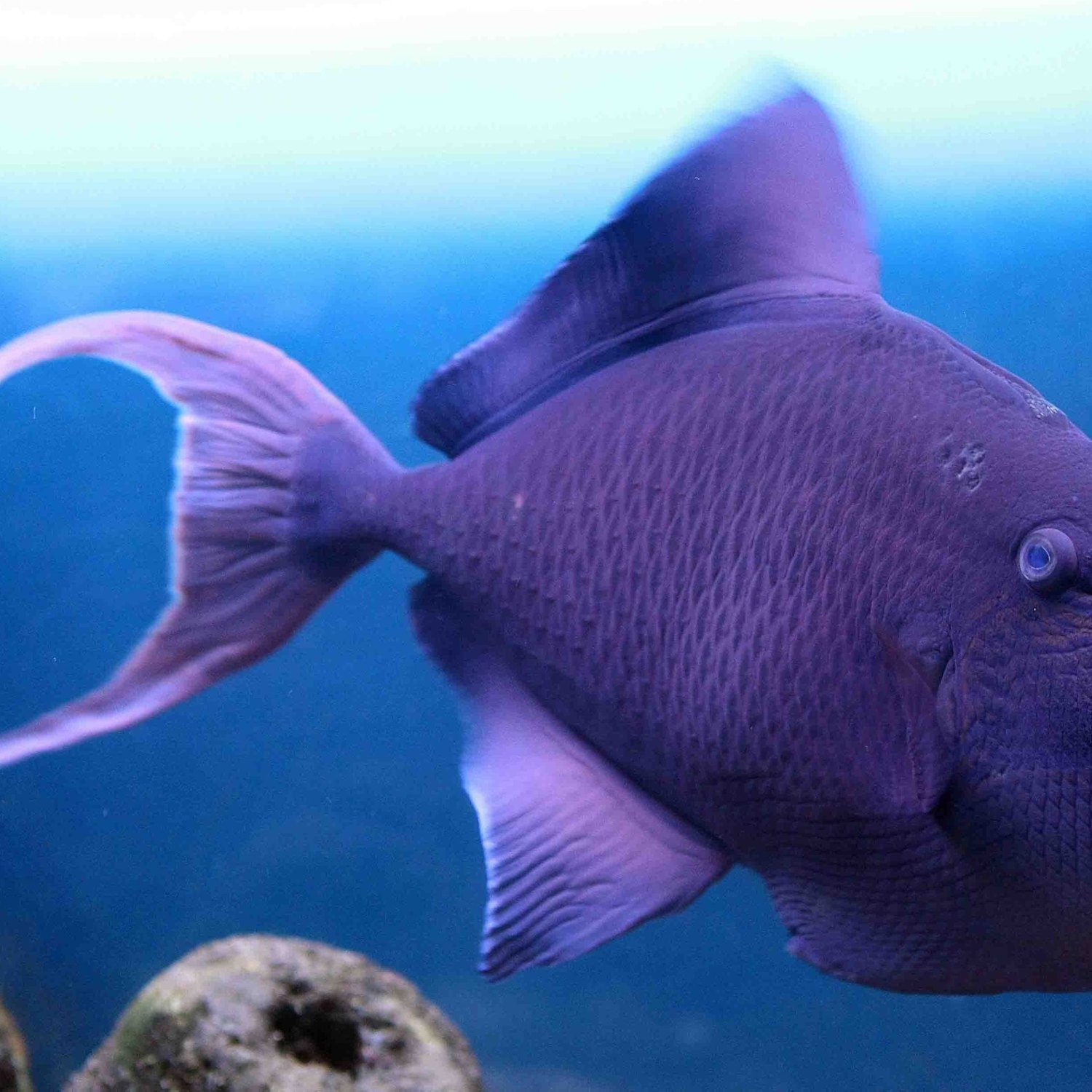
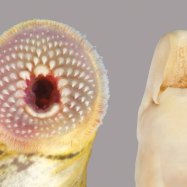
Triggerfish
Limited to the local region
Learn about the fascinating Triggerfish, commonly found in Indonesian waters. This fish stays close to home, although its exact age remains a mystery. Males put on a show for females by making nests, making them quite the catch! #IndonesianFish #ReefLife
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: Triggerfish
Habitat: Coral reefs and rocky areas
Color: Varies depending on species, typically vibrant and contrasting colors
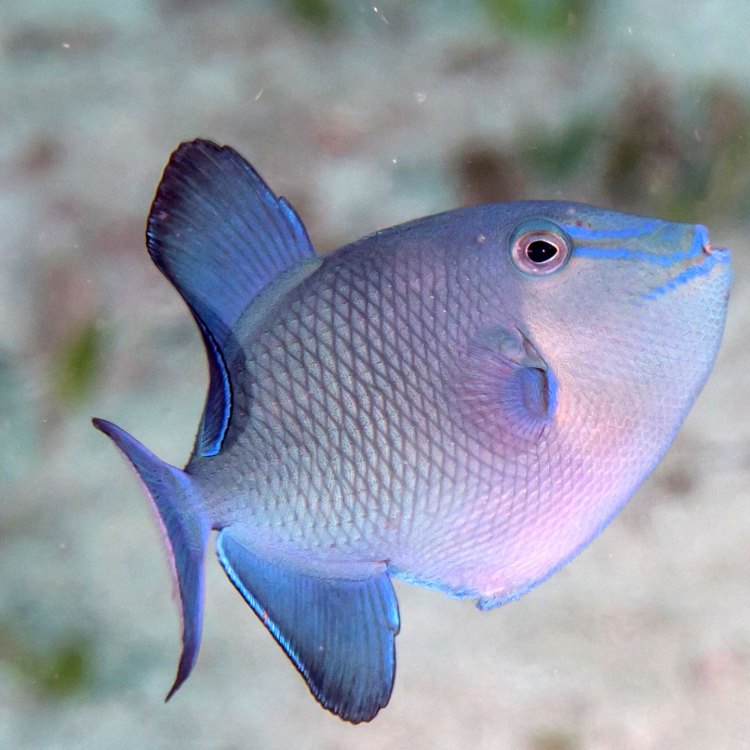
The Beautiful and Fascinating World of Triggerfish
From vibrant coral reefs to rocky areas, triggerfish are a stunning sight in the waters all across the world. With their unique appearance and intriguing behaviors, these fish have captured the attention of marine enthusiasts and casual observers alike. But beyond their eye-catching colors and impressive jaws, what makes these creatures truly remarkable? In this article, we'll dive into the remarkable world of triggerfish and explore their habitats, feeding habits, distribution, reproduction, and more.The Basics: Scientific Name, Common Name, and Habitat
Scientifically known as Balistidae, triggerfish are a family of fish that can be found in tropical and subtropical oceans worldwide Triggerfish. Their common name comes from their triangular, trigger-like dorsal fin, which they can lock in place to secure themselves in small crevices. Triggerfish can be found in various countries with coral reef ecosystems, including the Red Sea, the Caribbean, and the Indo-Pacific region.Feeding Habits: What do Triggerfish Eat?
Triggerfish are considered opportunistic feeders, meaning they will eat whatever they come across in their habitat. Their diet primarily consists of invertebrates such as crustaceans, worms, and sea urchins. They also enjoy munching on algae and small fish. These fish have powerful jaws and teeth, specifically designed for biting and crushing their prey, making them capable predators in their underwater domain. They use their strong teeth to crack open hard-shelled prey, such as crabs and clams, with ease.Geographic Distribution: Where Can You Find Triggerfish?
As mentioned earlier, triggerfish can be found in tropical and subtropical oceans worldwide. They are not limited to one particular geographical region, and their presence has been observed in various countries, including Australia, Japan, Costa Rica, and South Africa Tenpounder. While they are mainly found near coral reefs or rocky areas, some species have been spotted in open waters, at depths up to 50 meters. Their widespread distribution makes them a vital part of the marine food chain in many regions.Colorful and Contrasting: The Aesthetics of Triggerfish
Triggerfish come in a wide range of colors, with vibrant and contrasting hues that make them stand out in the ocean. The color and pattern of their skin can vary greatly between species. Some species have bold, bright colors, while others have more muted tones. Some even have dark spots or stripes to help them blend in with their surroundings. These colors not only make them visually appealing but also serve as a form of camouflage to protect them from potential predators.Shape and Size: Unique Physical Features of Triggerfish
Triggerfish have a distinct body shape that sets them apart from other fish. They are deep-bodied, meaning they have a vertical range that is much deeper than it is wide, giving them a laterally compressed appearance. This body shape allows them to maneuver through narrow crevices and spaces in the reef, making them well-adapted to their habitat. The average length of triggerfish varies between 15-30 cm (6-12 inches), with some species growing up to 60 cm (24 inches) in length. They fall under the medium-sized category when compared to other fish species.Reproduction and Mating Behavior of Triggerfish
Triggerfish reproduce through sexual reproduction, with males actively creating nests to attract females. The male triggers use their fins to create depressions in the sandy seabed that serve as their mating ground. These depressions can vary in size and shape but are typically sparse and circular. When a female approaches the nest, the male begins a series of courting behaviors, ranging from flaring their fins to changing their color. Once the female lays her eggs, both the male and female will protect the nest until the eggs hatch, at which point the male will abandon the nest.Migration Patterns: Triggerfish in Their Local Regions
Unlike some fish species, triggerfish do not have a set migration pattern. They are known to remain in their local regions and do not undertake long-distance migrations. They will move around within their habitat and may even travel to different areas depending on food availability or breeding. However, their movements are limited to the local region, and they do not embark on journeys that take them too far from their home.The Fascinating World of Triggerfish
Triggerfish are undoubtedly one of the most captivating and intriguing fish species in our oceans. Their unique appearance, feeding habits, reproduction behavior, and migration patterns make them a must-see for any marine enthusiast or curious observer. Their ability to blend into their surroundings while also being bold and bright in color is just one of the many fascinating aspects of these fish. And with their widespread distribution, you never know when you might catch a glimpse of these beautiful creatures in the wild. So, next time you're exploring a coral reef or rocky area, keep an eye out for triggerfish, and you might just witness their captivating behavior firsthand.
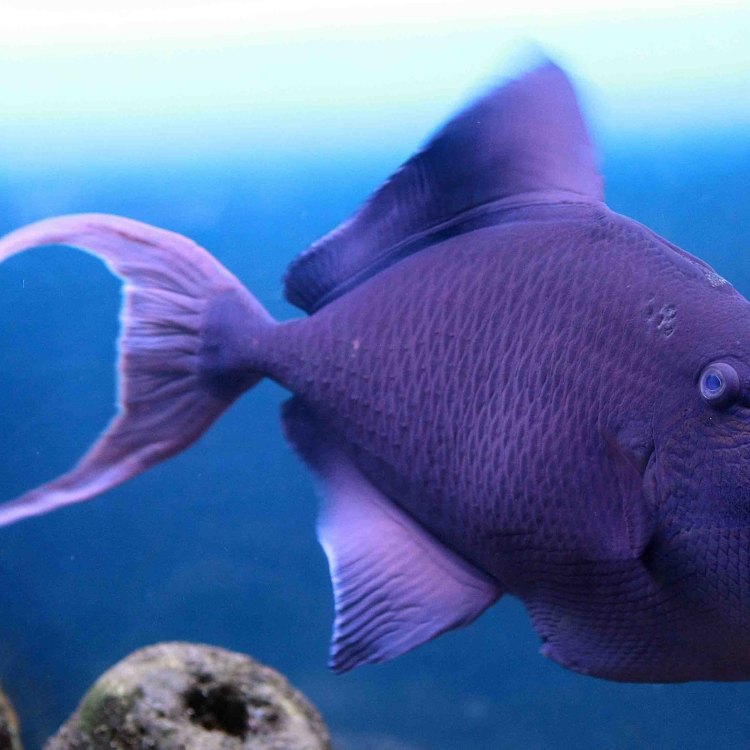

Triggerfish
Fish Details Triggerfish - Scientific Name: Balistidae
- Category: Fish T
- Scientific Name: Balistidae
- Common Name: Triggerfish
- Habitat: Coral reefs and rocky areas
- Feeding Habitat: Invertebrates, algae, and small fish
- Feeding Method: Bites and crushes prey using powerful jaws and teeth
- Geographic Distribution: Tropical and subtropical oceans worldwide
- Country Of Origin: Found in various countries with coral reef ecosystems
- Color: Varies depending on species, typically vibrant and contrasting colors
- Body Shape: Deep-bodied and laterally compressed
- Length: Varies depending on species, typically between 15-30 cm (6-12 inches)
- Adult Size: Varies depending on species, typically between 30-60 cm (12-24 inches)
- Age: Unknown
- Reproduction: Sexual reproduction
- Reproduction Behavior: Males create nests and court females through displays
- Migration Pattern: Limited to the local region
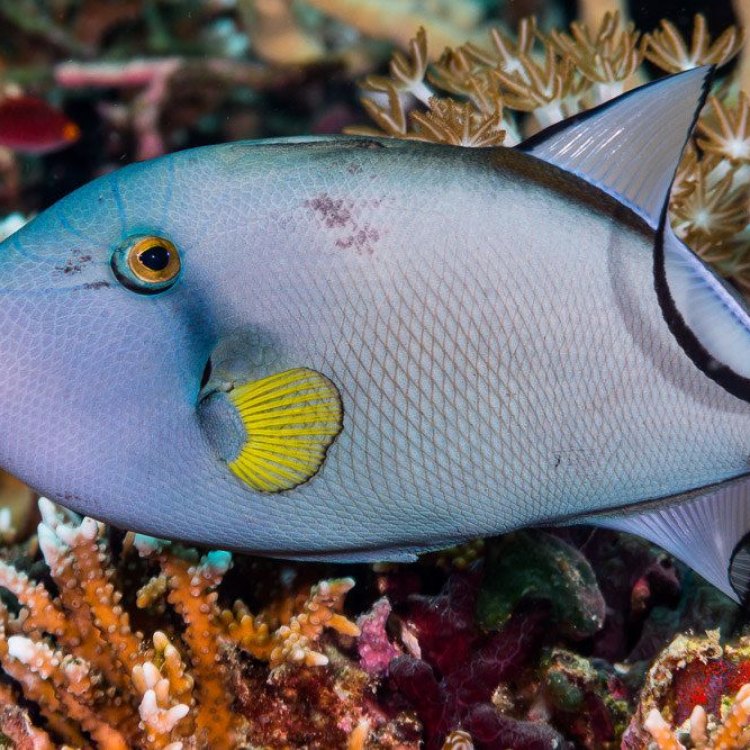

Triggerfish
- Social Group: Solitary or in small groups
- Behavior: Territorial and aggressive
- Diet: Omnivorous, feeding on a variety of prey including invertebrates and algae
- Predators: Large predatory fish and sharks
- Prey: Invertebrates, algae, and small fish
- Environmental Threats: Habitat destruction, overfishing, pollution
- Conservation Status: Varies depending on species, some are of conservation concern
- Special Features: Strong jaws and teeth, trigger-like dorsal fin
- Interesting Facts: Triggerfish are known for their ability to lock themselves into small crevices using their dorsal spine, and their ability to change coloration rapidly to blend in with their environment
- Reproduction Period: Varies depending on species
- Nesting Habit: Males build nests on the seafloor
- Lifespan: Varies depending on species, typically 8-12 years
- Habitat Threats: Coral reef degradation and destruction
- Population Trends: Varies depending on species, some populations are declining
- Habitats Affected: Coral reefs and rocky areas
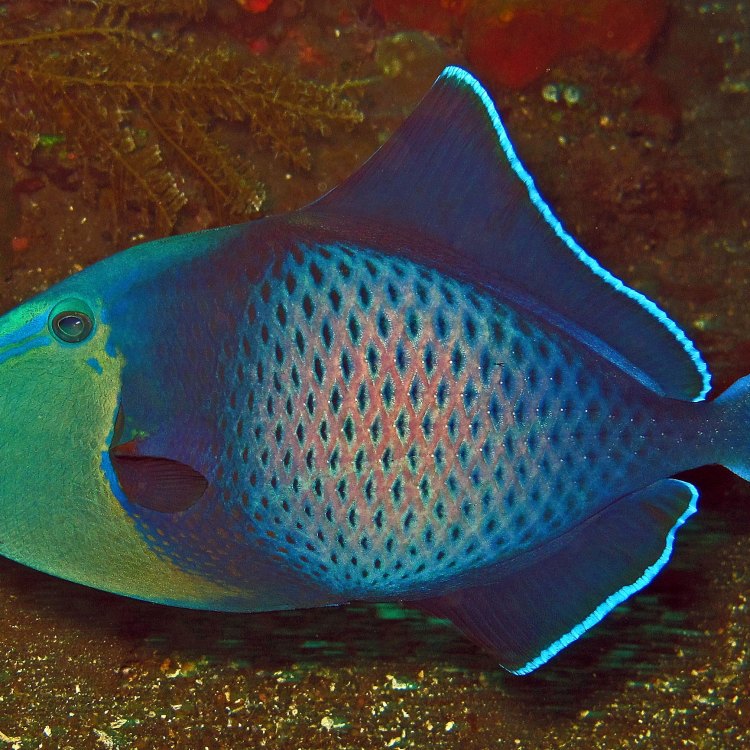

Balistidae
The Triggerfish: Solitary But Strong
In the vast and vibrant world of marine life, there is a group of fish that has captured the attention of many with its unique features and intriguing behavior. These fish are known as triggerfish, and they have gained a reputation for being solitary, territorial, and aggressive creatures.But there is more to this fish than meets the eye. In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of triggerfish, their behavior, diet, predators, and threats to their existence RadioDouRosul.com.
First, let's get to know them better. Triggerfish belong to the family Balistidae, which includes about 40 species found throughout the world's oceans. They are primarily found in tropical and subtropical waters, swimming near coral reefs and rocky areas. They are recognized by their distinct shape, with a large head, small mouth, and a round or elongated body.
Triggerfish are not social creatures. They are either solitary or found in small groups, mostly during their breeding season. However, they are territorial and fiercely protect their chosen space, which they mark with their urine to warn off intruders.
Their aggressive nature is evident in their behavior towards other fish, particularly smaller ones. They will chase, nip, and even bite at their prey to establish dominance Tompot Blenny. They are also known to attack larger fish and humans if they feel threatened.
But this behavior is not entirely negative. It is a survival tactic that ensures they have enough food and space to thrive in their habitat. Their diet reflects this as well - triggerfish are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of prey such as invertebrates, algae, and small fish. They have powerful jaws and sharp teeth that allow them to crunch through shells and crustaceans, making them a significant predator on the reef.
However, triggerfish are not the only creatures in the ocean with a taste for these fish. They face threats from large predatory fish and sharks who see them as a delicious meal. This is why they have evolved to protect themselves, not just through their aggressive behavior but also through their unique features.
One of the prominent features of the triggerfish is its trigger-like dorsal fin, which is responsible for its name. This fin is made up of three spines, the first of which is locked in an upright position. When the fish feels threatened, it can quickly raise this spine, locking it into place, making it challenging to be swallowed by a predator or removed from its hiding spot. Unfortunately, this feature has also made them a popular fish for aquariums, leading to overexploitation of their population in the wild.
The triggerfish also have the unique ability to change their coloration rapidly. They can do this by adjusting their dark and light pigment cells to blend in with the surrounding environment, acting as a natural camouflage. This makes it harder for predators to spot them, increasing their chances of survival. This ability also plays a crucial role in their reproduction.
Reproduction period varies among triggerfish species, but most of them breed during the summer and fall months, when the water is warm. During this time, male triggerfish build nests on the seafloor, using their teeth to dig out a shallow depression, which they then defend aggressively. Females will visit the nests to lay their eggs, and the males will then fertilize and guard them until they hatch.
This reproductive behavior is essential in maintaining the population of triggerfish, as they can be quite sensitive to environmental threats. Like their fellow marine creatures, triggerfish are facing a multitude of hazards that put their existence at risk.
Habitat destruction is one of the main threats to the triggerfish. Coral reefs, their preferred home, are being destroyed at an alarming rate due to human activities, such as pollution and climate change. This not only affects the triggerfish population but also disrupts the entire marine ecosystem.
Overfishing is another major threat to triggerfish. They are often caught as bycatch in large fisheries, or targeted for their desirable meat or for the aquarium trade. This has led to a decline in some triggerfish populations, resulting in their listing on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
And unfortunately, that's not all - pollution from oil spills, plastic waste, and chemicals also poses a significant threat to these fish. As they feed on algae and small prey, they can easily ingest toxins, which can have a devastating effect on their health.
But the good news is that some triggerfish species are still thriving, and their numbers are stable. Sadly, others are not as lucky, and their populations are declining. This decline is a warning sign of the ripple effect it will have on the entire marine environment if we do not take action to protect them.
Conservation efforts are being made to protect these fish. Marine protected areas, where fishing is prohibited, have been established to provide a safe haven for triggerfish and other marine life. Awareness campaigns are being conducted to educate the public about the importance of preserving coral reefs and the impact of overfishing.
As individuals, we can also play our part in protecting the triggerfish and all marine life. By making sustainable seafood choices, reducing our plastic consumption, and supporting responsible tourism practices, we can create a positive impact.
In conclusion, the triggerfish may be solitary and aggressive, but they have a soft side too. They are fascinating creatures that have adapted to their environment in remarkable ways, from their territorial nature to their unique features. However, like all marine life, they are facing numerous threats that have the potential to wipe them out. It is up to us to take action and protect these creatures before it's too late. Let's work together to ensure the survival of the triggerfish and all marine life for generations to come.

The Beautiful and Fascinating World of Triggerfish
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.