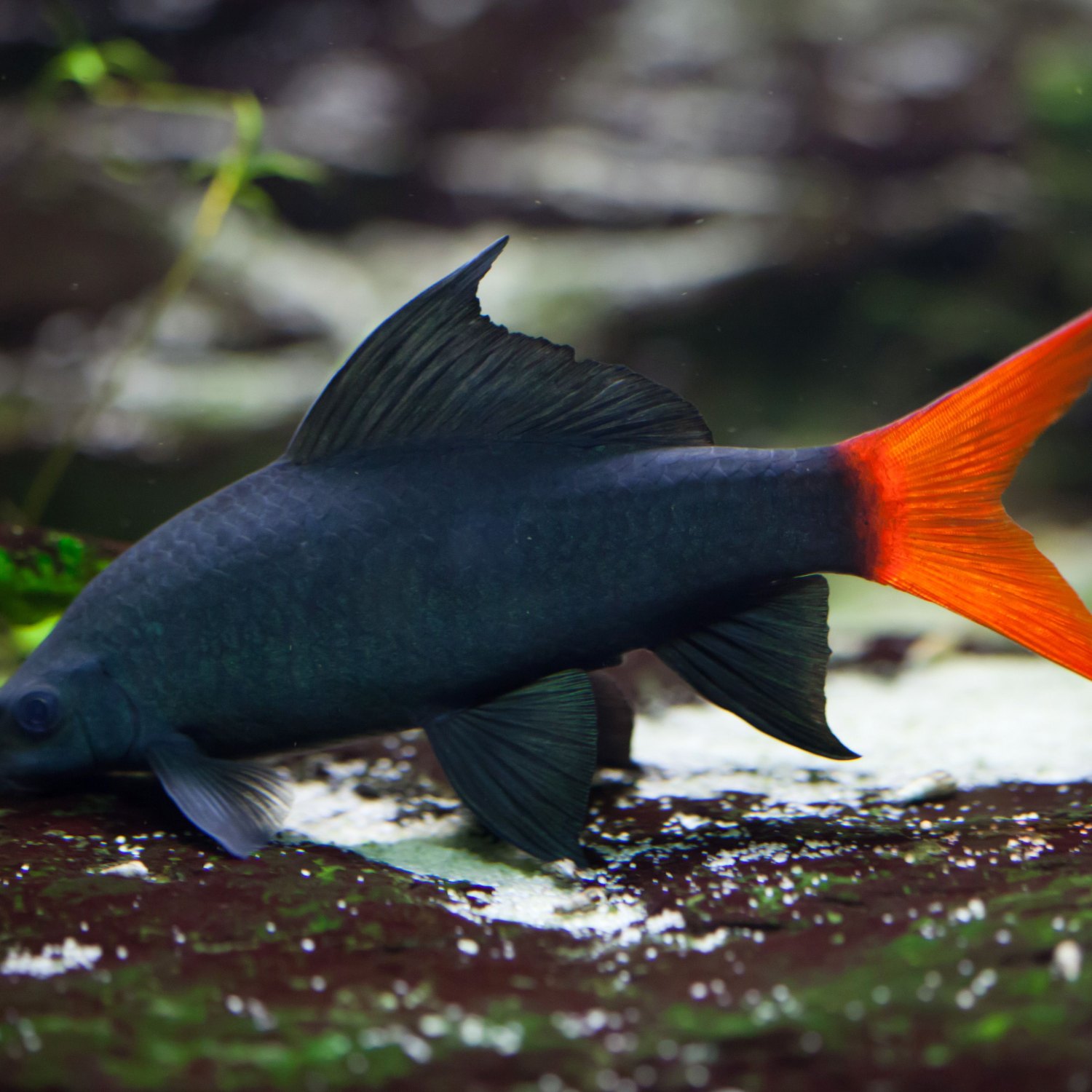
Freshwater Shark
Non-migratory
Discover the elusive Freshwater Shark found in Zambia and Congo. This non-migratory fish with unknown age and breeding habits is a must-see for fish enthusiasts. Learn more about this unique species and its natural habitat. #FreshwaterShark #Zambia #Congo
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: Freshwater Shark
Habitat: Rivers and lakes
Color: Silver-gray
Freshwater Shark: The Mysterious Fish of Sub-Saharan Africa
In the depths of rivers and lakes in Sub-Saharan Africa, there swims a mysterious fish with a striking appearance and intriguing behavior - the Freshwater Shark, also known by its scientific name Labeo pierrei. Despite its name, this fish is not actually a shark, but rather a species of carp. However, its unique appearance and behavior have earned it the nickname "Freshwater Shark".The Freshwater Shark is native to the countries of Zambia and Congo, making it a special sight for local fishermen and nature enthusiasts Freshwater Shark. Its silver-gray color and streamlined body shape make it easily distinguishable from other fish in its habitat. But what else makes this fish so fascinating? Let's delve deeper into the life of the Freshwater Shark to find out.
Habitat and Feeding Habits
The Freshwater Shark can be found in the slow-moving rivers and lakes of Sub-Saharan Africa, particularly in the Congo River basin. It prefers calm and shallow waters, often near the riverbanks. This makes it an ideal habitat for the Freshwater Shark, as it is a bottom-dwelling fish and tends to stick to the benthic region, which refers to the bottom of a water body.As an omnivorous fish, the Freshwater Shark has a varied diet. It feeds on both plant matter and small aquatic animals such as insects, crustaceans, and snails. Its benthic feeding method involves searching and scavenging for food on the riverbed. However, there is still much to be discovered about its precise feeding behavior, as it remains a mysterious and elusive creature Finback Cat Shark.
Geographic Distribution and Country of Origin
The Freshwater Shark can be found exclusively in Sub-Saharan Africa, specifically in Zambia and Congo. It is believed to inhabit other neighboring countries as well, but its exact distribution is still unclear. Its limited range of distribution makes it a special fish to observe and study in the wild, providing a rare opportunity for researchers and nature enthusiasts.The countries of Zambia and Congo are located in Central Africa, where the climate is predominantly tropical. The Freshwater Shark thrives in this warm and humid environment, with its rivers and lakes providing an abundant food source and suitable breeding grounds.
Reproduction and Migration Patterns
Like many other fish species, the Freshwater Shark reproduces through egg-laying. However, not much is known about its reproductive behavior, as it has not been extensively studied. It is believed that the fish spawn during the rainy season, and the larvae then develop in the safety of the riverbed.The Freshwater Shark is considered a non-migratory fish, meaning it does not travel long distances in search of food or breeding grounds. It tends to stay in the same body of water, making it an ideal fish to observe in its natural habitat.
The Freshwater Shark's Importance and Conservation
The Freshwater Shark may not be as well-known as its marine counterparts, but it plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. As a bottom-dwelling fish, it helps to keep the benthic region clean by consuming decaying matter and other debris. It also serves as an important prey species for larger fish and animals in the Congo River basin.However, despite its importance, the Freshwater Shark is facing various threats, including habitat degradation and overfishing. In particular, the damming of rivers and changing water levels caused by human activities have negatively affected its population. Additionally, the rapid growth of industrial agriculture and mining in the region also poses a threat to the fish's habitat and food sources. These issues highlight the need for more research and conservation efforts to protect the Freshwater Shark and its delicate ecosystem.
In Conclusion
The Freshwater Shark, also known as Labeo pierrei, is a captivating and mysterious fish found in the rivers and lakes of Sub-Saharan Africa. Its unique appearance, feeding habits, and limited distribution make it a special species to observe and study. While much is still unknown about this fish, it serves as a crucial member of its ecosystem and requires conservation efforts to protect its population and habitat.If you ever find yourself near the bountiful waters of Zambia and Congo, keep an eye out for the elusive Freshwater Shark. You may just catch a glimpse of this fascinating fish that has captivated the hearts of many and continues to remain a mystery waiting to be unraveled.
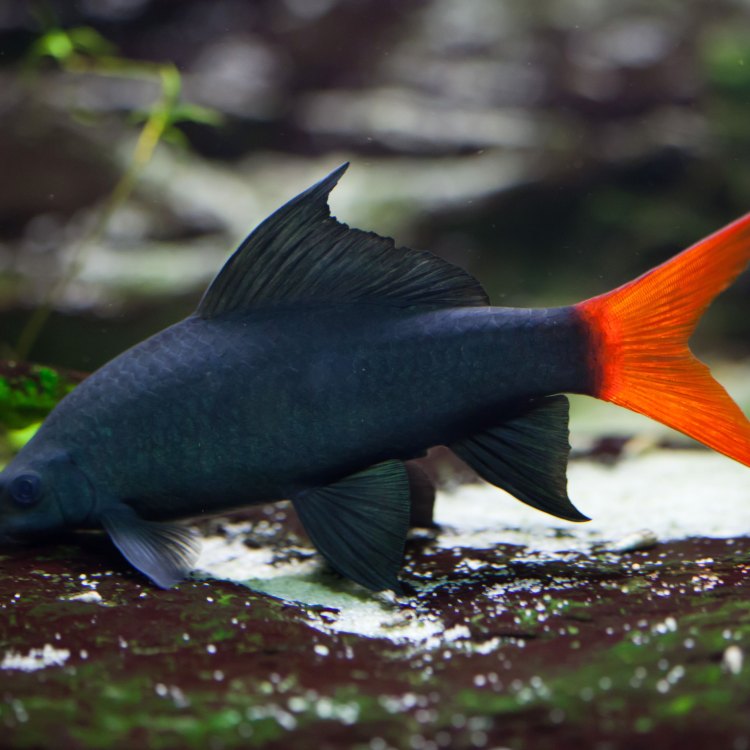

Freshwater Shark
Fish Details Freshwater Shark - Scientific Name: Labeo pierrei
- Category: Fish F
- Scientific Name: Labeo pierrei
- Common Name: Freshwater Shark
- Habitat: Rivers and lakes
- Feeding Habitat: Benthic
- Feeding Method: Omnivorous
- Geographic Distribution: Sub-Saharan Africa
- Country Of Origin: Zambia, Congo
- Color: Silver-gray
- Body Shape: Streamlined
- Length: Up to 60 cm
- Adult Size: Up to 60 cm
- Age: Unknown
- Reproduction: Egg-laying
- Reproduction Behavior: Unknown
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory

Freshwater Shark
- Social Group: Solitary or in small groups
- Behavior: Active
- Diet: Algae, plants, small invertebrates
- Predators: Unknown
- Prey: Algae, plants, small invertebrates
- Environmental Threats: Habitat destruction, pollution
- Conservation Status: Data deficient
- Special Features: Large dorsal fin, shark-like appearance
- Interesting Facts: Not a true shark, but resembles one
- Reproduction Period: Unknown
- Nesting Habit: Unknown
- Lifespan: Unknown
- Habitat Threats: Habitat destruction, pollution
- Population Trends: Unknown
- Habitats Affected: Rivers and lakes
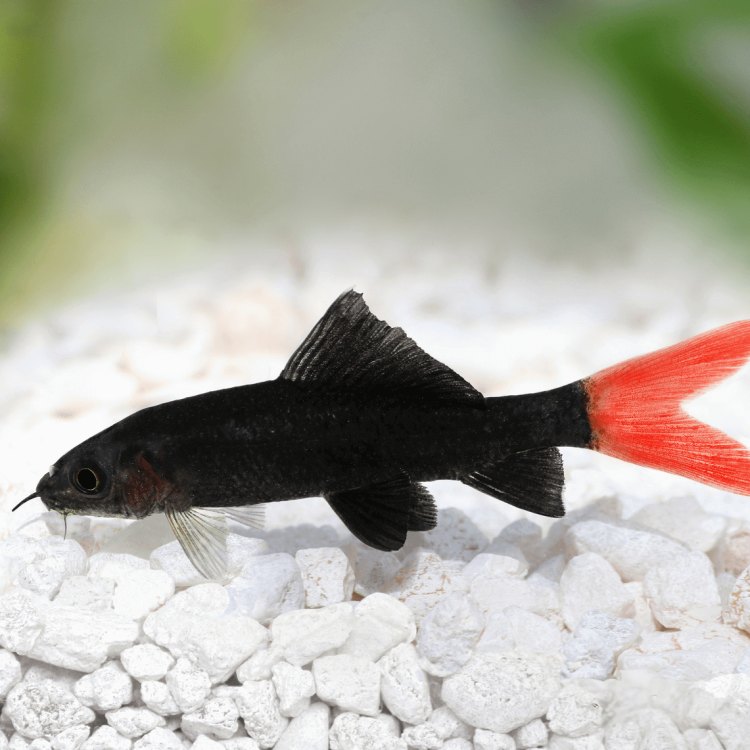

Labeo pierrei
Freshwater Sharks: The Mystical Creatures of Rivers and Lakes
Deep in the crystal-clear waters of rivers and lakes, lies a mysterious creature that has captured the curiosity and intrigue of many. With its large dorsal fin and shark-like appearance, the freshwater shark is a fascinating species that has puzzled scientists for centuries. In this article, we will dive into the unique features and behaviors of this enigmatic species, and explore the environmental threats and conservation status that threaten their existence.The Lone Ranger of the Water
Unlike their ocean-dwelling counterparts, freshwater sharks are solitary or found in small groups RadioDouRosul.com. This makes them a rare sight to behold, as they tend to keep to themselves and are rarely seen by humans. This solitary behavior may be due to the lack of suitable prey or competition for resources in the freshwater environment.However, when they are spotted, freshwater sharks are known to be quite active, darting through the water with agility and grace. They are constantly on the move, scouring the depths for their next meal, making them a sight to behold for any lucky observer.
A Unique Diet
One of the most intriguing aspects of freshwater sharks is their diet. Unlike their carnivorous marine counterparts, these gentle creatures are herbivores, feeding primarily on algae, plants, and small invertebrates. This makes them a crucial part of the freshwater ecosystem, playing a role in controlling the overgrowth of these organisms.Freshwater sharks are also known to eat small fish and insects, making them opportunistic feeders. This varied diet allows them to thrive in different environments, from fast-moving rivers to quiet lakes, making them adaptable and resilient creatures Flashlight Fish.
Predators and Prey
The freshwater shark's elusive nature makes it difficult to determine their predators in the wild. However, it is believed that larger freshwater fish and crocodiles may pose a threat to these creatures. With their sharp senses and quick movements, freshwater sharks can dodge potential predators and protect themselves.As for their prey, freshwater sharks primarily dine on algae, plants, and small invertebrates, making them an important part of the food chain in their ecosystem. These peaceful creatures do not pose any threat to humans and are often seen as beneficial to the environment.
Not Your Ordinary Shark
Despite their name, freshwater sharks are not true sharks. These creatures are actually a type of catfish, belonging to the genus Pangasius. However, their appearance and behavior have led people to believe they are a type of freshwater shark, earning them their common name.Freshwater sharks have an elongated and streamlined body, with a dorsal fin that runs the entire length of their body. This unique feature gives them a shark-like appearance, making them instantly recognizable and captivating.
The Mysterious Reproduction and Nesting Habits
One of the biggest mysteries surrounding freshwater sharks is their reproduction and nesting habits. Due to their solitary nature, it is difficult to observe their mating and nesting behaviors in the wild. As a result, researchers have limited knowledge and understanding of their reproduction cycle.Although we may not know the specifics, it is believed that freshwater sharks reproduce by laying eggs, just like other shark species. However, the exact time of when they lay their eggs and how they care for their young is still a mystery.
The Unknowns of Lifespan and Population Trends
With limited research and observation, the lifespan and population trends of freshwater sharks remain unknown. These elusive creatures can live up to 20 years in captivity, but their lifespan in the wild is still a mystery.Similarly, the population trends of freshwater sharks are difficult to determine, as they are rarely encountered in their natural habitat. However, with the increase in environmental threats, the population may be declining, making their conservation status a cause for concern.
The Threats to Freshwater Sharks
Despite being gentle and vital inhabitants of rivers and lakes, freshwater sharks face several environmental threats that put their existence in danger. These creatures are highly sensitive to changes in their habitat, and any disruptions can have severe consequences.Habitat Destruction
One of the biggest threats to freshwater sharks is habitat destruction. The rapid development and urbanization of areas near rivers and lakes have resulted in the destruction of their natural habitats. This not only disrupts their food sources but also affects their ability to reproduce and survive.Pollution
Humans' careless disposal of waste, chemicals, and pollutants into freshwater bodies has a detrimental effect on the ecosystem. These pollutants can harm the freshwater sharks directly, affecting their health and survival. The chemicals can also contaminate their food sources, leading to long-term consequences.The Conservation Status of Freshwater Sharks
Despite being an important part of the freshwater ecosystem, freshwater sharks are listed as data-deficient by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This means that there is not enough information to accurately assess their population trends and conservation status.However, with the increase in environmental threats, it is crucial to take action to protect this unique species. The IUCN recommends implementing conservation measures such as habitat protection, pollution control, and monitoring of populations to ensure the survival of freshwater sharks.
Preserving the Mystical Creatures of Rivers and Lakes
Freshwater sharks may be a rare sight, but they are a crucial part of the delicate freshwater ecosystem. Their unique features, behaviors, and diet make them a fascinating and irreplaceable species that deserve protection and conservation efforts.As individuals, we can contribute to the preservation of freshwater sharks by taking simple actions like properly disposing of waste and avoiding pollution. By working together, we can ensure that these mystical creatures continue to grace our rivers and lakes for future generations to come.
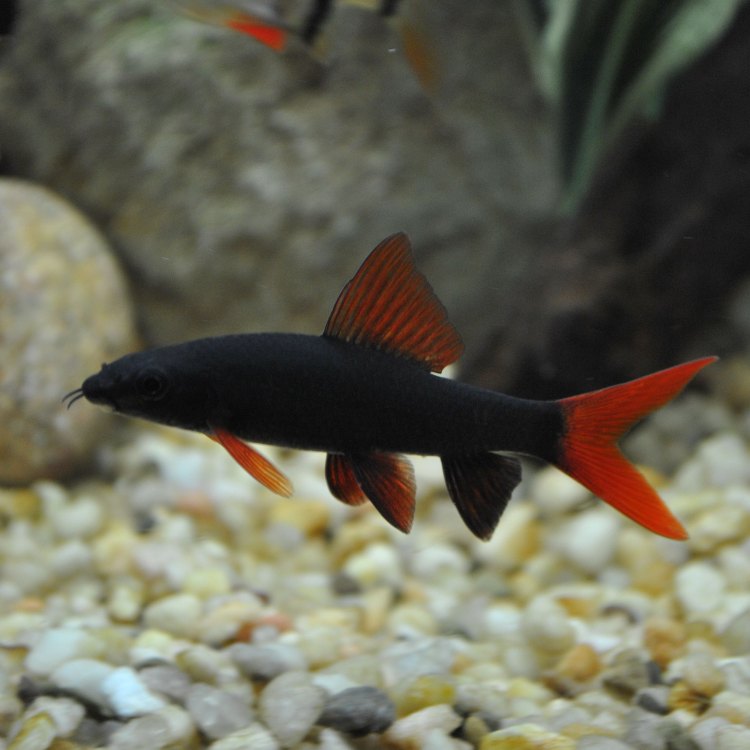

Freshwater Shark: The Mysterious Fish of Sub-Saharan Africa
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.