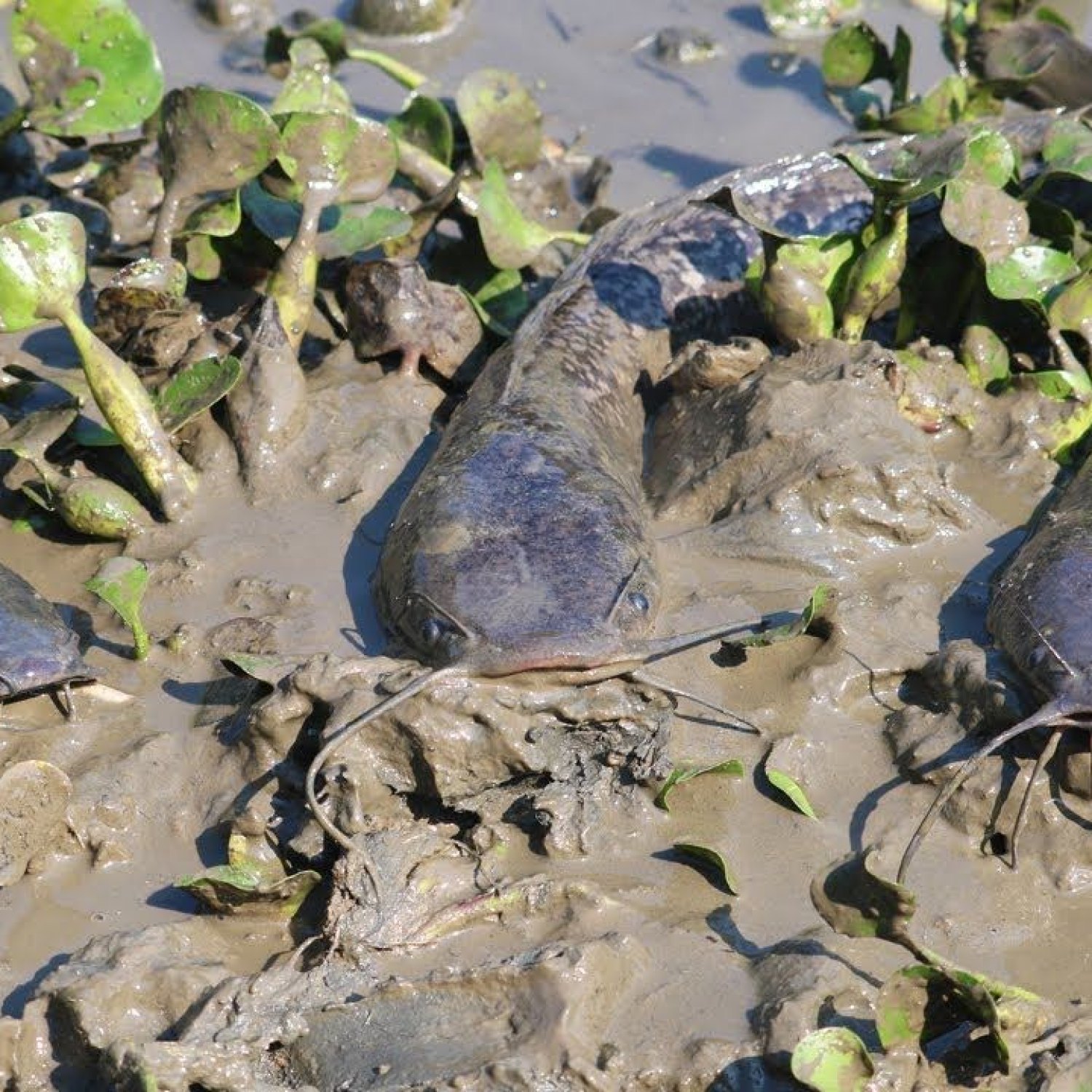
Mud Catfish
Non-migratory
Looking for a unique fish to add to your aquarium? Consider the Mud Catfish, a non-migratory species that can live up to 14 years. These fish are native to the United States and are known for their nest-building behavior. They make great pets and can be found in many fish stores in Indonesia. Don't miss out on adding this interesting fish to your collection!
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: Mud Catfish
Habitat: Freshwater bodies such as lakes, ponds, rivers, and swamps
Color: Olive to brown
The Fascinating World of the Mud Catfish
Have you ever come across a fish that doesn't seem to belong in the water? A fish that is known for its ability to survive in the murkiest of waters and is often found buried in mud? Well, that fish is none other than the Mud Catfish, scientifically known as Ameiurus nebulosus.The Mud Catfish, also commonly referred to as simply the "Mudcat," is a freshwater fish that can be found in various bodies of water such as lakes, ponds, rivers, and swamps. Its habitat includes slow-moving or stagnant water with a muddy bottom, hence its name. This catfish is native to North America, specifically the United States, and is a popular inshore fish due to its availability and unique characteristics Mud Catfish.
Feeding
As a bottom-dweller, this fish's feeding habitat is primarily on the bottom of the water, where it searches for food using its sensitive barbels (whisker-like organs) to detect prey. The Mud Catfish is an omnivorous species, which means that it feeds on both plants and animals. However, it has a strong preference for small fish, crustaceans, worms, and insects. It uses its powerful jaws and sharp teeth to crush and consume its prey.
Physical Characteristics
The Mud Catfish has a unique appearance that sets it apart from other catfish species. Its body is olive to brown in color, making it almost indistinguishable from the muddy waters it resides in. This coloration helps provide camouflage and protection from predators. Its body is slender and elongated, making it an efficient swimmer.
The Mud Catfish can grow up to a length of 20 inches, with an average adult size of 12-20 inches Menhaden. Some specimens have even been recorded to reach up to 27 inches in length. Its lifespan can reach up to 14 years in the wild, making it a long-lived fish.
Reproduction
Mud Catfish reproduce sexually, with males and females coming together to mate during the spring and summer months. Males typically build nests in cavities under logs, rocks, or vegetation to attract females. These nests are made of plants, mud, and debris and are carefully guarded and maintained by the male until the eggs hatch.
The female Mud Catfish can lay up to 1,000 eggs at a time, and the male will continue to guard the nest and protect the eggs until the fry (baby fish) are ready to swim on their own. It is a remarkable sight to see a male Mud Catfish fiercely protecting its nest and fry from potential predators.
Geographic Distribution and Migration
The Mud Catfish is found in abundance throughout North America, covering most of the eastern and central parts of the United States. It has also been introduced into some western states like Washington, Oregon, and California.
Unlike other catfish species, the Mud Catfish is a non-migratory fish, meaning it does not undertake long-distance journeys like other migratory fish species such as salmon. Its movements are relatively limited, and it mostly stays in its feeding and breeding habitat.
Threats and Conservation
The Mud Catfish is not listed as an endangered species; however, its populations are declining in some parts of its native range. This is mainly due to habitat loss and pollution in some areas. The fish's ability to survive in contaminated waters can, unfortunately, lead to the accumulation of toxins in its tissues, making it unsafe for human consumption.
Efforts are being made to protect and preserve the Mud Catfish's habitat, including creating protected areas and regulating pollution levels in freshwater bodies. Sustainable fishing practices are also in place to ensure the species' longevity and abundance.
Fishing for Mud Catfish
The Mud Catfish is a popular sport fish, and its unique characteristics and strong fighting abilities make it a favorite among anglers. It is often caught using bait such as worms, crayfish, or cut bait. It is important to note that the Mud Catfish's sharp spines can cause injury if not handled carefully. So, if you're planning on reeling in a Mud Catfish, make sure to be gentle and use pliers to handle it safely.
In addition to recreational fishing, the Mud Catfish is also an essential commercial seafood species, providing a significant source of income for many fishermen in the United States.
In Conclusion
The Mud Catfish is a fascinating fish that has adapted to thrive in unique and challenging environments. Its slimy, bottom-dwelling behavior may not make it the most attractive fish, but its resilience and contribution to the ecosystem are undeniable. Its ability to survive in polluted waters and its role as both a predator and prey make it a vital species in the freshwater food chain.
Next time you come across a muddy swamp or a slow-moving river, remember to keep an eye out for the elusive Mud Catfish. Its presence is a testament to nature's remarkable ability to adapt and thrive in even the harshest conditions.
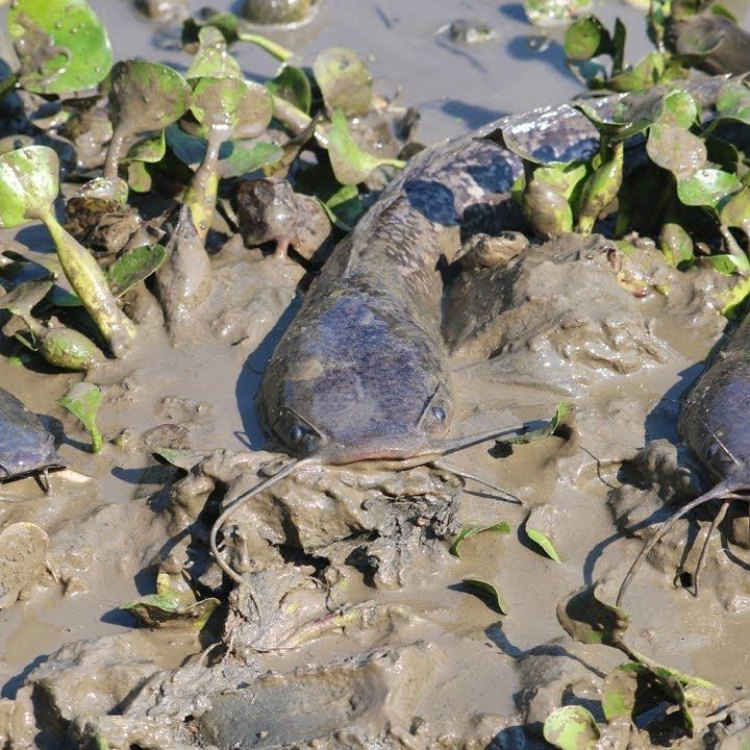

Mud Catfish
Fish Details Mud Catfish - Scientific Name: Ameiurus nebulosus
- Category: Fish M
- Scientific Name: Ameiurus nebulosus
- Common Name: Mud Catfish
- Habitat: Freshwater bodies such as lakes, ponds, rivers, and swamps
- Feeding Habitat: Bottom-dweller
- Feeding Method: Omnivorous
- Geographic Distribution: North America
- Country Of Origin: United States
- Color: Olive to brown
- Body Shape: Slender and elongated
- Length: Up to 20 inches
- Adult Size: 12-20 inches
- Age: Up to 14 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproduction Behavior: Nest builder
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory
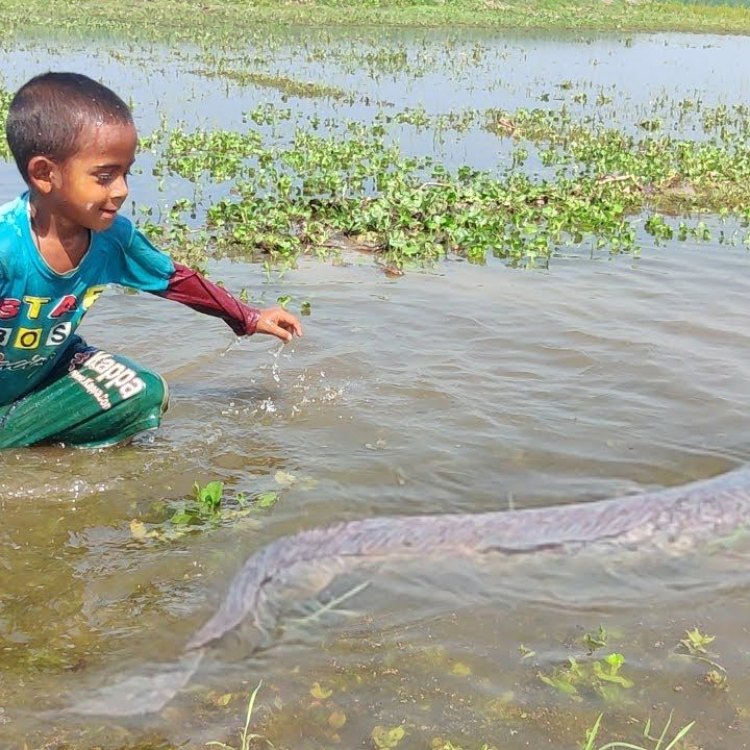

Mud Catfish
- Social Group: Solitary
- Behavior: Nocturnal
- Diet: Insects, small fish, worms, and plant matter
- Predators: Larger fish and birds
- Prey: Insects, small fish, worms, and plant matter
- Environmental Threats: Habitat destruction and pollution
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Special Features: Whisker-like barbels, slimy skin, and sharp spines on the dorsal and pectoral fins
- Interesting Facts: They are known for their ability to survive in low-oxygen environments
- Reproduction Period: Spring and summer
- Nesting Habit: Males construct nests in submerged vegetation
- Lifespan: Up to 14 years
- Habitat Threats: Habitat destruction and pollution
- Population Trends: Stable
- Habitats Affected: Freshwater bodies
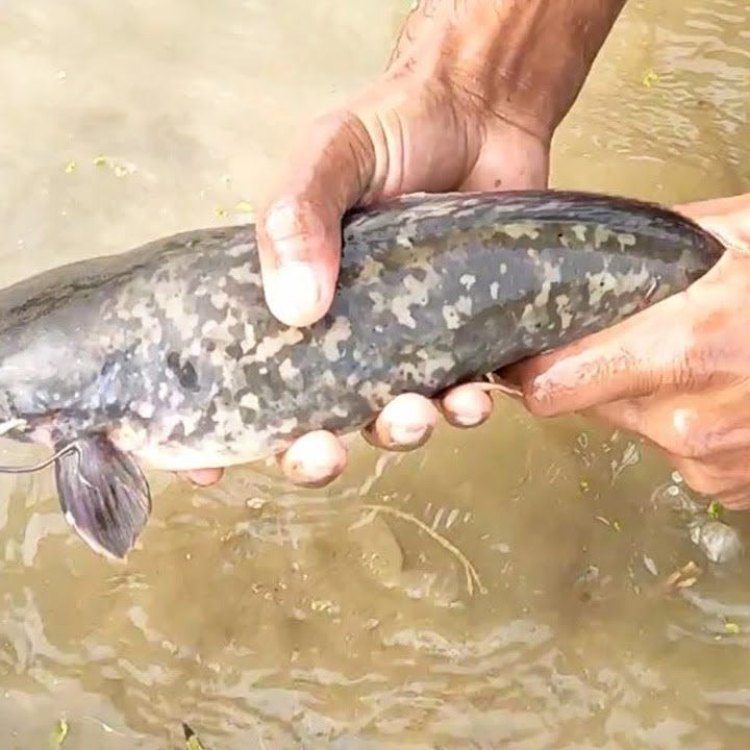

Ameiurus nebulosus
The Enigmatic Mud Catfish: Surviving in a World of Threats
The Mud Catfish, scientifically known as Clarias batrachus, is a fascinating and enigmatic species that inhabits the freshwater bodies of Asia, Africa, and Oceania. This bottom-dwelling fish, with its slimy skin, sharp spines, and whisker-like barbels, is a curious creature that has captured the attention of many researchers and fish enthusiasts.But what makes this fish so unique? In this article, we will dive into the world of the Mud Catfish and explore its social behavior, diet, predators, threats, and special features, along with some interesting facts about this mysterious fish.
Solitary Creatures of the Night
The Mud Catfish is a solitary creature, and unlike many social species, they are not found in groups or schools RadioDouRosul.com. They prefer to live alone, venturing out only to hunt for food or to reproduce. This behavior of living in solitary can be attributed to their nocturnal nature. As the sun sets and darkness falls, these fish become more active, using their keen eyesight and sensitive whiskers to navigate the murky waters in search of food.Nocturnal behavior is also a survival strategy for the Mud Catfish as it helps them avoid predators. By staying hidden during the day, they are less likely to be spotted by their natural enemies. This also explains why they have such well-developed sensory organs, which enable them to be efficient hunters and avoid becoming prey.
A Versatile and Unique Diet
The Mud Catfish is a piscivorous species, meaning they primarily feed on other fish. However, they have a versatile diet and are known to consume a variety of food sources, including insects, small fish, worms, and plant matter. This diverse diet can be attributed to their bottom-dwelling nature, allowing them to feed on whatever is available in their habitat Manta Ray.Interestingly, the Mud Catfish is also known for its ability to survive in low-oxygen environments, thanks to its air-breathing ability. This enables them to supplement their diet with oxygen-rich air, allowing them to thrive in conditions where other fish may struggle to survive.
Predators and Prey
Like any other species, the Mud Catfish also has its fair share of predators and prey. Larger fish and birds, such as herons and storks, are known to prey on Mud Catfish, especially the younger and smaller ones. As bottom-dwellers, they are also vulnerable to predators that live on the same level, such as turtles and some species of freshwater crocodiles.On the other hand, the Mud Catfish preys on insects, small fish, worms, and plant matter. Their ability to adapt to a wide range of food sources makes them successful hunters, and their nocturnal behavior also gives them an added advantage.
Threats to Their Habitat and Conservation Status
Sadly, like many other species, the Mud Catfish is also facing threats to its habitat and survival. Habitat destruction due to human activities, such as dam construction, agricultural runoff, and water pollution, is a significant concern for this species. As bottom-dwelling fish, they rely heavily on the vegetation and structure provided by aquatic plants, which are being destroyed at an alarming rate.Water pollution is also a significant threat to the Mud Catfish as they are highly sensitive to changes in water quality. Pollutants such as wastewater, pesticides, and industrial waste can cause serious harm to the fish, affecting their health and reproductive abilities.
Despite these threats, the Mud Catfish is currently listed as "Least Concern" on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, which is a testament to their ability to adapt and survive in varying environmental conditions. However, continuous monitoring and conservation efforts are essential to ensure the long-term survival of this unique species.
Special Features and Interesting Facts
The Mud Catfish has several unique features that add to its mystique and make it stand out from other freshwater fish. The most notable are its whisker-like barbels, slimy skin, and sharp spines on the dorsal and pectoral fins.The barbels, which are located around the mouth, are used for tasting and detecting food in the murky waters. This is especially helpful as they primarily rely on their sense of smell to locate food. The slime on their skin serves as a protective layer, helping them glide through the bottom sediments without getting injured. And the sharp spines on their fins act as a defense mechanism against potential predators.
Apart from these physical features, the Mud Catfish is also known for its ability to survive in low-oxygen environments. They do so by breathing air through their gills and supplementing it with air gulped from the surface. This unique adaptation enables them to survive in habitats where other fish may perish.
Reproduction for Mud Catfish occurs during the spring and summer months. During this period, males construct nests in submerged vegetation, where females lay their eggs. The males then guard the eggs and young fry until they are ready to venture out on their own.
In Conclusion
The Mud Catfish is a fascinating and mysterious species that is worth studying and preserving. Their solitary and nocturnal behavior, versatile diet, and unique features make them stand out in the world of freshwater fish. Despite facing threats to their habitat, their population remains stable, and they are currently classified as "Least Concern" on the conservation status scale.However, it is imperative to understand the importance of preserving the natural habitats of these creatures and reducing our impact on their environment. Continuous efforts to conserve water bodies and prevent pollution can go a long way in ensuring the survival and wellbeing of the Mud Catfish and other aquatic species. Let's do our part in protecting the delicate balance of nature and appreciate the uniqueness of these amazing creatures that call our freshwater bodies home.
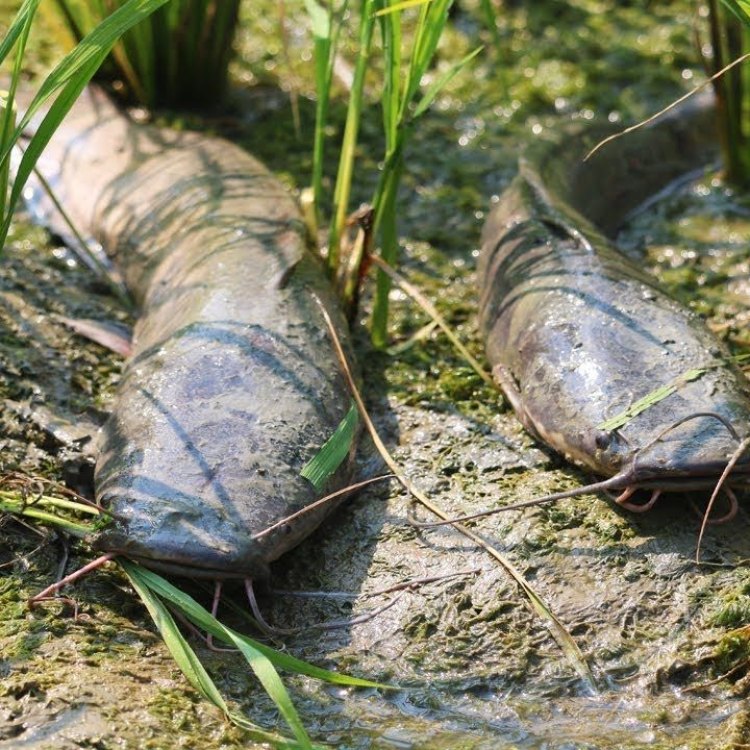

The Fascinating World of the Mud Catfish
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.