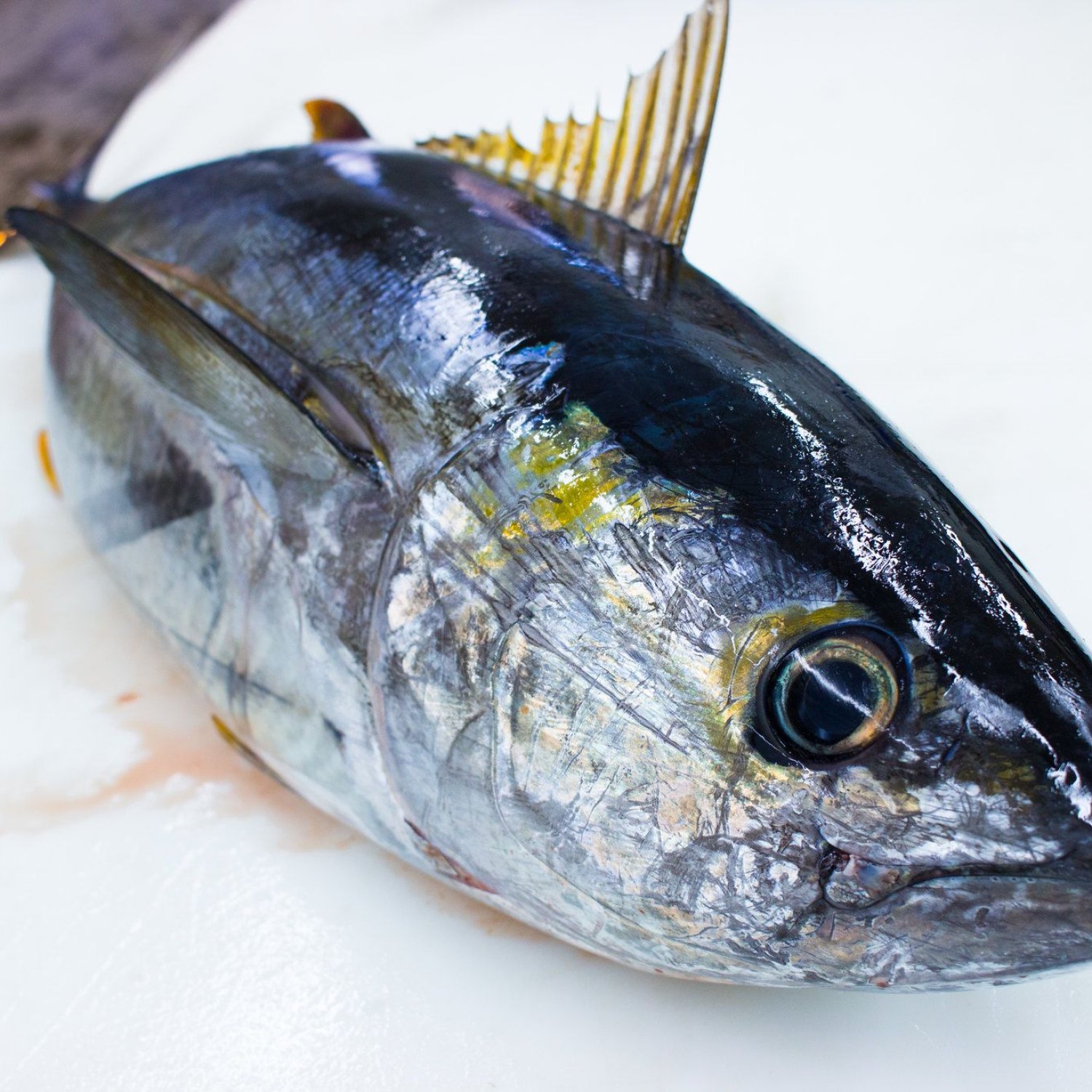
Yellowfin Tuna
They undertake significant migrations, following the warmer water temperatures. They may travel long distances in search of food or to spawn.
Did you know Yellowfin Tuna undertake epic migrations in search of food and to spawn? These beautiful and tasty fish can live up to 6-7 years and are native to the oceans around the world. During spawning, they gather in groups and release their eggs and sperm into the open ocean. #YellowfinTuna #Migration #Reproduction
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: Yellowfin Tuna
Habitat: Yellowfin Tuna inhabit tropical and subtropical waters worldwide. They prefer to stay closer to the surface in warm waters.
Color: They have a metallic dark blue to blackish back with yellow sides and a silver-white belly. The fins and tail are also yellow.
The Thrilling World of Yellowfin Tuna: The Ultimate Catch for Anglers
Yellowfin Tuna, scientifically known as Thunnus albacares, is a highly sought-after fish species in the fishing world. With its stunning appearance, extraordinary strength, and delicious taste, it's no wonder why anglers all over the world are drawn to this magnificent fish.These tuna are a prime example of the wonders that lie beneath the surface of our oceans. In this article, we'll dive deep into the life of the Yellowfin Tuna, exploring their habitat, feeding behaviors, distribution, physical characteristics, and more Yellowfin Tuna. So buckle up and get ready to embark on a thrilling journey with the Yellowfin Tuna.
The Habitat of Yellowfin Tuna
Yellowfin Tuna is a cosmopolitan fish found in tropical and subtropical waters around the world. They prefer to inhabit warmer waters, staying closer to the surface, making them more accessible to anglers and fishermen.These tuna are pelagic, meaning they live in the open ocean and do not stay near the seabed or shorelines. They have a wide range of habitats, from the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans, but they are most abundant in the tropical and subtropical regions.
Their preferred habitat is near floating objects, such as seaweed or debris, as they attract smaller fish and organisms, which in turn attract Yellowfin Tuna. They are also found near underwater seamounts and ridges, where there is a high concentration of food.
Feeding Habits and Methods
Yellowfin Tuna are opportunistic predators and have a varied diet. They feed on a range of fish species, including anchovies, sardines, herring, and mackerel, as well as squid and crustaceans like shrimp and krill Yellowtail Clownfish.They are at the top of the food chain in the ocean and have a vital role in keeping the aquatic ecosystem balanced. As apex predators, they have a significant impact on controlling the population of their prey. Their ability to hunt a diverse range of food sources makes them a critical species in maintaining the health of our oceans.
Yellowfin Tuna hunt in the open ocean, near the surface, or in the upper part of the water column. They use their keen eyesight to spot their prey and their incredible speed to catch them. They can reach speeds of over 40 miles per hour, making them one of the fastest fish in the ocean.
The Fascinating Distribution of Yellowfin Tuna
Yellowfin Tuna are truly a global fish, found in the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans. However, their distribution is not evenly spread throughout these oceans. They are more abundant in the Western Pacific and Eastern Pacific oceans, with large populations also found in the Indian Ocean and the Western Atlantic.Their distribution is highly influenced by water temperature, as they prefer to swim in warm waters. This is why they are mostly found in tropical and subtropical regions, as these waters provide the perfect temperature for them to thrive.
The Stunning Appearance and Physical Characteristics of Yellowfin Tuna
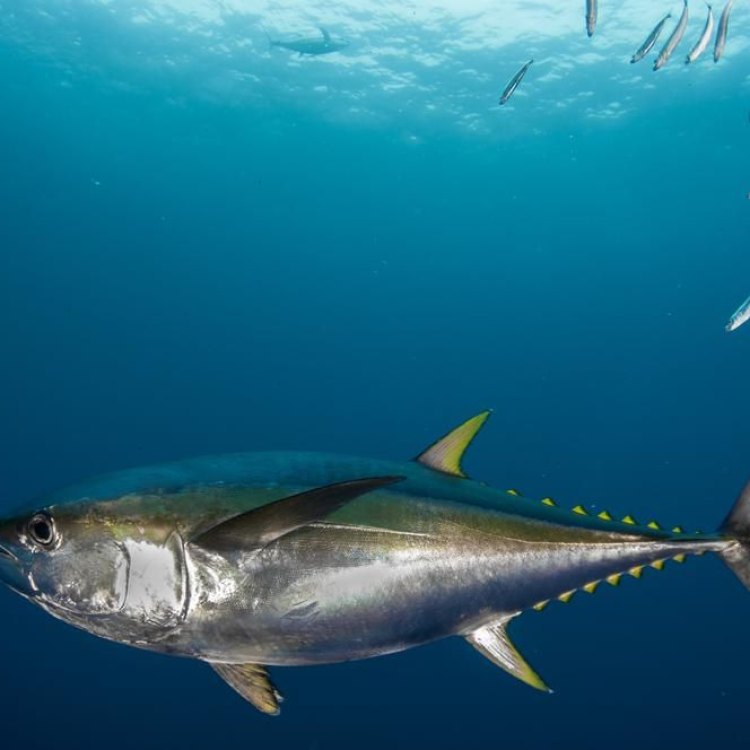
One of the most striking features of Yellowfin Tuna is their beautiful metallic dark blue to blackish back, which contrasts with their yellow sides and silver-white belly. This coloration is what gives them their common name, Yellowfin Tuna.They also have long yellow dorsal and anal fins and a yellow tail, adding to their stunning appearance. These vibrant colors serve a dual purpose - they act as camouflage, helping the fish blend in with the surrounding water, and also attract prey and potential mates.
In terms of physical characteristics, Yellowfin Tuna have a torpedo-shaped body, with a streamlined design that allows them to move swiftly and efficiently through the water. They have powerful, muscular bodies with a thick layer of fat, which helps them regulate their body temperature in colder waters.
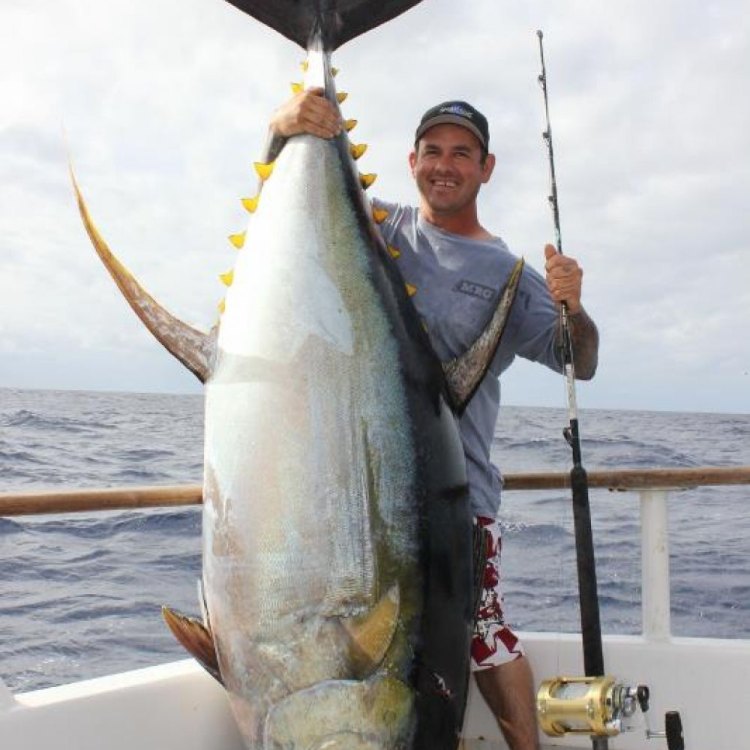
On average, Yellowfin Tuna can grow up to 7.5 feet (2.3 meters) in length and weigh up to 400 pounds (180 kilograms). However, the largest recorded Yellowfin Tuna weighed a whopping 445 pounds (202 kilograms) and was caught off the coast of Cabo San Lucas, Mexico.
The Fascinating Life Cycle of Yellowfin Tuna
Yellowfin Tuna reach their adult size at around 4-6 years of age, and they can live up to 6-7 years. However, their lifespan varies depending on several factors, such as water temperature, food availability, and fishing pressure.These tuna are oviparous, meaning they reproduce by laying eggs. During spawning, they gather in large groups and release their eggs and sperm into the water. The eggs are buoyant and develop in the open ocean, where they are less likely to be preyed upon.
The reproductive behavior of Yellowfin Tuna is one of the most fascinating aspects of their life cycle. These large groups of tuna gather together and swim in a circular pattern, releasing their eggs and sperm into the water at the same time. This synchronized spawning helps increase the chances of fertilization and the survival of their offspring.
The Migration Patterns of Yellowfin Tuna
Unlike many other fish species, Yellowfin Tuna undertake significant migrations throughout their lifetime. They follow the warmer water temperatures, allowing them to find suitable feeding grounds and favorable spawning conditions.They may travel long distances, moving across entire oceans, in search of food or to spawn. Their migratory patterns are not random; they are highly influenced by currents, water temperature, and the availability of food.
These migrations play a crucial role in the survival and reproduction of Yellowfin Tuna. They allow the fish to access different food sources, ensuring their diet is varied and nutritious, while also giving them the opportunity to reproduce in optimal conditions.
In Conclusion
Yellowfin Tuna is a magnificent fish species that has captured the hearts of anglers and fishermen worldwide. Its stunning appearance, incredible strength, and delicious taste make it a highly sought-after catch. However, it is essential to remember that these fish play a vital role in maintaining the balance of our oceans.As responsible fishermen, we must respect their natural habitat and protect their populations to ensure they continue to thrive for years to come. So next time you're out on the water, keep your eyes peeled for the dazzling Yellowfin Tuna, and if you're lucky enough to catch one, let it be a moment of awe and appreciation for the wonders of our oceans.
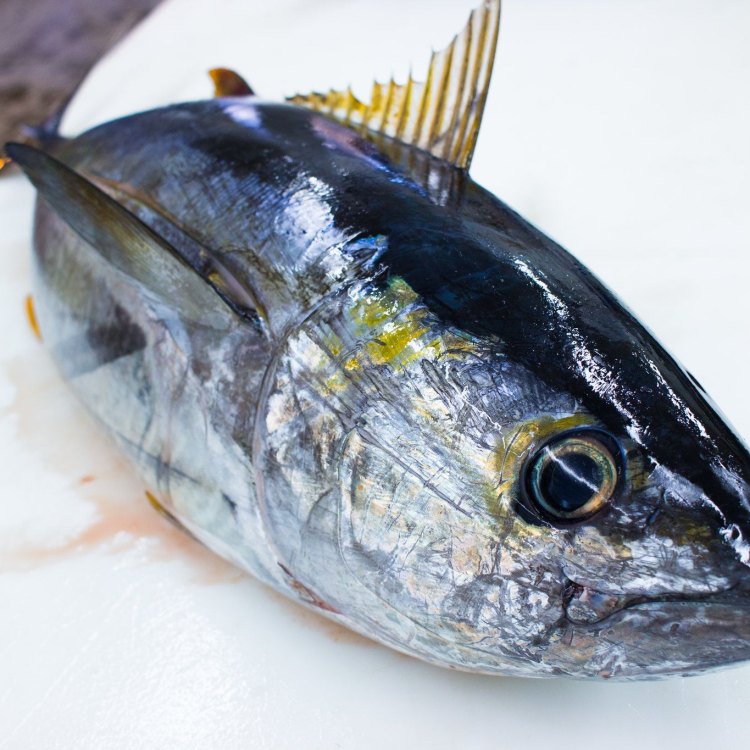

Yellowfin Tuna
Fish Details Yellowfin Tuna - Scientific Name: Thunnus albacares
- Category: Fish Y
- Scientific Name: Thunnus albacares
- Common Name: Yellowfin Tuna
- Habitat: Yellowfin Tuna inhabit tropical and subtropical waters worldwide. They prefer to stay closer to the surface in warm waters.
- Feeding Habitat: Yellowfin Tuna feed in the open ocean, near the surface or in the upper part of the water column.
- Feeding Method: They are opportunistic predators and feed on a variety of fish, squid, and crustaceans.
- Geographic Distribution: Yellowfin Tuna are found in the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans. They are most abundant in the tropical and subtropical areas.
- Country Of Origin: Yellowfin Tuna are native to the tropical and subtropical waters of the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans.
- Color: They have a metallic dark blue to blackish back with yellow sides and a silver-white belly. The fins and tail are also yellow.
- Body Shape: Yellowfin Tuna have a streamlined and torpedo-shaped body, enabling them to swim fast and efficiently.
- Length: They can grow up to 7.5 feet (2.3 meters) in length.
- Adult Size: Yellowfin Tuna reach their adult size at around 4-6 years of age.
- Age: They can live up to 6-7 years.
- Reproduction: Yellowfin Tuna are oviparous, meaning they reproduce by laying eggs.
- Reproduction Behavior: During spawning, they gather in groups and release their eggs and sperm into the water. The eggs are buoyant and develop in the open ocean.
- Migration Pattern: They undertake significant migrations, following the warmer water temperatures. They may travel long distances in search of food or to spawn.
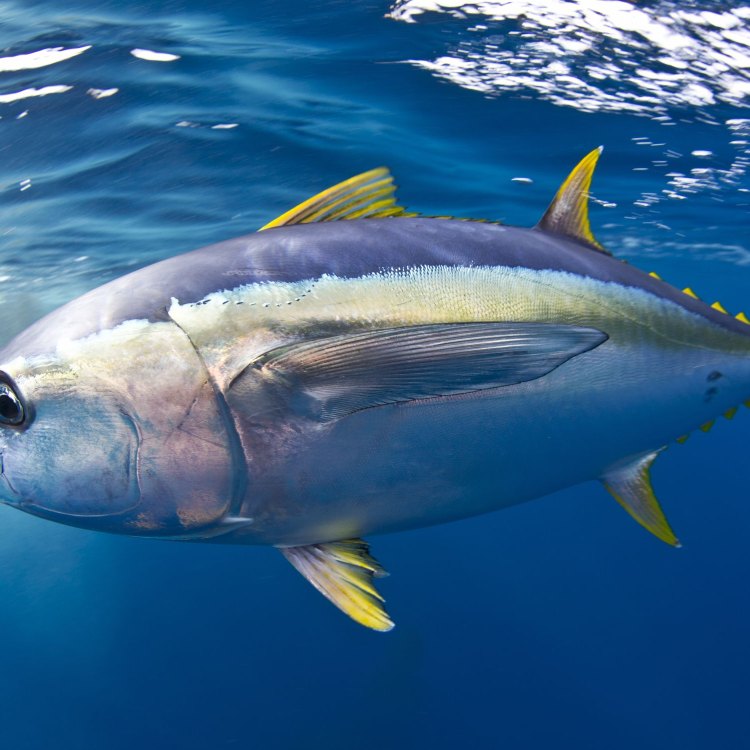

Yellowfin Tuna
- Social Group: Yellowfin Tuna are typically solitary or form small groups.
- Behavior: They are highly migratory and known for their speed and endurance.
- Diet: Their diet consists of a variety of fish, squid, and crustaceans.
- Predators: Predators of Yellowfin Tuna include larger fish such as sharks, as well as marine mammals like dolphins and seals.
- Prey: They prey on smaller fish, squid, and crustaceans.
- Environmental Threats: Yellowfin Tuna face threats from overfishing, habitat loss, and pollution.
- Conservation Status: The conservation status of Yellowfin Tuna is listed as Near Threatened by the IUCN.
- Special Features: One of the distinguishing features of Yellowfin Tuna is the bright yellow dorsal fin and tail.
- Interesting Facts: Yellowfin Tuna are highly valued for their culinary uses and are a popular sport fish. They are known for their strength and speed, making them a challenging catch.
- Reproduction Period: Yellowfin Tuna reproduce throughout the year, with peak spawning occurring during the warmer months.
- Nesting Habit: Yellowfin Tuna do not build nests as they are pelagic and do not have specific nesting habitats.
- Lifespan: They have an average lifespan of 6-7 years.
- Habitat Threats: Habitat threats for Yellowfin Tuna include climate change, overfishing, and pollution.
- Population Trends: Population trends for Yellowfin Tuna vary by region. In some areas, they are stable, while in others, they are declining.
- Habitats Affected: Yellowfin Tuna primarily inhabit pelagic and coastal waters.

Thunnus albacares
The Magnificent Yellowfin Tuna: A Strong and Adaptable Ocean Nomad
The ocean is a vast and mysterious world, filled with hundreds of thousands of unique and fascinating species. One such species is the Yellowfin Tuna, a fish that roams the open waters of the world's tropical and subtropical regions. With its vibrant yellow fin and impressive speed and strength, the Yellowfin Tuna is a popular sport fish and highly valued for its culinary use. But beyond its physical appearance and human uses, there is so much more to learn and appreciate about this magnificent creature RadioDouRosul.com.Yellowfin Tuna, also known as Thunnus albacares, are part of the Scombridae family, which includes other tuna species like the Bluefin and Skipjack tuna. They are sleek, streamlined fish with a torpedo-shaped body, making them incredibly fast and agile swimmers. They can grow up to 8 feet in length and weigh between 200-400 pounds, with females typically larger than males.
One of the distinguishing features of Yellowfin Tuna is their bright yellow dorsal fin and tail, which gives them their name. This yellow coloration is thought to serve as a form of camouflage, as it blends in with the sunlight reflecting off the ocean's surface, making them harder to spot by potential predators.
Speaking of predators, Yellowfin Tuna, like many other marine animals, face threats from larger predatory fish and marine mammals like sharks, dolphins, and seals. In turn, they prey on smaller fish, squid, and crustaceans, maintaining a delicate balance in the marine ecosystem. However, the greatest threat to their survival comes from human activities, such as overfishing, habitat loss, and pollution.
Yellowfin Tuna are highly migratory fish, and they are known for their speed and endurance, allowing them to cover large distances in search of food and suitable breeding grounds Yellow Moray. Their diet consists of a variety of prey, including fish, squid, and crustaceans, making them an important part of the food chain in the ocean.
When it comes to reproduction, Yellowfin Tuna follow a different approach than most fish species. They reproduce throughout the year, with peak spawning occurring during the warmer months. Unlike other fish that lay their eggs in nests, Yellowfin Tuna release their eggs and sperm into the water, where the eggs are fertilized, and the larvae hatch and grow. This method of reproduction is called broadcast spawning, and it allows for a large number of eggs to be fertilized at once, increasing their chances of survival.
As pelagic (open ocean) fish, Yellowfin Tuna do not build nests or have specific nesting habitats. They are nomadic, constantly moving in search of food and suitable conditions. However, this way of life also exposes them to various threats, including climate change, overfishing, and pollution. These environmental threats not only affect the Yellowfin Tuna but also impact the entire marine ecosystem.
Due to these threats, the conservation status of Yellowfin Tuna is listed as Near Threatened by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This means that although their current population is still relatively stable, there is a risk of their numbers declining in the future, and conservation efforts must be taken to prevent this from happening.
Population trends for Yellowfin Tuna vary by region. In some areas, such as the Indian Ocean, their population is declining due to overfishing and unsustainable fishing practices. However, in other areas, such as the Pacific Ocean, their population is relatively stable. These differences in population trends highlight the importance of sustainable management and conservation practices to protect this species and maintain a healthy balance in the ocean's ecosystems.
Yellowfin Tuna primarily inhabit pelagic and coastal waters, making them an important species for both commercial and recreational fishing. They are highly valued for their culinary uses, with their firm, pink flesh considered a delicacy in many cuisines around the world. They are also a popular sport fish, with many anglers seeking the challenge of catching one of these powerful and speedy fish.
Despite their name, the Yellowfin Tuna can also be found in various shades, ranging from yellow to silver to blue. These color variations are seen in different populations of Yellowfin Tuna, with some showing a preference for certain habitats and conditions. This adaptation allows for a better chance of survival in their unpredictable and ever-changing environment.
The average lifespan of Yellowfin Tuna in the wild is 6-7 years, with females living longer than males. However, these numbers can vary depending on factors such as fishing pressure, food availability, and environmental conditions. As a highly migratory species, Yellowfin Tuna may also travel long distances in their lifespan, facing various challenges and adapting to different environments along the way.
In conclusion, Yellowfin Tuna are a fascinating and vital species in the ocean. Their adaptability and resilience allow them to thrive in a constantly changing environment. However, human activities and environmental threats pose a significant risk to their survival, emphasizing the need for sustainable management and conservation efforts. May we continue to appreciate and protect this magnificent ocean nomad, ensuring its existence for generations to come.

The Thrilling World of Yellowfin Tuna: The Ultimate Catch for Anglers
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.