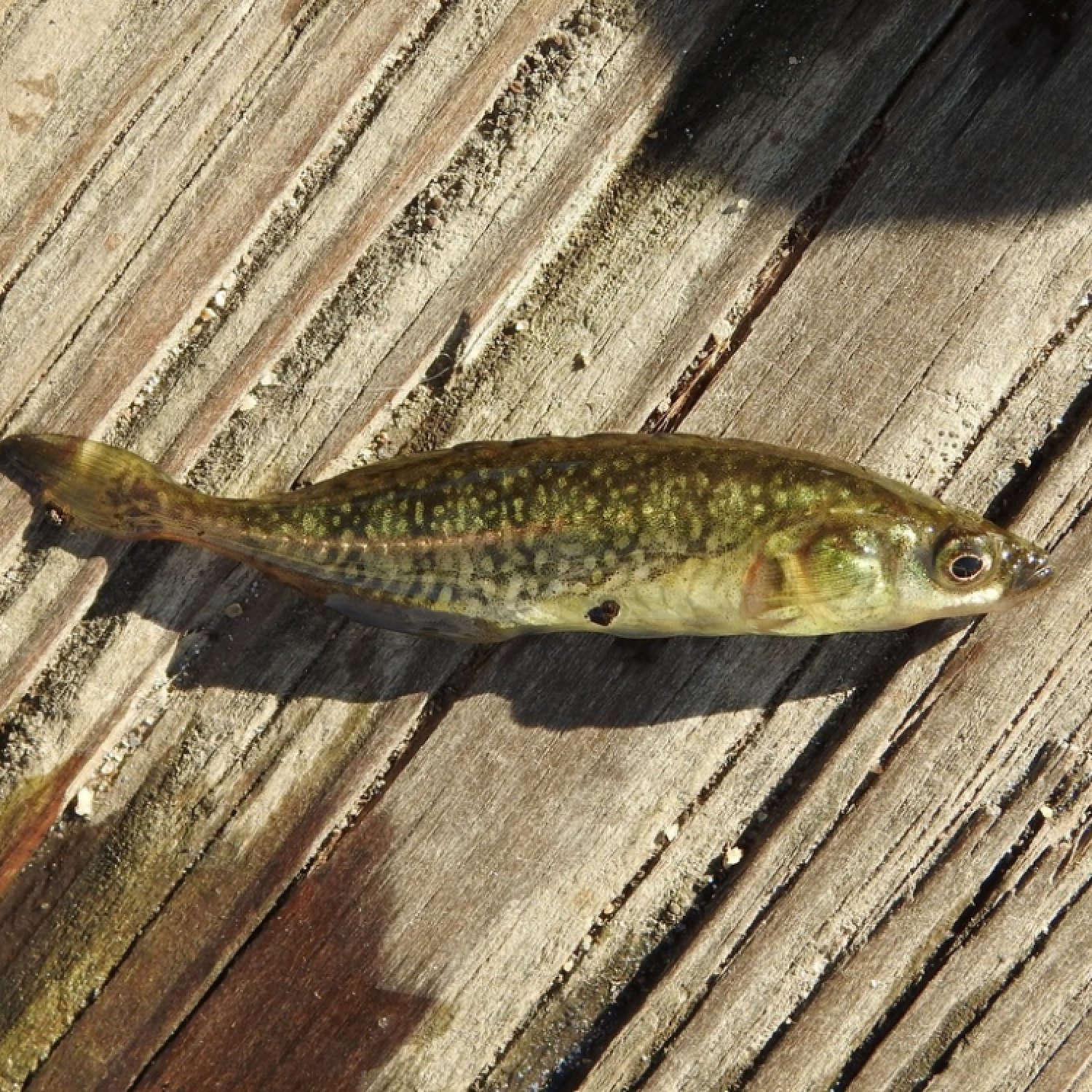
Brook Stickleback
Brook Sticklebacks are not known for long-distance migrations.
Did you know that Brook Sticklebacks, found in the US & Canada, have a short lifespan of 1-3 years? These fish are known for their elaborate nests and courtship displays during breeding season. Males guard and care for the eggs until they hatch. Learn more about these fascinating fish!
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: Brook Stickleback
Habitat: Brook Sticklebacks inhabit freshwater environments such as rivers, streams, and lakes with slow-moving or calm water.
Color: The males are brightly colored during the breeding season, with a red belly and blue-greenish back. The females are less colorful, with a light brown or olive color.
The Fascinating World of the Brook Stickleback
The world is filled with an incredibly diverse array of creatures, each with their unique characteristics that make them stand out. One such creature is the Brook Stickleback, also known as Culaea inconstans. This small fish may not be the most well-known or glamorous, but it has a fascinating story to tell. Let's dive into the world of the Brook Stickleback and discover what makes it so unique Brook Stickleback.A Home in Freshwater Environments
The Brook Stickleback can be found in freshwater environments such as rivers, streams, and lakes, with slow-moving or calm water. These habitats provide the perfect conditions for these fish to thrive. They are most commonly found in eastern and central parts of North America, specifically in the United States and Canada.One of the reasons these fish are so widespread is that they are incredibly adaptable. They are not fussy about their living conditions and can thrive in a variety of freshwater environments. This makes them resilient and able to colonize new areas quickly.
A House Full of Food
The Brook Stickleback's ideal feeding habitat is in vegetation-rich areas, where they can hunt for small invertebrates and plankton. These fish are opportunistic feeders, meaning they will eat whatever is available to them. They use their small mouths to suck in and ingest their prey, making them efficient and quick predators Bluefish.The presence of vegetation is crucial for the survival of the Brook Stickleback. Not only does it provide them with a source of food, but it also offers them shelter from predators. These fish are also known to feed on algae, providing a valuable service by keeping aquatic vegetation in check.
A Splash of Color
The male Brook Sticklebacks are known for their bright colors during the breeding season. They have a red belly and a blue-greenish back, making them stand out from their female counterparts. Their colorful appearance is not just for show; it serves a crucial purpose in the reproductive process.The females, on the other hand, are less colorful, with a light brown or olive color. This difference in coloration between the males and females is known as sexual dimorphism. It is a common phenomenon in the animal world and serves as a way for the males to attract females during the breeding season.
A Unique Body Shape
The Brook Stickleback has a slender cylindrical body shape, making it stand out from other fish species. It has long dorsal and anal fins that give it a distinct appearance. These fins play a crucial role in the fish's movement and also help them maintain balance in the water.Their slender body shape also allows them to navigate through dense vegetation with ease, making it easier for them to find food and shelter. It is a great example of how evolution has helped these fish adapt to their environment.
The Size of a Brook Stickleback
The average length of a Brook Stickleback is around 2-4 inches, making them relatively small creatures. However, what they lack in size, they make up for in their unique characteristics and adaptations.Their adult size is typically around 2-4 inches, but they can grow up to 5 inches in some cases. This makes them an ideal pet for those looking to add a small and unique fish to their aquarium.
The Secret to a Long Life
The lifespan of a Brook Stickleback is around 1-3 years, making them a relatively short-lived species. However, this does not mean that they cannot live a long and fulfilling life. In the wild, they face various challenges, such as predation, competition for resources, and harsh environmental conditions, which affect their lifespan.In captivity, with proper care and conditions, they can live up to five years. Regular water changes, a nutritious diet, and a suitable tank environment are all essential for the health and longevity of these unique fish.
The Miracle of Reproduction
One of the most fascinating aspects of the Brook Stickleback's life is its reproductive habits. These fish are sexually dimorphic, meaning the males and females have different characteristics. During the breeding season, the males will build elaborate nests made of aquatic vegetation to attract females.The male Brook Stickleback will display courtship behaviors to entice females to enter their nest. After spawning, the male takes on the responsibility of guarding and caring for the eggs, ensuring their survival until they hatch. It is a testament to the dedication and nurturing nature of these small fish.
Migrating Within Their Habitat
Brook Sticklebacks are not known for long-distance migrations, but they do sometimes move within their habitat. During the breeding season, males will build their nests in shallow areas of the water, while they may move to deeper areas during colder months.In some cases, these fish have also been observed moving to adjacent streams or lakes in search of new nesting sites. However, these movements are relatively short distances and do not qualify as migrations in the traditional sense.
In Conclusion
The Brook Stickleback may not be the most well-known or glamorous fish out there, but it is undoubtedly one of the most fascinating. From their unique body shape to their colorful appearance, and their dedicated parenting habits, there is so much to discover about these small creatures.Their adaptability, resilience, and nurturing nature make them a valuable species in the ecosystem. As with any animal, it is essential to understand and appreciate their role in nature and strive to protect and conserve them for future generations to come.
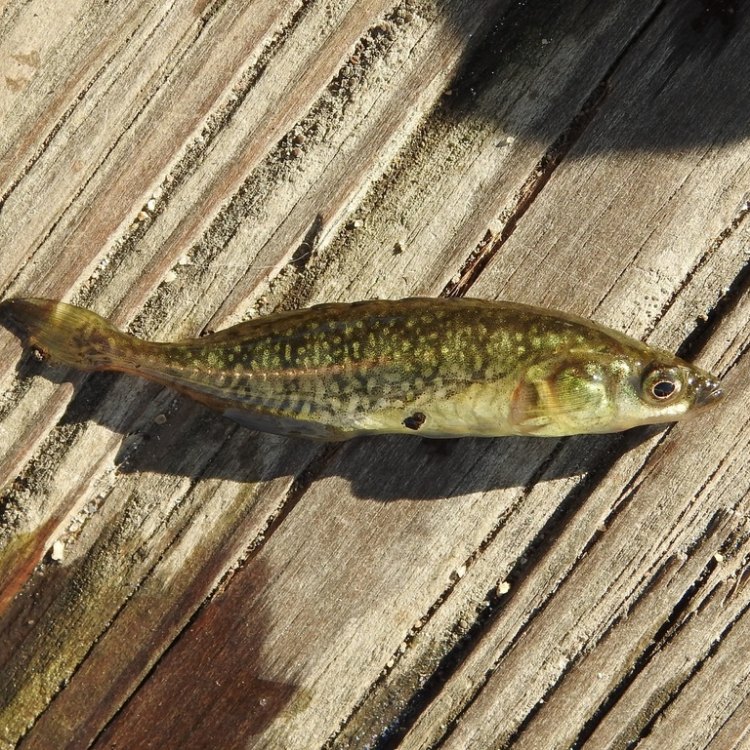

Brook Stickleback
Fish Details Brook Stickleback - Scientific Name: Culaea inconstans
- Category: Fish B
- Scientific Name: Culaea inconstans
- Common Name: Brook Stickleback
- Habitat: Brook Sticklebacks inhabit freshwater environments such as rivers, streams, and lakes with slow-moving or calm water.
- Feeding Habitat: They can be found feeding in vegetation-rich areas, where they hunt for small invertebrates and plankton.
- Feeding Method: Brook Sticklebacks use their small mouths to suck in and ingest their prey.
- Geographic Distribution: They are native to North America and are found in the eastern and central parts of the continent.
- Country Of Origin: United States and Canada
- Color: The males are brightly colored during the breeding season, with a red belly and blue-greenish back. The females are less colorful, with a light brown or olive color.
- Body Shape: Brook Sticklebacks have a slender body shape that is cylindrical in appearance. They have long dorsal and anal fins.
- Length: They usually grow to be around 2-4 inches in length.
- Adult Size: The adult size of Brook Sticklebacks is typically around 2-4 inches.
- Age: The lifespan of Brook Sticklebacks is around 1-3 years.
- Reproduction: They are sexually dimorphic, meaning males and females have different characteristics. The males build nests, court females, and provide parental care to the eggs and young.
- Reproduction Behavior: During the breeding season, male Brook Sticklebacks build elaborate nests made of aquatic vegetation. They display courtship behaviors to attract females and entice them to enter the nest. After spawning, the male guards and cares for the eggs until they hatch.
- Migration Pattern: Brook Sticklebacks are not known for long-distance migrations.
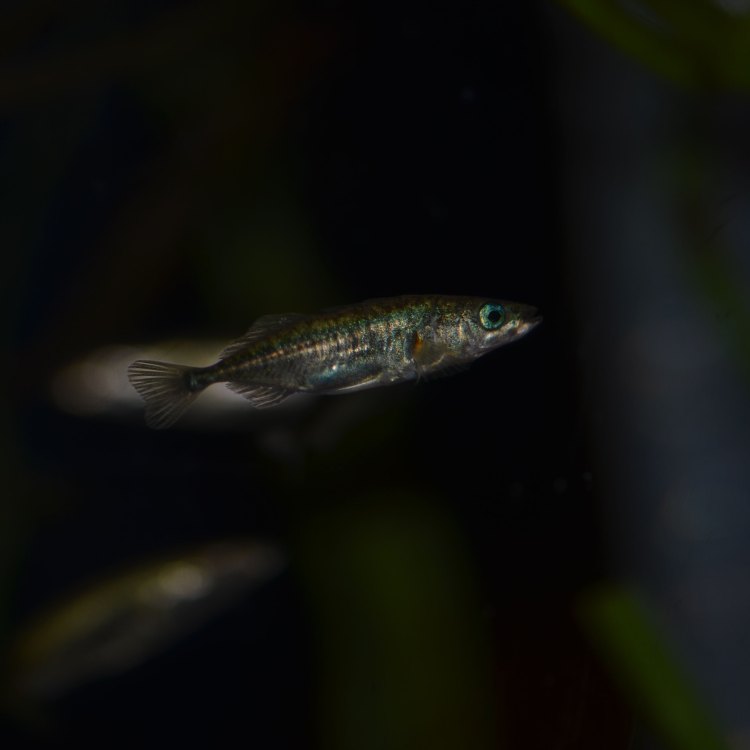

Brook Stickleback
- Social Group: They are generally solitary fish, but during the breeding season, males establish and defend territories around their nests.
- Behavior: Brook Sticklebacks are known to be highly territorial and will aggressively defend their nests from intruders.
- Diet: They are opportunistic feeders and primarily consume small invertebrates, zooplankton, and insect larvae.
- Predators: Brook Sticklebacks are preyed upon by larger fish, birds, and aquatic predators such as turtles and water snakes.
- Prey: They feed on small invertebrates, zooplankton, and insect larvae.
- Environmental Threats: Habitat degradation, pollution, and predation by invasive species are some of the environmental threats to Brook Stickleback populations.
- Conservation Status: They are not currently listed as a species of concern by conservation organizations.
- Special Features: Males develop bright colors during the breeding season to attract females.
- Interesting Facts: Brook Sticklebacks are known for their intricate nest-building behaviors. They construct nests out of grasses and vegetation, and the male guards the nest and provides parental care until the young hatch.
- Reproduction Period: The reproduction period for Brook Sticklebacks typically occurs in the spring and early summer.
- Nesting Habit: Males construct nests made of aquatic vegetation and defend their territories around the nests.
- Lifespan: Brook Sticklebacks have a lifespan of around 1-3 years.
- Habitat Threats: Habitat degradation due to human activities, such as agriculture and urbanization, can pose threats to Brook Stickleback populations.
- Population Trends: Population trends for Brook Sticklebacks are generally stable, but local declines can occur due to habitat loss and degradation.
- Habitats Affected: Habitats that are affected by the presence of Brook Sticklebacks include freshwater streams, rivers, and lakes with vegetation-rich areas.

Culaea inconstans
The Fascinating World of Brook Sticklebacks
Under the shimmering waters of freshwater streams, rivers, and lakes, lies a small, but mighty fish that is both fascinating and tenacious - the Brook Stickleback. This small, spiny fish may seem unassuming at first glance, but upon closer inspection, its unique features and behaviors reveal a deep admiration for survival and reproduction.In this article, we will embark on a journey to explore the life of Brook Sticklebacks, from their solitary lifestyle to their intricate nest-building behaviors. We will also uncover the environmental threats that these mighty fish face and their importance in their respective habitats RadioDouRosul.com.
Social Group
Brook Sticklebacks, scientifically known as Culaea inconstans, are generally solitary fish. They prefer to live and forage on their own, rather than in large schools like other fish species. However, during the breeding season, which typically occurs in the spring and early summer, males establish and defend territories around their nests.
Behavior
The Brook Stickleback is known for its highly territorial behavior. They fiercely guard their nesting sites, often attacking intruders who come too close. This behavior is especially prominent during the breeding season when males are defending their nests. This aggressive behavior is a means of ensuring reproductive success and protecting their offspring.
A Brook Stickleback defending its nest. Source: Bonytongue.flickr.com/photos/gretchenjoanna/8098592088" target="_blank">Flickr.
Diet
Despite their tiny size, Brook Sticklebacks are opportunistic feeders. They primarily consume small invertebrates, such as insect larvae, zooplankton, and aquatic insects. They use their spines to hunt and capture their prey, making them a formidable predator in their habitat.
Predators
Brook Sticklebacks may be skilled predators, but they are also vulnerable to larger fish, birds, and aquatic predators such as turtles and water snakes. These predators are a constant threat to Brook Stickleback populations, as they can easily prey upon them in their own habitats.
Prey
While Brook Sticklebacks have their own set of predators, they are also prey themselves. They are an important part of the food chain in their habitats, providing a vital source of food for larger fish and birds.
Environmental Threats
Unfortunately, Brook Stickleback populations are not only threatened by natural predators but also by human activities. Habitat degradation, pollution, and predation by invasive species are some of the environmental threats that these fish face. As humans continue to encroach on their habitats for agricultural and urbanization purposes, their populations are at risk of decline.
Conservation Status
Despite these threats, Brook Sticklebacks are not currently listed as a species of concern by conservation organizations. However, their importance in maintaining a healthy ecosystem cannot be overstated, and it is crucial to continue monitoring their populations and addressing any declines.
Special Features
One of the most striking features of Brook Sticklebacks is their ability to change colors. During the breeding season, males develop bright red and blue coloration on their belly and fins. This transformation is a way for males to attract females and signal their readiness to breed.
A male Brook Stickleback with bright red and blue colors during breeding season. Source: Wikipedia.
Interesting Facts
Apart from their unique behaviors and color-changing abilities, Brook Sticklebacks are known for their intricate nest-building behaviors. They construct nests out of grasses and vegetation, often in shallow waters or submerged in aquatic vegetation. The male then guards the nest and provides parental care until the young hatch, which can take a few weeks.
Their nesting habits have been studied extensively by biologists, and it has been found that males with larger and more elaborate nests tend to attract more females. This behavior further highlights the importance of their nests in the reproductive success of Brook Sticklebacks.
Reproduction Period
As mentioned earlier, the reproduction period for Brook Sticklebacks typically occurs in the spring and early summer. During this time, males are at their peak, displaying their vibrant colors and defending their nests. Once the eggs are laid, the male will continue to guard and protect them until the young hatch.
Nesting Habit
Males are responsible for constructing the nests for breeding, and they take this role very seriously. They construct the nest out of aquatic vegetation, carefully weaving and binding the plants together with their saliva, creating a secure structure for the eggs. After the eggs are laid, the male will continue to guard the nest from predators until the young hatch.
Lifespan
The average lifespan of Brook Sticklebacks is around 1-3 years. During this time, they go through several breeding seasons, adding to the population of their species.
Habitat Threats
As mentioned earlier, habitat degradation due to human activities is a significant threat to Brook Sticklebacks. Agriculture, urbanization, and pollution can all have detrimental effects on their habitats, causing a decline in their populations.
Population Trends
While overall population trends for Brook Sticklebacks are generally stable, local declines can occur due to habitat loss and degradation. This means that some populations may be at risk of extinction if proper conservation measures are not taken.
Habitats Affected
Brook Sticklebacks are an essential part of their freshwater habitats. They thrive in clean and clear water, usually with vegetation-rich areas. These habitats not only provide a home for the Brook Sticklebacks but also support a diverse community of aquatic plants and animals.
In conclusion, Brook Sticklebacks may be small, solitary fish, but they play a crucial role in their freshwater habitats. From their aggressive territorial behavior to their vibrant color-changing abilities, they have captured the fascination of biologists and nature enthusiasts alike. As we continue to understand and appreciate these remarkable fish, let us also remember to protect their habitats and ensure their survival for generations to come.

The Fascinating World of the Brook Stickleback
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.