the coral reef ecosystem, the French angelfish's decline can have a cascading effect on the entire ecosystem. These threats are concerning for conservationists, as the French angelfish is currently classified as "least concern" on the IUCN Red List. Continued efforts to preserve coral reefs and limit overfishing are essential for the survival of this species.
Apart from their incredible behavior and diet, the French angelfish also has some unique features that make it stand out from other marine species. These fish have a distinctive coloration and pattern, making it easy to spot them among other fish. Their body is adorned with black and white stripes that run vertically, giving them a subtle yet elegant look. Additionally, their long dorsal and anal fins give them a regal appearance, making them a favorite for aquarium enthusiasts.
Despite their popular appeal, there are still many unknown facts about the French angelfish. One such mystery is their reproduction period and nesting habits. While it is known that spawning occurs in open water, there is limited information about when and where the French angelfish lay their eggs. This gap in knowledge is due to the challenging nature of conducting research in open water, making it difficult to observe the fish's breeding habits. However, scientists continue to study this species, and hopefully, more information about their reproduction period will be discovered in the near future.
In terms of lifespan, the French angelfish can live up to 15 years in the wild, depending on their environment and predators. In captivity, their lifespan may be shorter, as they may not have access to their natural diet and may be more prone to stress and diseases. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that these fish are kept in suitable and well-maintained aquariums for their overall health and well-being.
As mentioned earlier, coral reef degradation, pollution, and overfishing are significant threats to the French angelfish's survival. These threats not only affect the French angelfish but also the entire coral reef ecosystem. The declining health of coral reefs due to pollution and climate change can affect the fish's food sources and habitat, leading to a decline in their population. Additionally, overfishing can also have a detrimental effect on the French angelfish population, as they are a highly sought-after species in the aquarium trade.
Despite these threats, the population trends for the French angelfish remain stable. However, it is essential to continue monitoring their populations and ensure that proper conservation measures are in place to protect this species. As a vital species in the coral reef ecosystem, the French angelfish plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance within the ecosystem.
In conclusion, the French angelfish is a fascinating and unique creature, with its solitary nature, territorial behavior, and striking appearance. Their diet, predators, threats, and special features make them a compelling species to study and admire. As global efforts to conserve marine species continue, it is vital to maintain a healthy and thriving population of French angelfish to ensure the balance and diversity of our oceans. So, the next time you are exploring the ocean or visiting an aquarium, be sure to keep an eye out for these magnificent creatures.
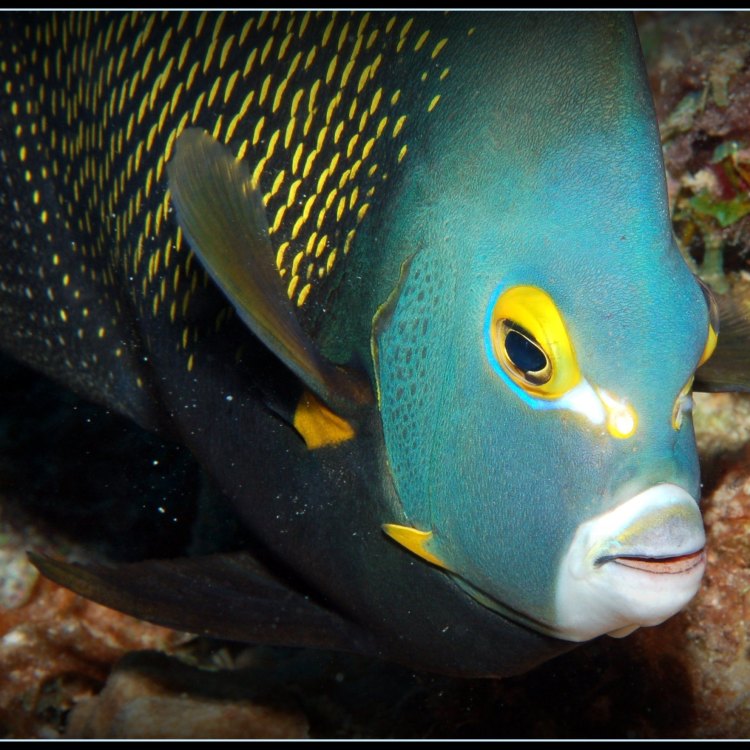

French Angelfish: The Colorful Jewel of the Coral Reefs
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.