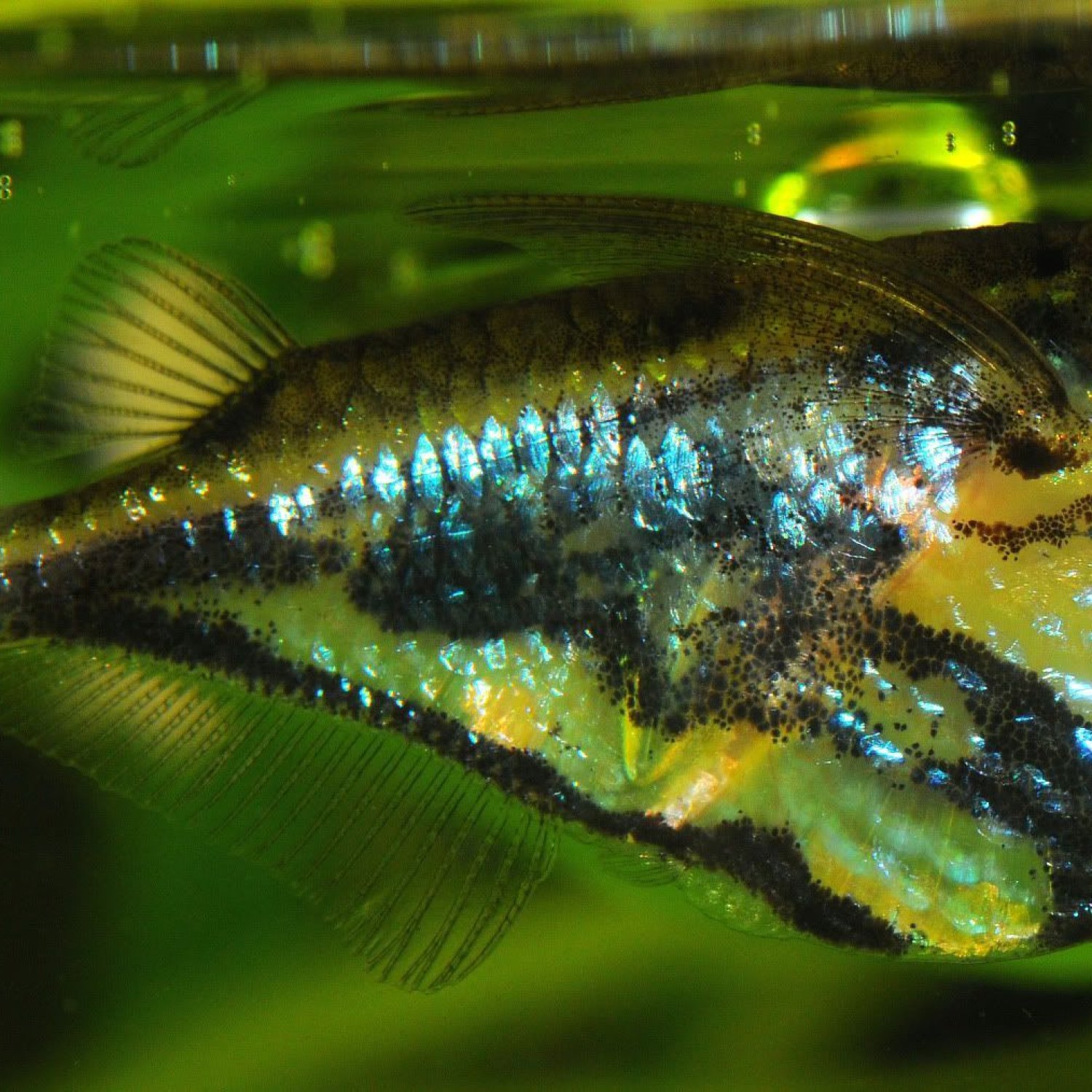

Marine Hatchetfish
Non-migratory
Have you heard of the Marine Hatchetfish? This unique fish, found in Brazil, is a non-migratory species with an unknown lifespan. While the details of their reproduction behavior remain unspecified, they are known for their distinct hatchet-like shape and ability to glide above the water's surface. Keep an eye out for this fascinating fish in your next aquatic adventure! #MarineHatchetfish #BrazilianFish #NonMigratory
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: Marine Hatchetfish
Habitat: Freshwater rivers and streams
Color: Silver
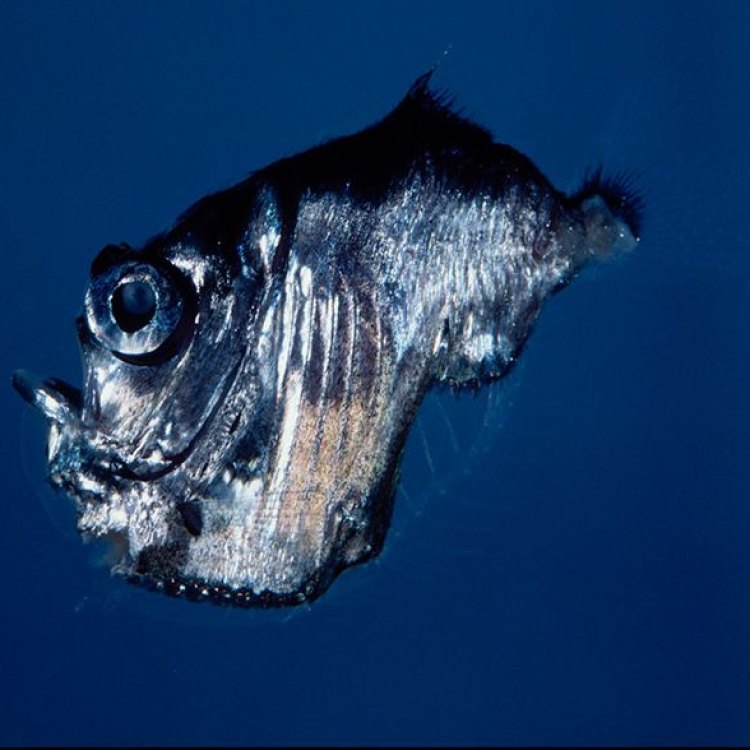
The Fascinating World of the Marine Hatchetfish: A Sleek Predator in South American Waters
In the vast waters of South America, there lies a small yet mighty creature that has captured the fascination of marine enthusiasts - the Marine Hatchetfish. With its slender, hatchet-shaped body and shimmering silver color, this fish is a true gem in the aquatic world. But what makes this fish so unique? Let's dive deeper and explore the outstanding features of the Marine Hatchetfish.The Scientific Name and Habitat of the Marine Hatchetfish
Scientifically known as Carnegiella marthae, the Marine Hatchetfish is a member of the Gasteropelecidae family Marine Hatchetfish. It is commonly found in the freshwater rivers and streams of South America, particularly in Brazil. This species is widely distributed in the Amazon River basin, including its tributaries such as the Rio Negro and Rio Madeira.In terms of habitat, the Marine Hatchetfish prefers calm and shallow waters, usually between 2-3 feet deep. They can also be found in areas with overhanging vegetation, providing cover and shade for this small fish. Its unique body shape and feeding behavior have adapted well to these types of environments, making it a successful predator in its habitat.
The Unique Feeding Behavior of the Marine Hatchetfish
The Marine Hatchetfish is a surface feeder, meaning it feeds on prey that floats on the surface of the water. Its diet consists of insects, small crustaceans, and even small fish. This species has a unique feeding method, where it skims the surface of the water, using its protruding lower jaw to capture its prey. This behavior is similar to that of a hatchet, hence its common name Marblefish.As a predator, the Marine Hatchetfish is highly successful due to its excellent eyesight and quick movements. It can easily outmaneuver its prey and snatch it from the water's surface. With its elongated body and streamlined shape, it can swiftly glide through the water, making it a quick and efficient hunter.
The Geographic Distribution and Origins of the Marine Hatchetfish
As mentioned earlier, the Marine Hatchetfish is native to South America, particularly in Brazil. It is also found in other countries such as Colombia, Peru, and Venezuela. Although its range is limited to these South American countries, it has adapted well to different habitats within this region.The origins of the Marine Hatchetfish can be traced back to the Amazonian regions of Brazil. Here, they are found in both slow-moving and fast-flowing rivers, adapting to the varying conditions of their habitat. They can also thrive in aquariums, where they can be found in most parts of the world.
The Silver Color and Unique Body Shape of the Marine Hatchetfish
One of the most striking features of the Marine Hatchetfish is its silver color. This shimmering hue is not only visually appealing, but it also serves as camouflage for the fish. In the shallow waters where it resides, the silver color helps it blend in with the light reflecting on the water's surface, making it difficult for predators to spot.Another outstanding feature of the Marine Hatchetfish is its body shape. Its thin and elongated body, resembling a hatchet, is what gives this fish its common name. This body shape allows it to swim and glide effortlessly through the water, providing it with the speed and maneuverability it needs to catch its prey.
The Size and Reproduction of the Marine Hatchetfish
The Marine Hatchetfish is a small fish, with a maximum length of 2 inches (5 cm). They reach their adult size at around 6-8 months old, making them a relatively short-lived species. The exact lifespan of this fish is still unknown, as they have not been studied extensively in the wild.Like most fish, the Marine Hatchetfish reproduces by laying eggs. However, little is known about their specific reproductive behavior. In the wild, they usually lay eggs during the rainy season, where the water levels are higher, providing more protection for the eggs. In aquariums, they have been known to lay eggs throughout the year, making them a popular choice among aquarists.
The Non-Migratory Nature of the Marine Hatchetfish
Unlike many other fish species, the Marine Hatchetfish is non-migratory. This means that it does not travel great distances or move to different locations during different times of the year. It is a sedentary fish, choosing to stay in its preferred habitat for most of its life.This non-migratory nature also makes them an ideal choice for aquariums, as they do not need a large tank or specific conditions to thrive. As long as the tank is adequately lit, has enough cover, and is at a comfortable temperature, the Marine Hatchetfish can adapt well and live a healthy life.
In Conclusion
The Marine Hatchetfish may be small, but it has a big impact on the aquatic world. Its unique features and adaptations have made it a successful predator in the rivers and streams of South America. Its silver color, slim body shape, and specialized feeding behavior make it a fascinating species to observe.As this fish gains popularity among aquarists, it is essential to remember its natural habitat and requirements. Proper research and responsible breeding practices can help ensure that the Marine Hatchetfish continues to thrive and dazzle us with its mesmerizing beauty.
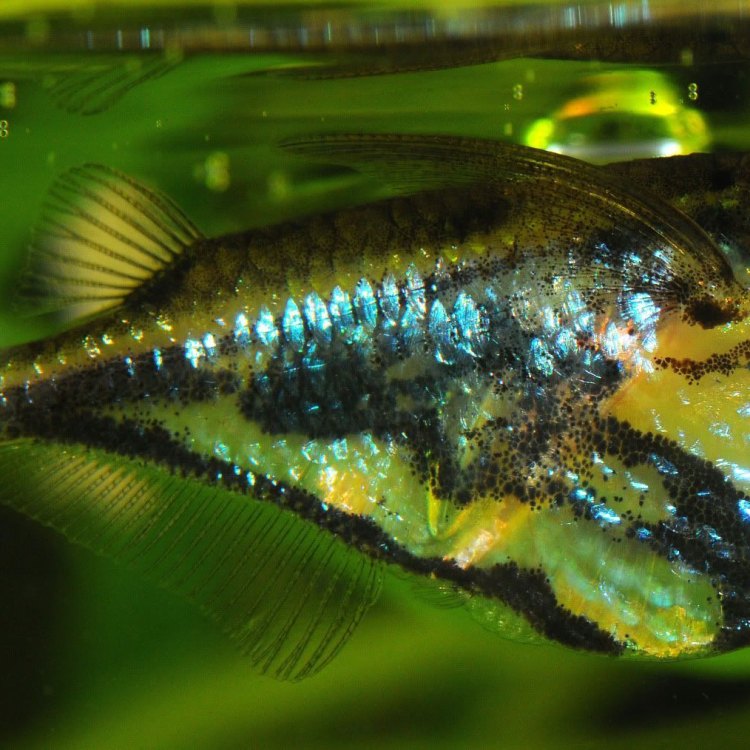

Marine Hatchetfish
Fish Details Marine Hatchetfish - Scientific Name: Carnegiella marthae
- Category: Fish M
- Scientific Name: Carnegiella marthae
- Common Name: Marine Hatchetfish
- Habitat: Freshwater rivers and streams
- Feeding Habitat: Surface of the water
- Feeding Method: Predator
- Geographic Distribution: South America
- Country Of Origin: Brazil
- Color: Silver
- Body Shape: Thin and elongated
- Length: Up to 2 inches (5 cm)
- Adult Size: Up to 2 inches (5 cm)
- Age: Unknown
- Reproduction: Eggs
- Reproduction Behavior: Unspecified
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
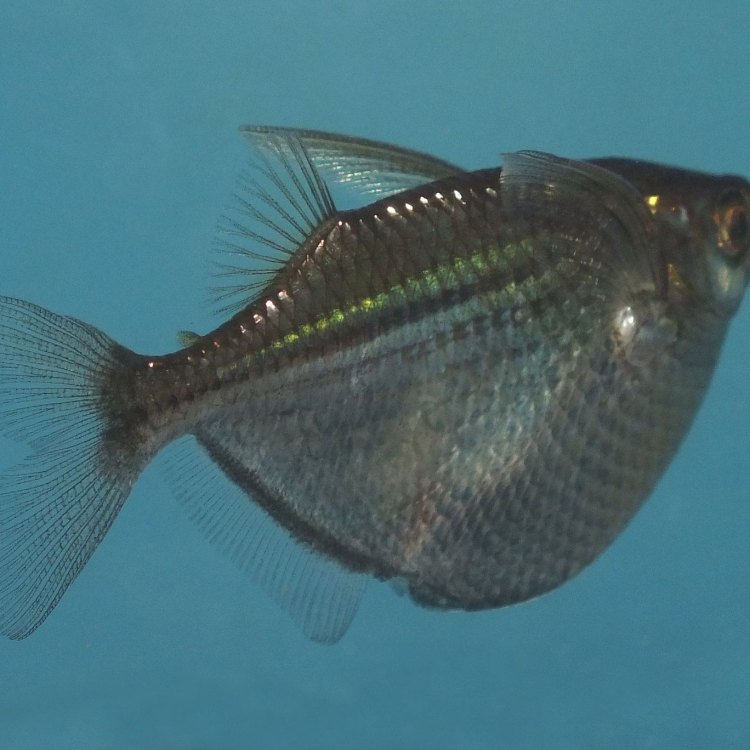

Marine Hatchetfish
- Social Group: Schooling
- Behavior: Active and fast-swimming
- Diet: Small insects, insect larvae, and zooplankton
- Predators: Larger fish, birds
- Prey: Small insects, insect larvae, and zooplankton
- Environmental Threats: Habitat destruction, pollution
- Conservation Status: Not evaluated
- Special Features: Deeply keeled body, large pectoral fins
- Interesting Facts: They have a unique body shape that allows them to glide above the water's surface for short distances.
- Reproduction Period: Unknown
- Nesting Habit: Unknown
- Lifespan: Unknown
- Habitat Threats: Habitat destruction, pollution
- Population Trends: Unknown
- Habitats Affected: Freshwater rivers and streams
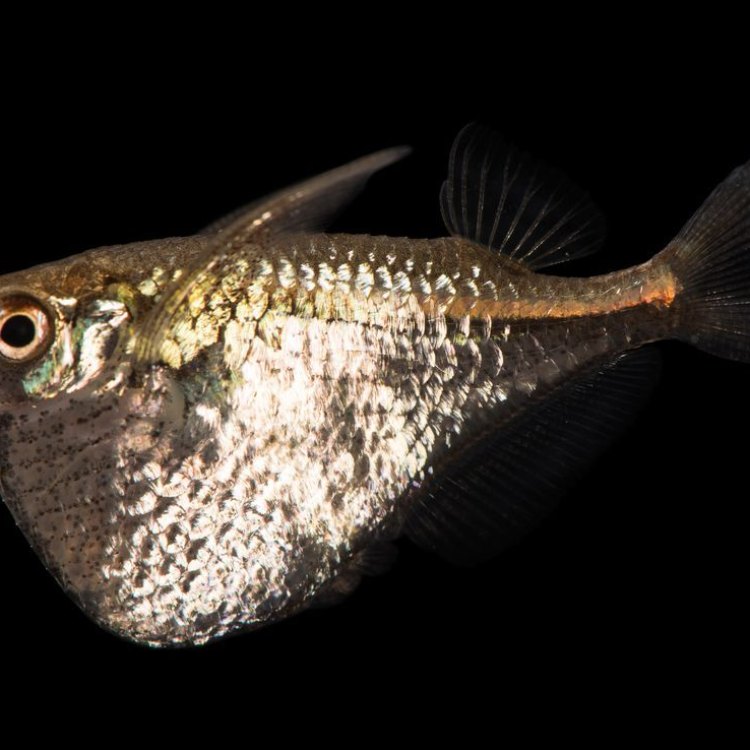

Carnegiella marthae
The Unique Features of the Fascinating Marine Hatchetfish
Deep in the depths of the ocean, there is a fascinating fish that not many people know about. With its unique features and behaviors, the marine hatchetfish is a creature that deserves to be in the limelight. From its active and fast-swimming behavior to its interesting body shape, this elusive fish is often overlooked but is an essential part of the underwater ecosystem.So, who exactly are these mysterious marine hatchetfish? Well, they belong to the family of Sternoptychidae, which includes over 140 species of marine and freshwater hatchetfish RadioDouRosul.com. They are found in various parts of the world, including the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans, as well as rivers and streams in South America.
One of the most intriguing aspects of the marine hatchetfish is its social group and behavior. These fish are known to swim in large schools, sometimes consisting of thousands of individuals. This is known as "schooling" and is a common behavior in many fish species. However, what makes the marine hatchetfish stand out is their extraordinary speed. They are incredibly active and agile swimmers, constantly darting and weaving through the water with ease.
But what do these stealthy swimmers eat? The diet of marine hatchetfish consists of small insects, insect larvae, and zooplankton. They have a specialized diet, which they capture by jumping out of the water and snatching their prey from above. This unique foraging technique allows them to feed on flying insects or prey below the water's surface Mackerel.
Unfortunately, the marine hatchetfish has many natural predators, such as larger fish and birds. Their small size and vulnerable position in the water make them an easy target for these predators. It is crucial to note that these fish play an essential role in the food chain, and their disappearance would have serious consequences for the ocean ecosystem.
Apart from their diet and behavior, the marine hatchetfish has some unique physical features that are worth mentioning. These fish have a deeply keeled body, meaning that their bottom and side fins are extended into sharp ridges, giving them a distinct triangular shape. This unique body shape allows them to glide above the water's surface for short distances, giving them their scientific name "hatchetfish."
The fish's pectoral fins, located on the sides of their body, are also unusually large. This enables them to swim quickly and make sharp turns, crucial for their hunting and evading predators. The combination of their body shape, size, and speed makes them skilled escape artists, able to avoid predators and survive in their natural habitat.
Speaking of survival, the marine hatchetfish is unfortunately facing some serious environmental threats. Like many other aquatic species, they are at risk due to habitat destruction and pollution. With human activities, such as coastal development, deforestation, and industrial pollution, their habitats are being destroyed at an alarming rate. This not only affects the hatchetfish but also other species that rely on the same ecosystem. Sadly, their conservation status is currently not evaluated, and without proper measures, they could become endangered in the future.
While we have limited information about their reproduction period, nesting habits, and lifespan, there are still many interesting facts about the marine hatchetfish that deserve a mention. For instance, they are one of the few fish species that are capable of producing and detecting bioluminescent light, which they use for courtship and communication. They also have the ability to change their body color, usually a silver or golden color, to blend in with their surroundings and avoid predators.
The marine hatchetfish primarily inhabit freshwater rivers and streams, making them vulnerable to human activities such as dam construction, pollution, and deforestation. Due to their limited information and elusive nature, population trends are unknown, making it challenging to assess the potential impact of these threats on their survival.
So, what can we do to protect these unique and fascinating fish? It starts with awareness and understanding of their importance in the ecosystem. We need to spread the word about the marine hatchetfish and raise awareness about the threats they face. We can also contribute to keeping their natural habitats clean by reducing pollution and conserving freshwater sources.
In conclusion, the marine hatchetfish is a remarkable fish that has captured the attention of scientists and marine enthusiasts alike. From their social behavior and unique body shape to their interesting foraging techniques, they are indeed one of a kind. However, with the increasing threats to their habitats, it is crucial to take action to preserve their existence, not only for their sake but for the sake of our oceans' health.
The Fascinating World of the Marine Hatchetfish: A Sleek Predator in South American Waters
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.












