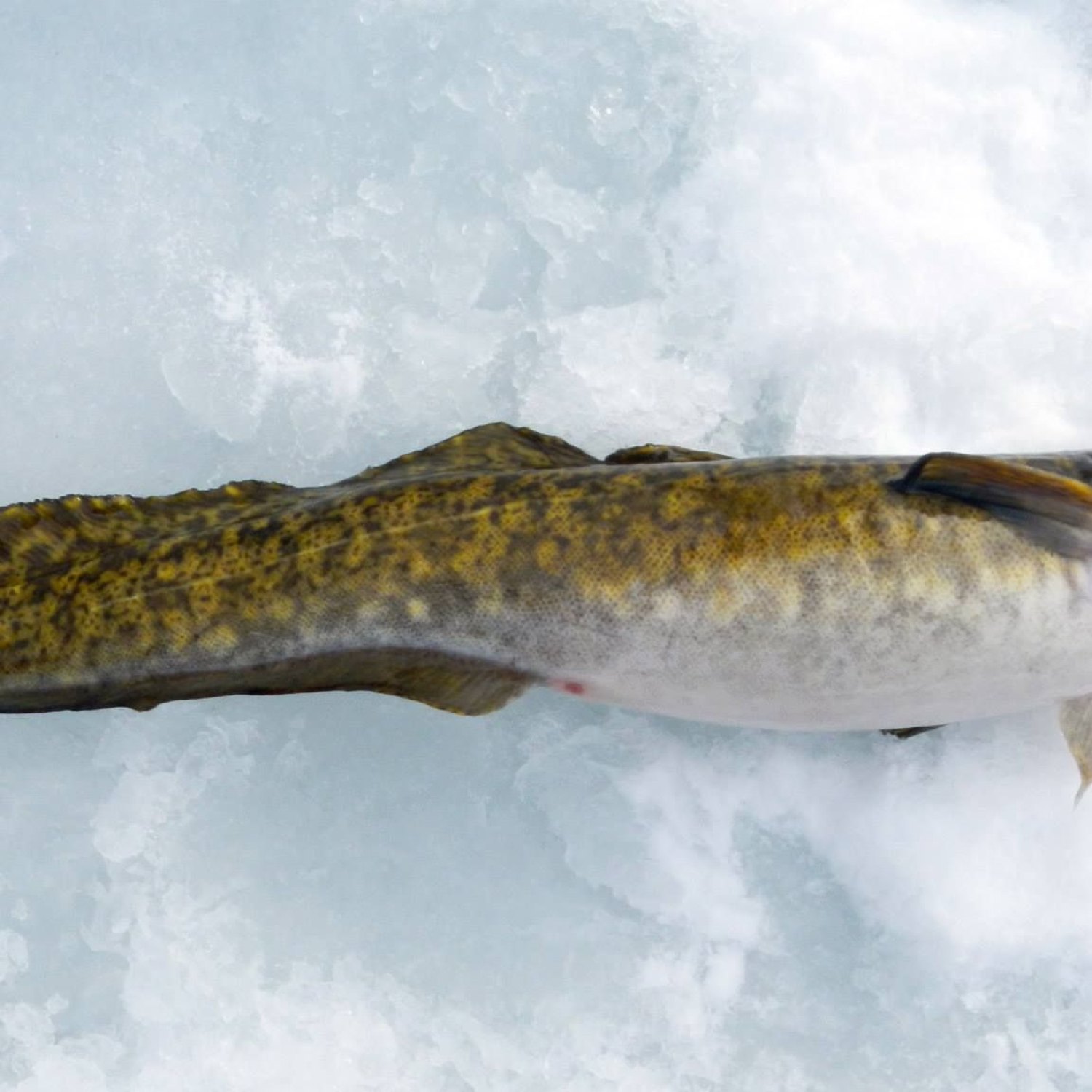

Cusk
Migrate to shallower waters during spawning season
Cusk, also known as the sea owl, is a deep-sea fish that can live up to 20 years. During spawning season, they migrate to shallower waters in Norway, Iceland, and Canada. Despite their mysterious nature, they are a popular catch among anglers. Have you ever spotted this elusive creature? #cusk #deepseafish #migratoryspecies #Norway #Iceland #Canada
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: Cusk
Habitat: Deep waters
Color: Brownish
A Deep Dive into the Fascinating World of Cusk: The Ambush Predator
Have you ever wondered what lies beneath the ocean's surface in the deep waters? All kinds of strange and fascinating creatures lurk in the depths, and one of them is the cusk (Brosme brosme). This elusive fish, also known as brisling, tusk, or cusk eel, is a true predator that roams the deep waters of the Atlantic Ocean. But despite its intimidating appearance, there's much more to this fish than meets the eye. In this article, we'll take a closer look at this mysterious creature and uncover its unique features and behavior Cusk.The Basics of Cusk
Cusk, as we already know, is a deep-water fish with an elongated, eel-like body shape. Its scientific name, Brosme brosme, is derived from the Greek word "brosma," which means projecting fish teeth. These teeth are indeed prominent, resembling large fangs that give the cusk a menacing look.This fish also has a brownish color, which blends perfectly with its benthic habitat. Its body is covered in small scales that help protect its sensitive skin in the harsh deep-water environment. The cusk's average length is about 1.3 meters (4.3 feet), but some records show that it can reach up to 2 meters (6 feet) in length. It's considered a large fish, with a maximum weight of 22 kilograms (50 pounds) Channel Catfish.
Where Can You Find Cusk?
Cusk is found in the depths of the Atlantic Ocean, specifically in the subarctic and temperate regions. It can be found in countries such as Norway, Iceland, and Canada, and also along the coast of New England in the United States. This fish prefers to stay in deep waters ranging from 100 to 600 meters (328 to 1968 feet) in depth, where it feeds and reproduces.A Master of Ambush
Cusk is an ambush predator, meaning it relies on its surprising and swift attack to catch its prey. Its benthic feeding habitat allows it to hide and patiently wait for unsuspecting prey to pass by. The cusk's diet consists of various benthic invertebrates, such as crustaceans, mollusks, and fish. It uses its sharp, fang-like teeth to grab and tear apart its prey, making it a formidable predator despite its slow-moving nature.The Mysteries of Cusk Reproduction
The cusk's reproductive behavior is still largely unknown, despite scientific research efforts. It's believed that this fish reproduces sexually, similar to other fish species, but the details of its mating habits and spawning patterns are still a mystery. What we do know is that cusk reaches sexual maturity at around 5 to 6 years of age, with some specimens living up to 20 years.During the spawning season, which varies from place to place, cusk migrate to shallower waters, around 50 to 100 meters (164 to 328 feet) deep. It's estimated that females can produce up to 1.5 million eggs. The eggs float in the water column until they hatch, and the larvae drift with the currents for about 6 months before settling on the ocean floor.
Why Is Cusk Important?
Cusk is not only a fascinating creature but also an essential part of the ocean ecosystem. As a predator, it plays a vital role in controlling the population of its prey. It's also a commercially valuable fish, particularly for its fillets, which are considered a delicacy in many countries. Unfortunately, like many other fish species, cusk populations have declined in recent years due to overfishing.In Norway, Iceland, and Canada, strict regulations are in place to manage cusk fisheries and ensure sustainable harvesting practices. These countries also work together to monitor cusk populations and collaborate on research to better understand this elusive fish.
A Final Thought on Cusk
While cusk may seem like a simple fish at first glance, it's an essential and fascinating creature that plays a significant role in the ocean's ecosystem. Its long lifespan, mysterious behavior, and unique adaptation to its deep-water environment make it a subject of ongoing research and continued fascination among marine enthusiasts.Next time you're near the Atlantic Ocean, take a moment to think about the fantastic creatures that live beneath its surface, and you might just catch a glimpse of the elusive cusk. And now that you know a bit more about this ambush predator, you'll recognize how truly special this fish is.

Cusk
Fish Details Cusk - Scientific Name: Brosme brosme
- Category: Fish C
- Scientific Name: Brosme brosme
- Common Name: Cusk
- Habitat: Deep waters
- Feeding Habitat: Benthic
- Feeding Method: Ambush predator
- Geographic Distribution: Atlantic Ocean
- Country Of Origin: Norway, Iceland, Canada
- Color: Brownish
- Body Shape: Elongated and eel-like
- Length: Up to 1.3 meters (4.3 feet)
- Adult Size: Up to 1.3 meters (4.3 feet)
- Age: Up to 20 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproduction Behavior: Unknown
- Migration Pattern: Migrate to shallower waters during spawning season
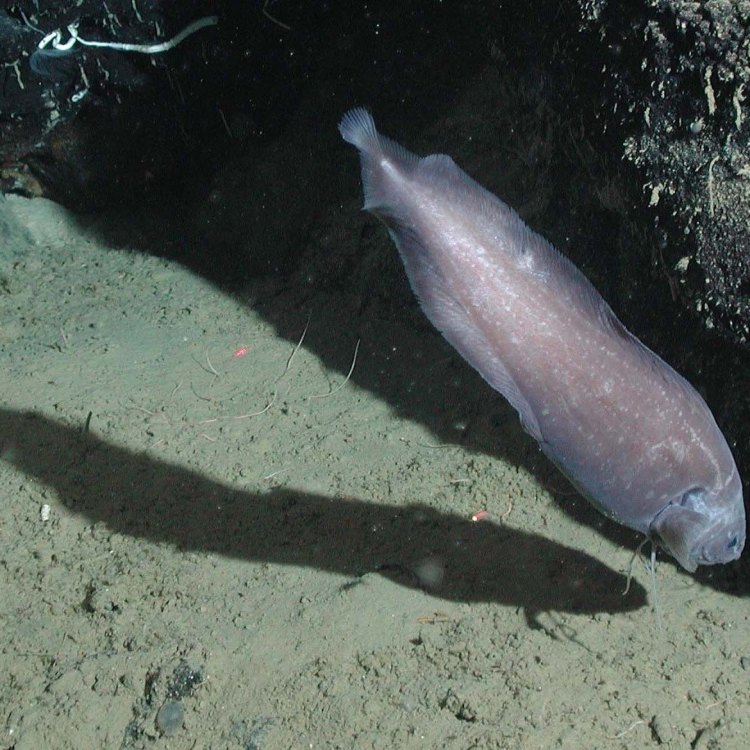

Cusk
- Social Group: Solitary
- Behavior: Nocturnal
- Diet: Fish, squid, crustaceans, and other bottom-dwelling organisms
- Predators: Sharks, seals, and larger fish
- Prey: Fish, squid, crustaceans, and other bottom-dwelling organisms
- Environmental Threats: Overfishing and fishing gear impacts
- Conservation Status: Not evaluated
- Special Features: Large mouth and chin barbel
- Interesting Facts: Cusk are considered a delicacy in many countries and are a popular food fish
- Reproduction Period: Unknown
- Nesting Habit: Unknown
- Lifespan: Up to 20 years
- Habitat Threats: Unknown
- Population Trends: Unknown
- Habitats Affected: Unknown

Brosme brosme
The Fascinating World of Cusk - A Deep Sea Discovery
Deep in the dark waters of the Atlantic Ocean, lives a creature that is rarely seen by humans - the cusk. This deep sea fish, also known by its scientific name Brosme brosme, belongs to the cod family and is native to the North Atlantic Ocean. Despite being an intriguing and important species in the marine ecosystem, the cusk remains a mystery to most people. In this article, we will take a closer look at this solitary and nocturnal fish, exploring its behavior, diet, predators, threats, and many other interesting facts RadioDouRosul.com.Social Group: Solitary
Unlike most fish, the cusk are solitary creatures. They prefer to live alone rather than in groups or schools, which is a common behavior among many other marine species. This makes it challenging for researchers to study their behavior, as they are rarely seen in large numbers. Cusk are territorial and will defend their space, making them even more elusive to humans.
Behavior: Nocturnal
As mentioned earlier, cusk are nocturnal creatures, which means they are most active at night. This behavior is believed to be an adaptation to their deep-sea habitat, where sunlight does not reach. During the day, cusk can be found hiding in caves or crevices, waiting for the cover of darkness to hunt for food. However, their exact sleeping patterns and resting habits are still unknown.
Diet: Fish, Squid, Crustaceans, and Other Bottom-Dwelling Organisms
Cusk are opportunistic predators, meaning they will eat whatever prey they come across Char. Their diet primarily consists of fish, including herring, capelin, and hake. They are also known to feed on squid, crustaceans, and other bottom-dwelling organisms. Their large mouth and strong teeth make them well equipped to catch and consume a variety of prey, making them an important part of the marine food chain.
Predators: Sharks, Seals, and Larger Fish
Despite their fierce appearance and strong teeth, cusk are preyed upon by several marine predators. Their main predators include sharks, seals, and larger fish such as halibut and cod. In some areas, commercial fisheries also target cusk, further reducing their population. As we will discuss later, human activities pose a significant threat to these deep-sea fish.
Prey: Fish, Squid, Crustaceans, and Other Bottom-Dwelling Organisms
As mentioned earlier, cusk are opportunistic predators, and their diet consists of various fish, squid, crustaceans, and other bottom-dwelling organisms. They play a crucial role in regulating the population of their prey, helping to maintain a balance in the ecosystem. Without cusk, the population of their prey would increase, leading to a decline in other marine species' numbers.
Environmental Threats: Overfishing and Fishing Gear Impacts
Unfortunately, the cusk population is facing significant threats from human activities, mainly due to overfishing and fishing gear impacts. Cusk were once widely harvested for their delicious meat, and they are still considered a delicacy in many countries. Their slow growth rate and late sexual maturity make them vulnerable to overfishing, as they cannot reproduce quickly enough to replenish their population. Additionally, fishing gear impacts, such as bottom trawling, can damage the seabed where cusk dwell, destroying their habitat and food sources.
Conservation Status: Not Evaluated
Despite the environmental threats facing the cusk population, they have not been evaluated by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This is mainly due to the lack of data and research on this deep-sea fish. However, several organizations, such as the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), have identified the need for more research and management efforts to ensure the long-term survival of the cusk.
Special Features: Large Mouth and Chin Barbel
The cusk has several unique physical features that separate it from other fish species. Its large mouth, equipped with sharp teeth, allows it to capture and consume its prey with ease. The cusk also has a chin barbel, which is a small fleshy appendage that hangs from its lower jaw. This barbel is thought to aid in locating food in the dark depths of the ocean.
Interesting Facts: Considered a Delicacy and a Popular Food Fish
Cusk have been a popular food fish for centuries, and they are still considered a delicacy in many countries. In Norway, cusk is a popular ingredient in fish cakes and soups, while in Iceland, it is used to make a traditional dish called 'Dried Fishhead Soup.' Cusk is also a popular dish in Portugal, where it is cooked with potatoes and cod roe to make a dish called 'Brosme a la Gomes de Sa.'
Reproduction Period: Unknown
Due to their deep-sea habitat and elusive behavior, the reproduction period of cusk is still unknown. However, it is believed that they follow a similar reproductive pattern to other cod family members. Female cusk are known to produce a large number of eggs, which are released into the water column, where they are fertilized by male sperm. The eggs then hatch into larvae, which eventually develop into juvenile cusk.
Nesting Habit: Unknown
Similar to their reproduction period, the nesting habit of cusk is still a mystery. Scientists believe that cusk may lay their eggs in deep-sea crevices or caves, where they are relatively safe from predators. However, confirmation of this behavior is yet to be made.
Lifespan: Up to 20 Years
Cusk have a relatively long lifespan compared to other fish species, living up to 20 years in the wild. Their slow growth rate and late sexual maturity contribute to their longevity. However, due to the lack of data on cusk, their exact lifespan is still unknown.
Habitat Threats: Unknown
Aside from the environmental threats posed by human activities, the exact habitat threats to cusk are still unknown. More research is needed to fully understand their habitat and the potential threats they may face, allowing for more effective conservation efforts.
Population Trends: Unknown
The population trends of cusk are also unclear due to a lack of data and research. However, it is safe to assume that their numbers have declined in recent years due to overfishing and habitat destruction. More efforts are needed to monitor and track the population trends of cusk to help inform conservation efforts.
Habitats Affected: Unknown
Cusk are a vital part of the deep-sea ecosystem, and any decline in their population can have significant effects on other marine species. Cusk play an important role in regulating the population of their prey, and their existence is crucial for maintaining balance in the marine food chain.
In conclusion, the cusk is a fascinating deep-sea fish that is still shrouded in mystery. Despite being a solitary and nocturnal creature, cusk play a vital role in the marine ecosystem. However, they face several threats from human activities, and more efforts are needed to conserve and protect this unique species. As we continue to explore the depths of the ocean, let us remember the importance of preserving the delicate balance of marine life and the need to protect creatures like the elusive cusk.
A Deep Dive into the Fascinating World of Cusk: The Ambush Predator
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.












