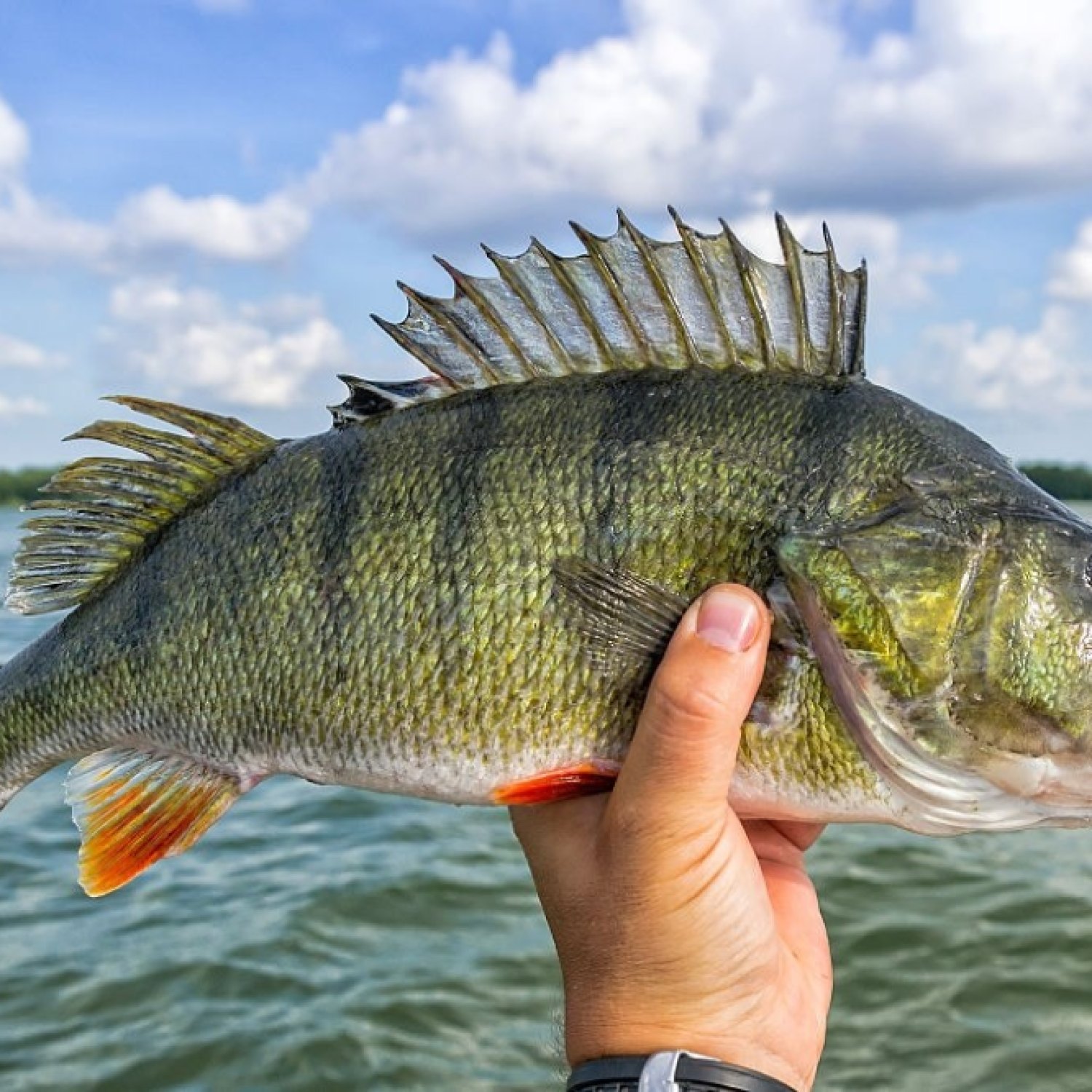
European Perch
Non-migratory
Did you know the European Perch, also known as ikan Turangan in Indonesia, can live up to 20 years? These non-migratory fish are commonly found in shallow waters across Europe. Keep an eye out for this species, as they spawn in groups during breeding season! #EuropeanPerch #IndonesiaFish #NonMigratoryFish
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: European Perch
Habitat: Freshwater lakes, rivers, and ponds
Color: Greenish-yellow with dark vertical bars
The Captivating European Perch: An Ambush Predator of European Waters
The European Perch, scientifically known as Perca fluviatilis, is a fascinating freshwater fish species that can be found throughout the lakes, rivers, and ponds of Europe. This species is highly sought after by anglers for its aggressive nature and delicious taste, making it a popular target for fishing enthusiasts. Let's dive deeper into the world of the European Perch to discover its outstanding features and unique characteristics.Habitat and Distribution
The European Perch is native to most of Europe, with its natural habitat spanning across the continent European Perch. This species can be found in freshwater bodies of water, including lakes, rivers, and ponds. They thrive in clear, shallow waters that are rich in vegetation, as these areas provide ample opportunities for hunting and shelter.Feeding Habits and Method
As an ambush predator, the European Perch is a formidable hunter that preys on smaller fish, insects, and crustaceans. This species has adapted to thrive in both the benthic and pelagic zones of their habitats, meaning they can feed on prey found on the bottom of the water or in the open water.The European Perch's feeding method involves waiting for unsuspecting prey to swim by and then quickly striking with its sharp teeth. This technique allows them to conserve energy while still being efficient hunters. Additionally, their coloration, which is greenish-yellow with dark vertical bars, helps them blend into their surroundings, making them excellent ambush predators.
Size, Growth, and Reproduction
The European Perch has a distinctive oval-shaped body that is laterally compressed, making it an agile and fast-swimming fish. This species can grow up to 50 cm in length, with adult sizes ranging between 20-30 cm Electric Catfish. They can live up to 20 years in the wild, with females reaching reproductive maturity at 2-3 years old and males at 1-2 years old.The European Perch reproduces sexually, with spawning usually occurring in the spring and early summer months. During this time, the females will lay their eggs in shallow waters, while the males fertilize them. The eggs are then left to hatch, and the fry will feed off their yolk sacs until they are ready to venture into the open waters.
Migration and Behavior
Unlike other fish species that migrate long distances, the European Perch is a non-migratory fish that prefers to stay in its native waters. However, during the breeding season, they may travel to shallow waters to spawn. This behavior also extends to their overall territorial nature, with each fish establishing its own hunting ground and defending it from intruding perch.In terms of behavior, the European Perch is a highly adaptable and intelligent fish. They are known to be territorial and aggressive, fiercely defending their hunting areas, and can even learn to associate certain sounds and movements with food sources. These qualities make them a favorite target for anglers, as they offer a challenging yet rewarding catch.
Conservation Status
The European Perch is not currently listed as an endangered or threatened species, but its populations have shown some decline in recent years. This decline is mainly due to habitat degradation, pollution, and overfishing. However, various conservation efforts, such as regulating fishing quotas and improving water quality, have been put in place to help protect this species and ensure its survival.In Conclusion
The European Perch is a captivating and remarkable freshwater fish species that inhabits the waters of Europe. Its adaptability, feeding habits, and aggressive nature make it a top predator in its habitat. With its unique physical features and behavior, this species is a joy to discover and observe in the wild. If you ever have the chance to encounter this ambush predator, be sure to admire its beauty but also remember to handle it with care and release it back into the water after a successful catch. Let's do our part in preserving and protecting this magnificent fish species for generations to come.
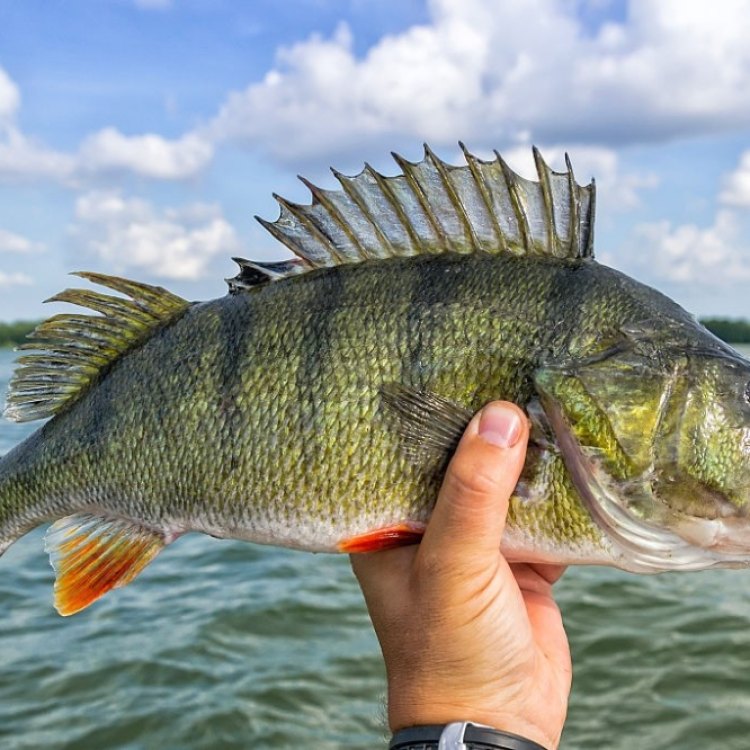

European Perch
Fish Details European Perch - Scientific Name: Perca fluviatilis
- Category: Fish E
- Scientific Name: Perca fluviatilis
- Common Name: European Perch
- Habitat: Freshwater lakes, rivers, and ponds
- Feeding Habitat: Benthic and pelagic zones
- Feeding Method: Ambush predator
- Geographic Distribution: Europe
- Country Of Origin: Most of Europe
- Color: Greenish-yellow with dark vertical bars
- Body Shape: Oval-shaped and laterally compressed
- Length: Up to 50 cm
- Adult Size: 20-30 cm
- Age: Up to 20 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproduction Behavior: Spawning in shallow waters
- Migration Pattern: Non-migratory

European Perch
- Social Group: Solitary or in small groups
- Behavior: Territorial and aggressive
- Diet: Insects, small fish, and crustaceans
- Predators: Pike, pikeperch, and larger fish
- Prey: Small fish, crustaceans, and invertebrates
- Environmental Threats: Habitat degradation and pollution
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Special Features: Prominent spines on dorsal and anal fins
- Interesting Facts: European Perch is a popular sport fish in Europe
- Reproduction Period: Spring
- Nesting Habit: Nest in shallow water among vegetation
- Lifespan: 10-20 years
- Habitat Threats: Pollution and the introduction of non-native species
- Population Trends: Stable
- Habitats Affected: Freshwater lakes, rivers, and ponds
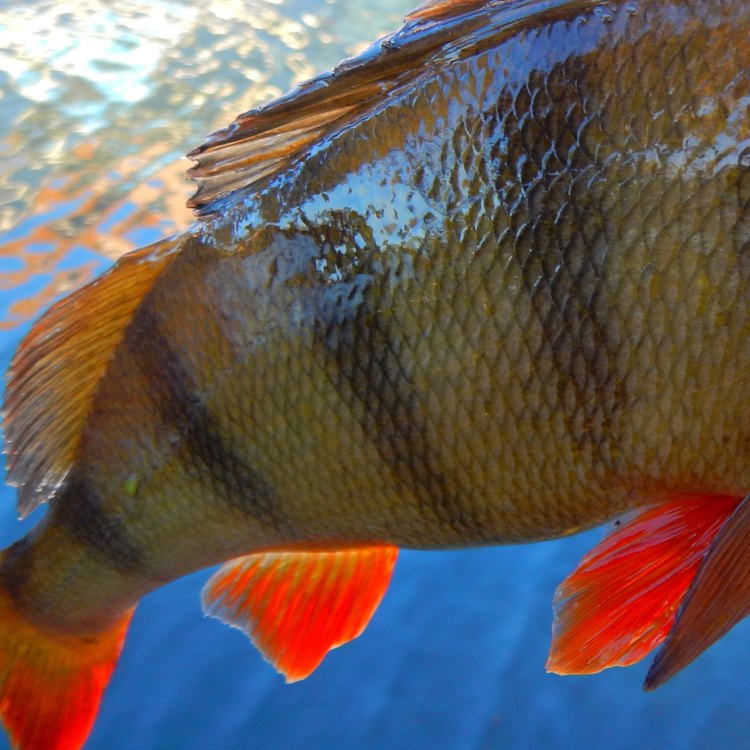

Perca fluviatilis
The Story of the European Perch: A Fascinating Fish in European Waters
The world is full of remarkable creatures, hidden beneath the depths of our oceans and lakes. But one fish, in particular, stands out for its unique characteristics and intriguing behavior. The European Perch, scientifically known as Perca Fluviatilis, is a freshwater fish that can be found in lakes, rivers, and ponds throughout Europe. It may not be as famous as some of its larger and more exotic cousins, but the European Perch has its own set of fascinating features that make it a true gem of European waters RadioDouRosul.com.From its solitary and territorial behavior to its diverse diet, and from its impressive spines to its interesting reproductive habits, the European Perch has captured the attention of fish enthusiasts and researchers alike. In this article, we will dive deep into the world of the European Perch and discover the unique features of this captivating fish.
A Solitary Creature with a Territorial Nature
One of the interesting aspects of the European Perch is its social behavior. Unlike other fish that prefer to swim in large schools, European Perches are solitary creatures that usually live alone or in small groups. They are known to be highly territorial and will defend their space from other fish, especially during their spawning season.As territorial fish, European Perches have been observed to exhibit aggressive behavior towards other fish that enter their territory. This is especially true for male Perches during the breeding season when they become fiercely protective of their nest and young.
A Diverse Diet of Insects, Small Fish, and Crustaceans
The European Perch is an opportunistic predator, meaning it has a varied diet and will feed on whatever is available in its habitat. Its diet mainly consists of insects, small fish, and crustaceans, making it a vital part of the food chain in freshwater ecosystems European Flounder.Being a predator fish, the European Perch uses its excellent vision and sharp teeth to hunt for food. It is known to ambush its prey, using its camouflage to blend into its surroundings. This makes it a formidable hunter and an essential part of the ecosystem.
A Not So Peaceful Existence: Predators and Prey
In the intricate balance of nature, every creature has its predators and prey, and the European Perch is no exception. Its main predators include larger fish, such as pike and pikeperch, as well as birds and mammals. The spines on its dorsal and anal fins act as a form of defense against these predators, making it difficult for them to swallow the European Perch whole.On the other hand, the European Perch also serves as prey for larger fish and birds, creating a constant cycle of predator-prey relationships in the ecosystem.
A Prickly Appearance: Prominent Spines on Dorsal and Anal Fins
One of the unique physical features of the European Perch is its prominent spines on its dorsal and anal fins. These spines serve multiple purposes, including protection against predators, and during courtship displays. The spines release a powerful toxin when threatened, making them a useful defense mechanism for the Perch.Interestingly, the number of spines on the European Perch's fins varies depending on its habitat, with those living in rivers and ponds having fewer spines compared to those in larger lakes.
A Favorite Sport Fish in Europe
Apart from its intriguing behavior and physical features, the European Perch is also a popular sport fish in Europe. Its aggressive nature and strong fighting ability make it an exciting catch for anglers. In fact, the Perch is one of the most sought-after sport fish in Europe, with many fishing competitions held in its honor.Additionally, the European Perch is also a prized food fish, often sold in fish markets or served in high-end restaurants across Europe. Its tasty and nutritious flesh makes it a favorite among seafood lovers.
Spring is the Season of Love: Reproduction and Nesting Habits
The breeding season for the European Perch begins in the spring, when the water temperature reaches around 12-16°C. During this time, the males turn bright orange-red and establish territories where they build a nest made of debris and vegetation.Once the nest is ready, the males will attract female Perches by vibrating their fins and making clicking noises. The female will then lay her eggs in the nest, and the male will fertilize them. The male Perch will then guard the nest until the eggs hatch, which usually takes around 3-4 weeks.
A Long Life of 10-20 Years in the Wild
The European Perch has a decent lifespan, with some living up to 10-20 years in the wild. However, their lifespan can be significantly shortened by environmental threats, pollution, and human interference.In captivity, European Perches have been known to live for up to 25 years, which is significantly longer than their lifespan in the wild. This highlights the potential impact of human activities on the survival of this species.
Thriving in Freshwater Habitats, but Facing Threats
The European Perch is a freshwater fish, most commonly found in lakes, rivers, and ponds. It has adapted to different environments and is known to thrive in both still and flowing waters. However, like many other freshwater species, the European Perch is facing numerous threats to its habitat.One of the main threats is habitat degradation, which occurs when human activities, such as damming or dredging, alter the natural flow of water. This can disrupt the Perch's spawning and feeding grounds, resulting in a decline in their population.
Pollution is another major threat to the European Perch, as it can affect the quality of water and make it unsuitable for the fish to survive. The introduction of non-native species, such as the sunbleak, has also had a significant impact on the Perch's population, as these invasive species compete for resources and can lead to the decline of native species.
Conservation Status: Least Concern, but Still in Need of Protection
The European Perch is currently listed as "Least Concern" on the IUCN Red List, meaning that it is not facing any immediate threat of extinction. However, this does not mean that the species is not in need of protection.With the continued degradation of freshwater habitats and the threat of pollution, there is a need for conservation efforts to protect the European Perch and other freshwater species. Measures such as habitat restoration, pollution control, and the management of non-native species should be taken to ensure the continued survival of this fascinating fish.
A Steady Population: A Good Sign for the Future
Despite the ongoing threats, the European Perch population is currently stable. This is a good sign for the future of this species, but it also calls for continued efforts to maintain this stability.Research and monitoring of European Perch populations are crucial in understanding their behavior and population trends. This will help in implementing conservation measures and ensuring the long-term survival of this species.
The European Perch: An Important Part of Europe's Ecosystem
In conclusion, the European Perch is a unique and fascinating fish with its solitary nature, diverse diet, and prominent spines. Its aggressive behavior and territorial nature make it a vital part of freshwater ecosystems, where it serves as both predator and prey.While facing threats to its habitat and survival, the European Perch continues to thrive in European waters. As responsible individuals, it is our duty to protect and preserve this species and its habitat for the benefit of current and future generations. By understanding the importance of the European Perch and taking necessary conservation measures, we can ensure the continued survival of this remarkable fish.

The Captivating European Perch: An Ambush Predator of European Waters
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.