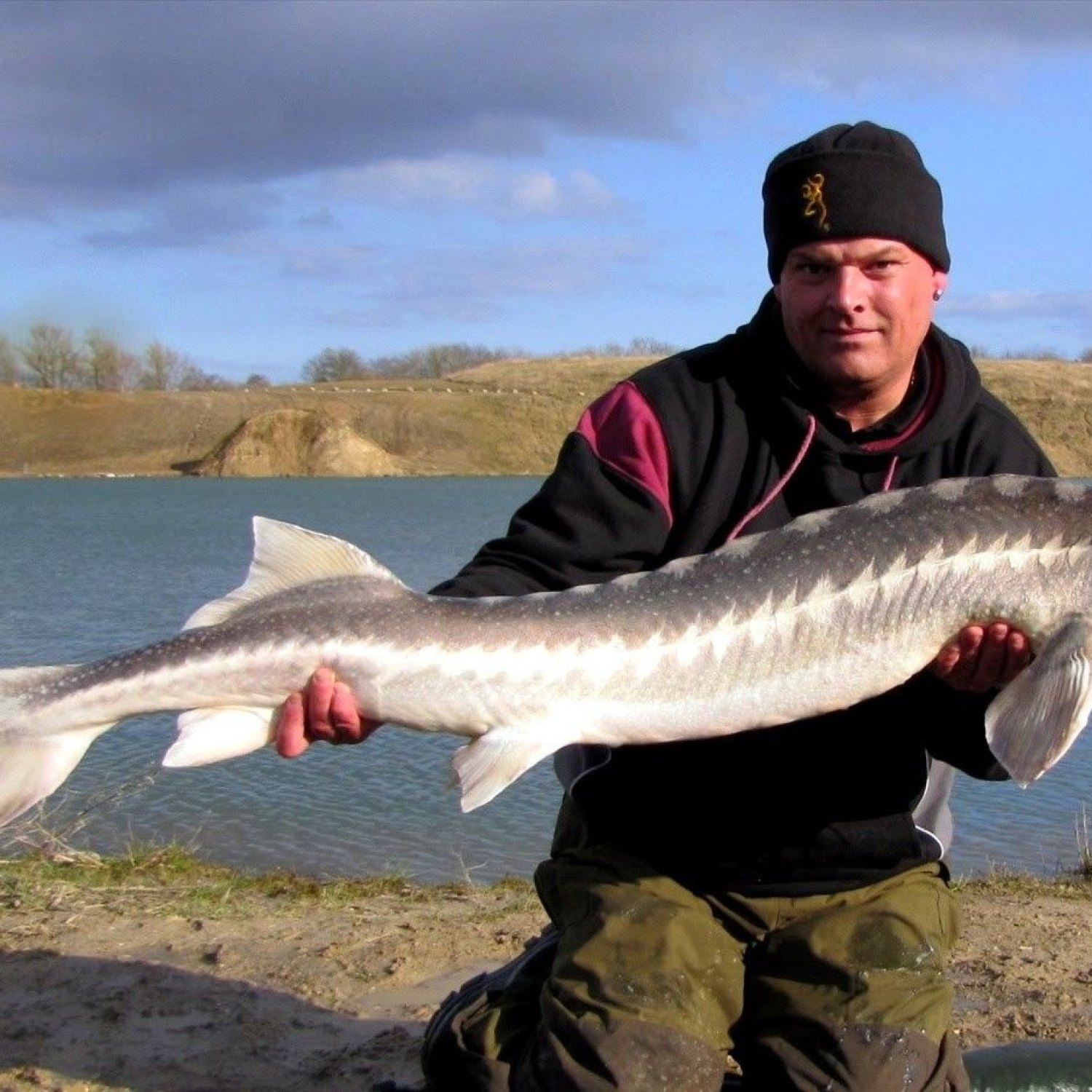
Russian Sturgeon
Anadromous
The Russian Sturgeon, also known as Diamond Sturgeon, is a remarkable fish that can live up to 60 years. It migrates from saltwater to freshwater for spawning. This anadromous fish is mainly found in Russia, but can also be found in other countries. #FishFacts #RussianSturgeon #Anadromous #Migration
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: Russian Sturgeon
Habitat: Freshwater, brackish water
Color: Gray to brown
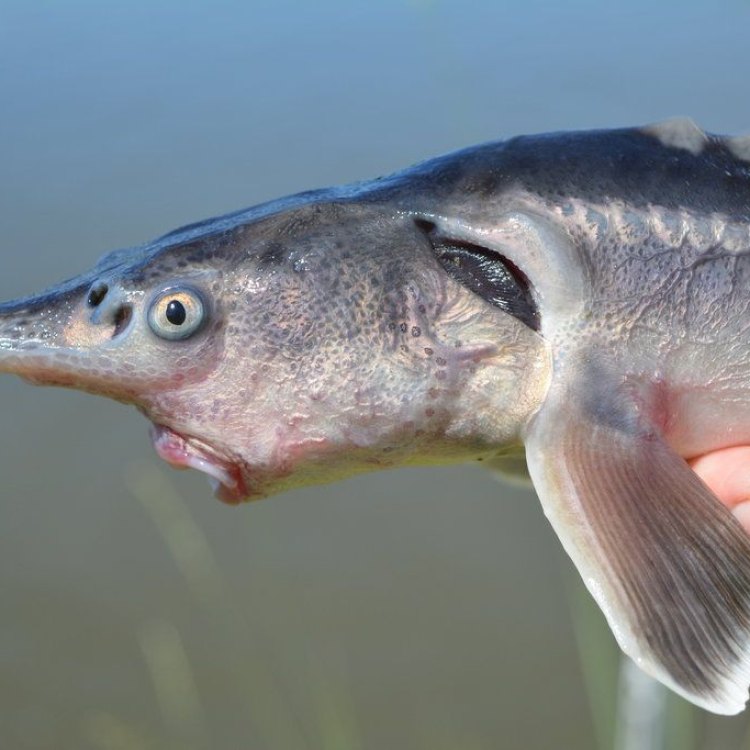
The Majestic Russian Sturgeon: A Rare and Endangered Species
Russia is a land of natural wonders, filled with diverse and unique wildlife. It is home to one of the largest and most impressive fish species in the world - the Russian Sturgeon, also known as Acipenser gueldenstaedtii. This magnificent fish is not only striking in appearance but also highly valued for its delicious caviar. However, despite its popularity, the Russian Sturgeon is a rare and endangered species, facing numerous threats in its natural habitat Russian Sturgeon. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of the Russian Sturgeon and discover what makes it such a remarkable and vital part of Russia's natural heritage.The Russian Sturgeon is a freshwater and brackish water fish, commonly found in the Black Sea, Caspian Sea, and Azov Sea. They have a broad geographic distribution, with their range extending from Russia to the countries of the Middle East. However, due to overfishing and habitat destruction, their population has drastically declined, and they are now classified as critically endangered on the IUCN Red List.
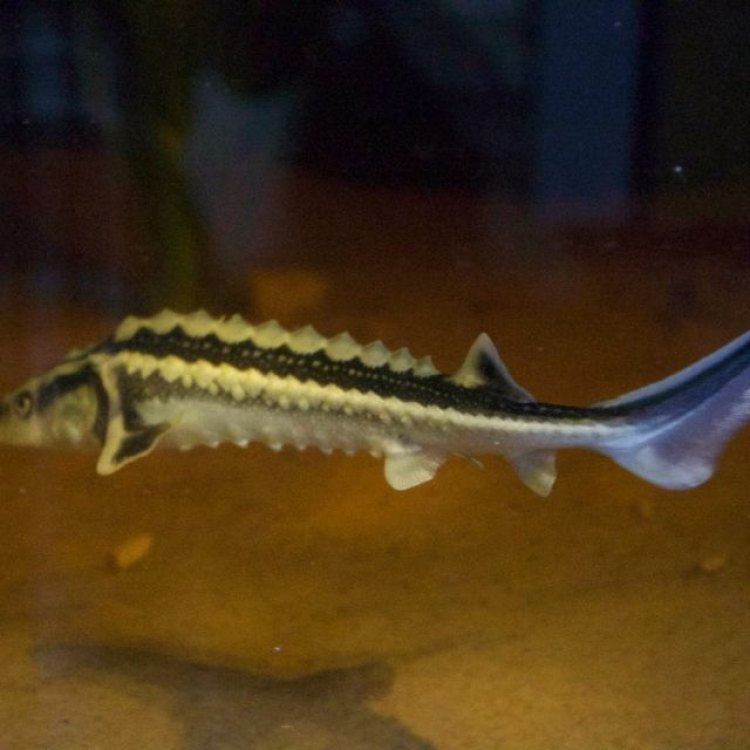
This impressive fish is also known as "black goldfish" due to its striking coloration. The Russian Sturgeon is usually gray to brown in color, with a scaly and elongated body shape. This gives them a sleek and cylindrical appearance, making them one of the most elegant fish species in the world. They can grow up to 7 feet in length and weigh up to a whopping 220 pounds, making them one of the largest freshwater fish in the world. It is no wonder why they are often referred to as a "living fossil" - they have remained relatively unchanged for millions of years Reef Triggerfish.
The Russian Sturgeon has a benthic feeding habitat, meaning they can be found at the bottom of rivers, lakes, and seas, where they feed on a variety of small fish, crustaceans, and mollusks. They are considered bottom feeders, meaning they consume these organisms by sucking in sediments and filtering out their food using their distinctive mouth and gill structures. This specialized feeding method makes them an essential part of the aquatic ecosystem, as they help maintain the health and balance of their environments.
One of the most fascinating aspects of the Russian Sturgeon is its reproductive behavior. Unlike many other fish species, they are sexually reproductive, with both males and females reaching sexual maturity around the age of 15. However, their reproductive behavior is unique, as they undertake an anadromous migration for spawning. This means that they travel from saltwater to freshwater to lay their eggs, usually in the same rivers where they were born. This complex reproductive behavior is crucial for the survival of the species, but it also makes them vulnerable to human activities, such as dam construction, which can disrupt their migration patterns.
The Russian Sturgeon has a relatively long lifespan, with some individuals living up to 60 years in the wild. This, combined with their slow growth rate, makes them highly susceptible to overfishing. In fact, their most significant threat comes from humans, who have been harvesting them for their prized caviar for centuries. Caviar, which is the unfertilized eggs of the female fish, is considered a delicacy and is highly sought after in the culinary world. Unfortunately, the demand for caviar has led to the decline of the Russian Sturgeon population, as many are caught before they have a chance to reproduce.
Furthermore, the Russian Sturgeon faces numerous other threats, including habitat loss and pollution. As urbanization continues to grow, their natural habitats are being destroyed, and water pollution from agricultural and industrial activities has been on the rise. These factors have further contributed to the decline of this magnificent species, making conservation efforts even more critical.
To protect and preserve the Russian Sturgeon, various conservation efforts have been put in place. For instance, bans on commercial harvesting and trade of their caviar have been implemented to reduce overexploitation. In addition, efforts are being made to restore their habitats and reduce pollution levels. However, more needs to be done to save this magnificent species from extinction.
In addition to their ecological importance, the Russian Sturgeon also holds significant cultural and economic value for the countries they inhabit. They are an important part of Russian cuisine and are also revered for their role in traditional ceremonies and celebrations. The caviar industry, which was once a significant contributor to the Russian economy, has also taken a hit due to declining Sturgeon populations.
In conclusion, the Russian Sturgeon is a rare and endangered species that plays a vital role in Russia's natural heritage. Its unique appearance, reproductive behavior, and ecological importance make it one of the most fascinating fish species in the world. However, their population has significantly declined due to overfishing, habitat destruction, and pollution. It is crucial for us to recognize the importance of this majestic fish and take action to protect and preserve its dwindling population. Let us work together to ensure that future generations can continue to marvel at the beauty and wonder of the Russian Sturgeon.
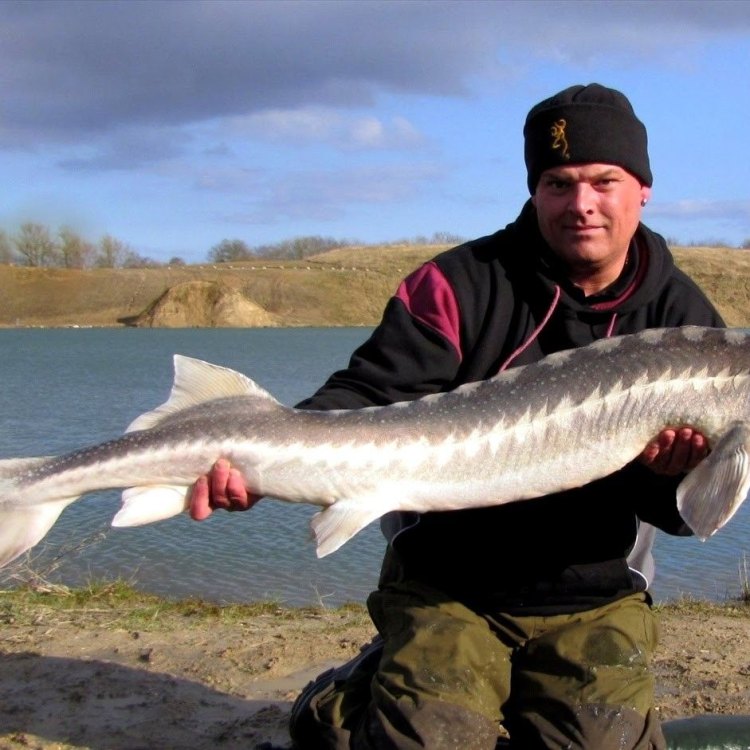

Russian Sturgeon
Fish Details Russian Sturgeon - Scientific Name: Acipenser gueldenstaedtii
- Category: Fish R
- Scientific Name: Acipenser gueldenstaedtii
- Common Name: Russian Sturgeon
- Habitat: Freshwater, brackish water
- Feeding Habitat: Benthic
- Feeding Method: Bottom feeder
- Geographic Distribution: Black Sea, Caspian Sea, Azov Sea
- Country Of Origin: Russia
- Color: Gray to brown
- Body Shape: Elongated and cylindrical
- Length: Up to 7 feet
- Adult Size: Up to 220 pounds
- Age: Up to 60 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproduction Behavior: Anadromous migration for spawning
- Migration Pattern: Anadromous

Russian Sturgeon
- Social Group: Solitary
- Behavior: Bottom-dwelling
- Diet: Invertebrates, small fish, crustaceans
- Predators: Humans, sharks, seals
- Prey: Insects, small fish, crustaceans
- Environmental Threats: Overfishing, habitat degradation, pollution
- Conservation Status: Critically Endangered
- Special Features: Bony plates along the sides of the body
- Interesting Facts: Russian Sturgeon is prized for its roe, which is used to make caviar.
- Reproduction Period: April to June
- Nesting Habit: Gravel or rocky areas
- Lifespan: Up to 60 years
- Habitat Threats: Habitat loss, pollution, dam construction
- Population Trends: Declining
- Habitats Affected: Rivers, estuaries

Acipenser gueldenstaedtii
The Endangered Russian Sturgeon: The Unique Features That Make It a Target for Overfishing and Conservation Efforts
The Russian sturgeon, also known as the beluga sturgeon, is a majestic and ancient fish species that has captured the attention of humans for centuries. With its sleek build and bony plates along its sides, this species has been heavily targeted for its caviar, leading to its critically endangered status. In this article, we will delve into the unique features and challenges faced by the Russian sturgeon, shedding light on the efforts being made to protect this remarkable species.Native to the Caspian and Black Sea basins, the Russian sturgeon can also be found in several major river systems in Europe, including the Volga, Danube, and Ural rivers RadioDouRosul.com. This fish is typically solitary, preferring to live alone on the river bottom rather than in large schools like other fish species. Its behavior is mainly bottom-dwelling, meaning it spends most of its time foraging for food on the riverbed.
Speaking of food, the Russian sturgeon has a varied diet that includes invertebrates, small fish, and crustaceans. It is also known to prey on insects, making it an important species in keeping insect populations in check. However, just like any other animal, the Russian sturgeon also has predators, which include humans, sharks, and seals. Unfortunately, it is not just these natural predators that pose a threat to the survival of this species.
The Russian sturgeon is heavily targeted by humans for its highly desirable eggs, which are used to make caviar. Caviar is considered a delicacy, and the Russian sturgeon’s eggs, in particular, are the most sought after, making it a lucrative and profitable commodity. This has led to the overfishing of this species, significantly impacting its population and putting it at risk of extinction Redlip Blenny.
But it’s not just overfishing that poses a threat to the Russian sturgeon. Dam construction has also affected this species, leading to habitat loss and fragmentation. Dams block the routes that sturgeons use during their annual spawning migrations. As a result, they are unable to reach their traditional nesting sites, causing a decline in their population numbers.
Furthermore, habitat degradation and pollution also threaten the Russian sturgeon. Oil spills, chemical waste, and other forms of pollution can be lethal to this aquatic species, making it challenging for them to survive. As sturgeons are long-lived, slow-growing fish species, they are particularly vulnerable to environmental threats, making it challenging for them to recover from population declines.
Despite the numerous challenges faced by the Russian sturgeon, efforts are being made to protect and conserve this remarkable species. One unique feature of this fish that has helped in its conservation is its reproductive behavior. The Russian sturgeon reproduces once a year, between April and June, during which they migrate upstream to spawn. Female sturgeons lay their eggs in gravel or rocky areas, where males fertilize them. This distinctive behavior makes it easier to track and monitor their spawning habits, which can inform conservation efforts.
Another unique feature of the Russian sturgeon is its bony plates along its sides. These plates, also known as scutes, act as a form of armor, protecting the fish from potential predators. However, these plates are also sought after by humans for commercial use, posing yet another threat to the survival of the Russian sturgeon.
Interestingly, the Russian sturgeon is also a long-lived species, with a lifespan that can reach up to 60 years. While this may seem like a considerable lifespan for a fish, it also means that it takes a long time for this species to replenish its population. Consequently, any decline in their population due to overfishing or other factors can have a significant impact and take a long time to recover.
The Russian sturgeon is listed as critically endangered on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List, which means it faces an extremely high risk of extinction in the wild. However, there is hope for the survival of this species, thanks to conservation efforts being made.
One such effort is the development and implementation of sustainable caviar production practices. Sustainable caviar production involves farming sturgeons and harvesting their eggs without harming their wild populations. This approach has helped lessen pressure on wild sturgeon populations and provides a much-needed alternative to overfishing.
Moreover, efforts are also being made to restore and protect the habitats of the Russian sturgeon. This includes working towards preventing further habitat loss and addressing pollution in their range countries.
There are also conservation and protection measures in place to regulate overfishing and trade of sturgeon products. The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) regulates the international trade of Russian sturgeon products, limiting their harvest and sale to ensure their survival in the wild.
In addition to these efforts, awareness and education initiatives are also crucial in protecting the Russian sturgeon. It is essential to educate people about the importance of preserving this species and the role they play in maintaining a healthy ecosystem. By raising awareness, people can make more informed choices regarding their consumption of caviar and contribute to the conservation of the Russian sturgeon.
In conclusion, the Russian sturgeon is a unique and remarkable species that has faced numerous challenges, pushing it to the brink of extinction. Its solitary nature, bottom-dwelling behavior, and varied diet make it an essential species in river ecosystems. However, the demand for its highly prized caviar has resulted in overfishing, habitat loss, and pollution, threatening its survival.
Despite these challenges, efforts are being made to protect and conserve the Russian sturgeon, from sustainable caviar production to habitat restoration and regulation of trade. It is vital to continue these efforts and raise awareness about the importance of preserving this endangered species. By doing so, we can help ensure that the Russian sturgeon remains a part of our world for generations to come.

The Majestic Russian Sturgeon: A Rare and Endangered Species
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.