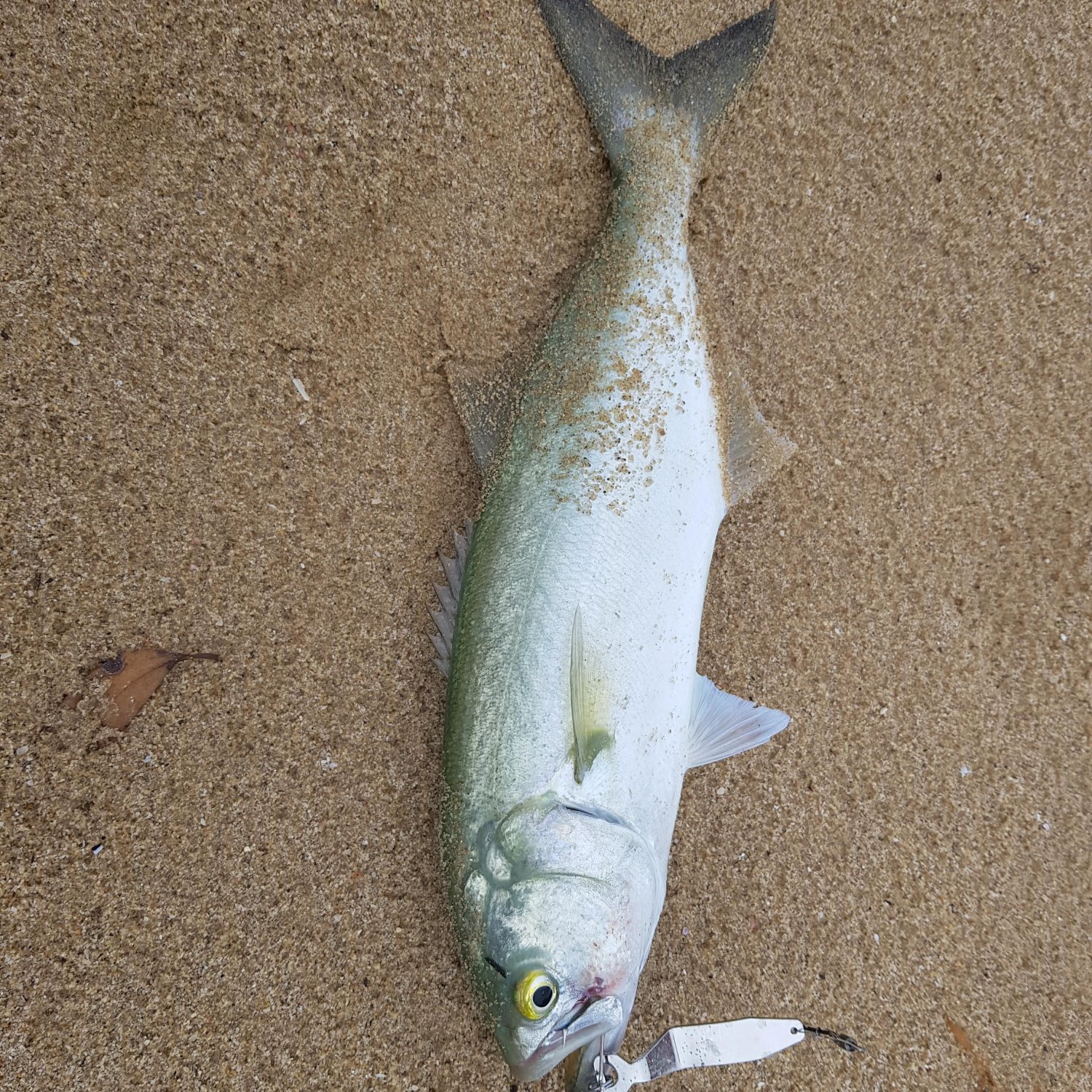

Tailor
Seasonal migration
Tailor fish, also known as snapper, is a common fish found in Australia. With a lifespan of up to 10 years, tailor fish migrate seasonally for breeding. Its spawning behavior makes it a popular catch among fishermen. It's a versatile fish, commonly used in dishes like fish and chips or grilled with herbs. Enjoy this tasty and healthy fish in moderation for a well-rounded diet. #TailorFish #AustralianFish #HealthyEating #SeasonalMigration
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: Tailor
Habitat: Coastal waters, Estuaries
Color: Greenish-blue on the back, Silvery-white on the belly
Tailor: The Oceanic Predator
With its sleek, elongated body and piercing greenish-blue color, the Tailor fish is a fierce and formidable predator in the coastal waters of the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific oceans. Also known by its scientific name, Pomatomus saltatrix, this fish is native to Australia and is often referred to as the Tailor King.From its distinct physical characteristics to its unique feeding habits and migration patterns, the Tailor is a fascinating species that deserves to be in the spotlight. In this article, we will dive deeper into the world of this oceanic predator and learn more about its behavior, habitat, and importance in the marine ecosystem Tailor.
The Perfect Predator
The Tailor fish is a coastal species, commonly found in estuaries, open waters, and nearshore areas. Its streamlined and elongated body, combined with its powerful muscles, allows it to swiftly move through the waters, making it a perfect predator. Its striking coloration, with greenish-blue on its back and silvery-white on its belly, camouflages it from its prey and helps it blend into the ocean environment.But what truly makes the Tailor a formidable predator is its diet. With its sharp teeth and powerful jaw, it is a carnivorous fish that feeds on a variety of prey, including small fish, crustaceans, and other marine creatures. This is why it is often referred to as the "Oceanic Predator."
A Worldwide Distribution
The Tailor fish has a wide geographical distribution, found in both the Atlantic and the Pacific oceans, as well as the Indian Ocean. It is also commonly found in countries such as Australia, New Zealand, Japan, and South Africa. In Australia, it is considered one of the most popular game fish, attracting many recreational fishermen every year Treefish.The Tailor's ability to adapt to different oceanic environments and its wide distribution pattern make it a significant species in the oceanic ecosystem. Its presence is crucial in maintaining the balance of the marine food chain.
A Surprising Size and Growth Rate
The Tailor fish can reach impressive sizes, with some reaching lengths of up to 90 cm. However, the average adult size of this species is around 60 cm. It is believed that the average life span of a Tailor fish is up to 10 years, but this can vary depending on their habitat and food availability.One unique aspect of the Tailor's growth rate is that it grows at an incredibly fast pace, especially during its juvenile stage. As a result, it is a highly sought-after fish amongst anglers, making it an important commercial fishery in many countries.
The Mating Ritual of the Tailor Fish
The Tailor fish is a sexual species, with males and females participating in a fascinating mating ritual known as "spawning." This behavior involves the female Tailor releasing her eggs into the water, with the males simultaneously releasing their sperm to fertilize the eggs. Once fertilized, the eggs will hatch into larvae after a few days, and the young Tailor fish will start their journey of growth and development.This mating ritual usually occurs during the warmer months when the waters are more conducive for the survival of the larvae. It is also believed that the Tailor fish have a unique homing instinct, and they return to the same coastal areas every year to spawn.
Seasonal Migration Patterns
Like many other fish species, the Tailor fish exhibits seasonal migration patterns. During the summer months, they tend to migrate closer to the coast, particularly to estuaries and bays, where they can easily find food and shelter. But as the colder months approach, they move back to deeper waters, where they settle in large schools.This seasonal migration pattern is not only influenced by food availability but also by the water temperature. Tailor fish are known to thrive in a water temperature range of 17-22 degrees Celsius, making it ideal for their growth and reproduction.
Importance in the Marine Ecosystem
The Tailor fish is not only a popular game fish but also an essential species in the marine ecosystem. As a predator, it plays a crucial role in controlling the population of its prey, helping maintain the balance of the food chain. Its migratory patterns also play a significant role in distributing nutrients and maintaining healthy habitats in different areas of the ocean.Furthermore, the Tailor fish also contributes to the economy by providing a significant source of income through recreational and commercial fishing industries. However, with the increasing demand for this species, it is essential to ensure sustainable fishing practices to prevent overfishing and maintain healthy populations.
Conclusion
The Tailor fish is a remarkable species that dominates the coastal waters of the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific oceans. From its physical characteristics to its unique behaviors, this fish is a fascinating creature that continues to capture the attention of researchers, fishermen, and ocean enthusiasts.As a top predator and an important species in the marine ecosystem, the Tailor fish plays a significant role in maintaining the balance of the oceanic food chain. Its distinct behaviors, such as spawning and seasonal migration patterns, make it a crucial part of the ocean's biodiversity. And as we continue to learn more about this oceanic predator, we must also ensure its long-term survival by practicing sustainable fishing methods, preserving their habitats, and protecting the ocean environment.

Tailor
Fish Details Tailor - Scientific Name: Pomatomus saltatrix
- Category: Fish T
- Scientific Name: Pomatomus saltatrix
- Common Name: Tailor
- Habitat: Coastal waters, Estuaries
- Feeding Habitat: Open water, Nearshore
- Feeding Method: Carnivorous
- Geographic Distribution: Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Pacific Ocean
- Country Of Origin: Australia
- Color: Greenish-blue on the back, Silvery-white on the belly
- Body Shape: Streamlined and elongated
- Length: Up to 90 cm
- Adult Size: Up to 60 cm
- Age: Up to 10 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproduction Behavior: Spawning
- Migration Pattern: Seasonal migration

Tailor
- Social Group: Solitary or in small groups
- Behavior: Active and fast-swimming
- Diet: Fish, Squid, Shrimp
- Predators: Sharks, Marine mammals
- Prey: Small fish, Invertebrates
- Environmental Threats: Overfishing, Habitat destruction
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Special Features: Strong jaws, Sharp teeth, Caudal fin with a distinctive notch
- Interesting Facts: Tailor are popular game fish due to their aggressive nature and strong fighting ability.
- Reproduction Period: Spring and summer
- Nesting Habit: Open water
- Lifespan: Up to 10 years
- Habitat Threats: Pollution, Coastal development
- Population Trends: Stable
- Habitats Affected: Coastal zones, Estuaries
Pomatomus saltatrix
Tailor: The Active and Aggressive Game Fish of the Sea
When we think of the ocean, we often imagine a vast and mysterious world filled with a diverse array of creatures. Among these creatures is the tailor, a small but fierce game fish that inhabits coastal zones and estuaries around the world. With its unique features and impressive behaviors, the tailor is a fascinating species that deserves our attention and protection.Tailor, or bluefish as they are also known, are found in temperate and subtropical waters of the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans RadioDouRosul.com. Their name comes from their tail, which has a distinctive notch, making it easier to identify them from other similar species. They are a popular game fish among recreational anglers due to their aggressive nature and strong fighting ability. But there is much more to these fish than just their popularity in the fishing community.
Social Group and Behavior
Tailor typically live solitary lives, although they can also be found in small groups. They are fast-swimming fish and constantly on the move, making them a challenging catch for anglers. This active behavior is due to their diet, which mainly consists of fish, squid, and shrimp. They have strong jaws and sharp teeth, allowing them to quickly catch and consume their prey. They are also known to be voracious eaters, often chasing after schools of baitfish and feeding in a frenzy.
Predators and Prey
Despite being a fierce predator themselves, tailor also have their own set of predators to watch out for Thresher Shark. Sharks and marine mammals, such as dolphins and seals, are known to prey on tailor. This is why tailor tend to be fast and agile, allowing them to evade their own predators.
As for their prey, tailor primarily feed on small fish and invertebrates. Their sharp teeth and strong jaws allow them to easily tear through the tough outer shells of crustaceans, making them a skilled hunter in the underwater world.
Environmental Threats and Conservation Status
Sadly, like many other marine species, tailor face a number of environmental threats that have contributed to their declining populations. Overfishing, habitat destruction, pollution, and coastal development are all serious concerns that impact these fish.
Overfishing, in particular, has had a significant impact on tailor populations. They are highly sought after by commercial fishermen due to their delicious taste, and unfortunately, their populations have not been able to keep up with the demand. This has led to their listing as a Least Concern species by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), indicating that they are not currently at risk of extinction but require monitoring due to potential threats.
Special Features and Interesting Facts
Aside from their impressive physical features and behaviors, tailor also have some interesting facts worth noting. As mentioned, they are known for their aggressive nature and strong fighting ability, making them a sought-after game fish. However, they also have a unique reproductive period. Tailor typically reproduce in the spring and summer months, with females releasing their eggs into the water column where they are fertilized by males.
Another interesting fact about tailor is their nesting habit. Unlike many other fish species, they do not build nests but instead spawn in open water. This makes their eggs and larvae vulnerable to being washed away or eaten by other fish.
Habitat Threats and Population Trends
Tailor primarily inhabit coastal zones and estuaries, making them susceptible to the threats posed by pollution and coastal development. These activities can disrupt their natural habitats, affecting their ability to find food, reproduce, and survive.
Despite these threats, the population trends for tailor are currently stable. This is due in part to conservation efforts aimed at reducing overfishing and protecting their habitats. However, continued monitoring and conservation efforts are crucial to ensuring their long-term survival.
Habitats Affected by Tailor
The presence of tailor in coastal zones and estuaries can have both positive and negative effects on these environments. On one hand, tailor help maintain balance in the food chain by controlling the populations of smaller fish and invertebrates. On the other hand, their aggressive feeding behaviors can also cause stress to other species and potentially disrupt the ecosystem.
In addition, their habitats are also affected by their own feeding habits. During feeding frenzies, tailor may cause damage to seagrass beds and other structures. While these impacts may seem minor, they can add up over time and have a significant impact on the overall health of the habitat.
In conclusion, tailor are more than just a popular game fish; they are a unique and important species in the ecosystem. Their active and aggressive nature makes them a fascinating species to study and observe in their natural habitats. However, their populations are under threat from a variety of human activities. It is crucial that we continue to monitor their populations and take action to protect their habitats, to ensure that these dynamic and fascinating fish will continue to thrive in our oceans for generations to come.

Tailor: The Oceanic Predator
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.












