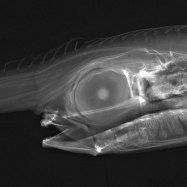
Horsefish
There is limited information on the migration patterns of horsefish.
The mysterious horsefish is a fascinating creature found in the western Atlantic Ocean. Little is known about their migration patterns and age, but they are known to reproduce by releasing eggs that develop into larvae. Keep an eye out for this elusive species on your next tropical dive! #Horsefish #Oceanlife
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: Horsefish
Habitat: They are found in warm tropical and subtropical waters, usually near the surface. They prefer sheltered areas such as coral reefs, mangroves, and seagrass beds.
Color: They have a silvery color with a black stripe along their sides and a distinctive horseshoe-shaped black mark on their body.
The Majestic Horsefish: A Unique Creature of the Atlantic Ocean
The ocean is full of fascinating creatures, and one that stands out with its distinctive appearance and behavior is the horsefish, scientifically known as Centriscus scutatus. This dynamic fish has captured the attention of many marine biologists and enthusiasts, with its striking physical attributes and interesting habits. Let's take a closer look at the horsefish and uncover what makes it such a unique and captivating species.The Habitat of Horsefish
The horsefish is commonly found in warm tropical and subtropical waters, typically near the surface Horsefish. It prefers sheltered areas such as coral reefs, mangroves, and seagrass beds, where it can find ample food and shelter. Its natural habitat is in the Atlantic Ocean, including the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea.Feeding Habits of Horsefish
One of the most intriguing aspects of the horsefish is its feeding behavior. These fish feed near the surface of the water, mainly on small fish and invertebrates. However, what sets them apart from other fish is their unique feeding mechanism. Horsefish have a long snout with a small mouth, which allows them to suck up prey items like a vacuum cleaner. This specialized feeding method gives them an advantage in capturing their prey quickly and efficiently.The Unique Physical Features of Horsefish
The horsefish has a distinctive appearance, making it easily recognizable among other fish. They have a silvery color with a black stripe along their sides and a distinctive horseshoe-shaped black mark on their body Hammerjaw. This marking is where they get their common name as the horsefish. Moreover, they have a compressed and elongated body, with a long snout and a tall, sail-like dorsal fin, which gives them a unique and striking appearance.The Power of Size: How Big Can a Horsefish Get?
When it comes to size, horsefish may not be the largest creature in the ocean, but they can grow up to 9 inches in length. While this may not seem very big, given their elongated body shape, they can appear much larger. Interestingly, adult horsefish typically range from 4 to 7 inches, making them smaller in comparison to other fish species. Unfortunately, the age of horsefish is still unknown, as there is limited information on their lifespan and growth rate.The Mysterious Reproduction of Horsefish
The process of reproduction in horsefish is still a mystery, as there is limited information available. However, it is known that they reproduce by spawning, releasing their eggs and sperm into the water. After spawning, the eggs hatch into larvae that drift in the open water before settling in suitable habitats. As they mature, they develop their unique shape and feeding habits.The Enigma of Migration Patterns
There is also limited information on the migration patterns of horsefish. It is believed that they do not travel long distances, and instead, they tend to stay within their preferred habitats. However, more research is needed to understand their migration patterns and behavior.The Horsefish: A Treasure of Tropical Waters
Horsefish are native to the tropical and subtropical waters of the western Atlantic Ocean. However, due to their unique and striking appearance, they have also become popular in the aquarium trade. As a result, they can now be found in aquariums around the world, allowing more people to appreciate their beauty and learn more about their habits.In conclusion, the horsefish is a fascinating creature of the Atlantic Ocean, with its unique physical features, specialized feeding habits, and mysterious reproductive behavior. As more research is conducted, we will uncover more information about this elusive species and gain a deeper understanding of its role in the ecosystem. For now, let us admire the beauty of the horsefish and recognize it as a true treasure of the ocean.

Horsefish
Fish Details Horsefish - Scientific Name: Centriscus scutatus
- Category: Fish H
- Scientific Name: Centriscus scutatus
- Common Name: Horsefish
- Habitat: They are found in warm tropical and subtropical waters, usually near the surface. They prefer sheltered areas such as coral reefs, mangroves, and seagrass beds.
- Feeding Habitat: They feed near the surface of the water, mainly on small fish and invertebrates.
- Feeding Method: They have a long snout with a small mouth, which allows them to suck up prey items like a vacuum cleaner.
- Geographic Distribution: They are found in the Atlantic Ocean, including the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea.
- Country Of Origin: They are native to tropical and subtropical waters of the western Atlantic Ocean.
- Color: They have a silvery color with a black stripe along their sides and a distinctive horseshoe-shaped black mark on their body.
- Body Shape: They have a compressed and elongated body, with a long snout and a tall, sail-like dorsal fin.
- Length: They can grow up to 9 inches in length.
- Adult Size: Adult horsefish typically range from 4 to 7 inches in length.
- Age: The age of horsefish is unknown.
- Reproduction: They reproduce by spawning, releasing their eggs and sperm into the water.
- Reproduction Behavior: After spawning, the eggs hatch into larvae that drift in the open water before settling in suitable habitats.
- Migration Pattern: There is limited information on the migration patterns of horsefish.

Horsefish
- Social Group: They are usually found in small groups or pairs.
- Behavior: They are relatively solitary and often hide among seagrass or mangroves, using their flattened bodies to blend in with their surroundings.
- Diet: They mainly feed on small fish and invertebrates, such as shrimp and small crabs.
- Predators: Their predators include larger fish and marine mammals.
- Prey: They prey on small fish and invertebrates, such as shrimp and small crabs.
- Environmental Threats: Horsefish face threats from overfishing, habitat loss, and pollution.
- Conservation Status: The conservation status of horsefish is not currently assessed.
- Special Features: They have a long, slender body and a unique shape, with a long snout and a tall dorsal fin that resembles a sail.
- Interesting Facts: Horsefish are masters of camouflage and can change their color to match their surroundings. They have been known to mimic dead leaves or pieces of seaweed to blend in with their environment.
- Reproduction Period: The reproduction period of horsefish is unknown.
- Nesting Habit: There is limited information on the nesting habits of horsefish.
- Lifespan: The lifespan of horsefish is unknown.
- Habitat Threats: Habitat loss and degradation, pollution, and climate change are potential threats to horsefish habitats.
- Population Trends: There is limited information on population trends of horsefish.
- Habitats Affected: Coral reefs, seagrass beds, and mangroves are the habitats that can be affected by the presence of horsefish.

Centriscus scutatus
The Fascinating World of Horsefish
The ocean is home to some of the most unique and fascinating creatures, and one such creature is the horsefish. With their long, slender bodies and striking features, horsefish are a sight to behold. In this article, we will explore the social behavior, diet, predators, and environmental threats faced by horsefish, along with some interesting facts and special features that make them stand out in the marine world.Social Group: Horsefish are usually found in small groups or pairs RadioDouRosul.com. Unlike some other marine creatures, they are relatively solitary and prefer to hide among seagrass or mangroves, using their flattened bodies to blend in with their surroundings. This social behavior allows them to avoid predators and increases their chances of survival.
Behavior: Due to their shy and solitary nature, horsefish can be elusive and challenging to spot in the wild. They are excellent at camouflage and have the unique ability to change their color to match their surroundings. This makes them masters of disguise and allows them to blend in seamlessly with their environment. They have been known to mimic dead leaves or pieces of seaweed to avoid detection from predators.
Diet: Horsefish mainly feed on small fish and invertebrates, such as shrimp and small crabs. They have a long, slender snout that helps them catch prey in hard-to-reach places. Their diet plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of marine ecosystems Houndshark. By consuming small fish and invertebrates, they help regulate their populations and prevent overpopulation of certain species.
Predators: Like many other marine creatures, horsefish also have natural predators. Larger fish and marine mammals such as dolphins and seals are known to feed on horsefish. Their unique shape and camouflage help them avoid detection from predators, but they still face threats in their natural habitats.
Prey: As mentioned earlier, horsefish feed on small fish and invertebrates. They are considered opportunistic feeders, meaning they will consume whatever is available in their surroundings. This makes them adaptable and able to survive in various environmental conditions.
Environmental Threats: Despite their unique defense mechanisms and adaptability, horsefish face threats from overfishing, habitat loss, and pollution. Overfishing can decimate their populations and disrupt the balance of marine ecosystems, while habitat loss and pollution can directly impact their survival and food sources. As for many other marine creatures, these threats put horsefish at risk of extinction.
Conservation Status: It is crucial to monitor and protect the populations of vulnerable marine creatures like horsefish. However, surprisingly, the conservation status of horsefish is not currently assessed. This highlights the need for further research and assessments to better understand the threats faced by horsefish and take steps to protect them.
Special Features: One of the most striking features of horsefish is their unique shape. They have a long, slender body and a long snout, giving them a horse-like appearance. Their dorsal fin is also tall and resembles a sail, which adds to their distinctive appearance. These features not only make them stand out in the marine world but also serve a purpose in their survival.
Interesting Facts: As mentioned earlier, horsefish are masters of camouflage. But did you know that they can also change their sex? If there is a shortage of males in an area, a female horsefish can change into a male to ensure the survival of the species. This is known as sequential hermaphroditism and is a rare and unique quality among marine creatures. Additionally, horsefish can also regenerate lost body parts, such as their fins. This ability helps them recover from injuries and increases their chances of survival.
Reproduction Period: The reproduction period of horsefish is currently unknown. Due to their elusive nature, it is challenging to study their breeding behaviors and habits. Further research is needed to understand their reproductive cycle and ensure the sustainability of their populations.
Nesting Habit: Due to limited information on the nesting habits of horsefish, it is unclear where they lay their eggs and how they care for their young. However, it is believed that they lay their eggs in seagrass beds or mangroves, as these habitats provide shelter and protection for their offspring.
Lifespan: The lifespan of horsefish is also unknown. It is difficult to determine the age of these elusive creatures, and their lifespan can vary depending on their natural habitats and environmental conditions.
Habitat Threats: Horsefish are typically found in coral reefs, seagrass beds, and mangroves, making these habitats vital to their survival. However, these habitats are under threat from various human activities such as overfishing, pollution, and climate change. The destruction and degradation of these habitats can have a devastating impact on horsefish populations and the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
Population Trends: Due to limited information on population trends, it is challenging to determine the health and status of horsefish populations. However, their solitary behavior and elusive nature make it difficult to monitor and study their numbers accurately. This highlights the need for further research and conservation efforts to understand and protect these unique creatures.
Habitats Affected: As horsefish play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems, their presence can have a direct impact on the health of their habitats. Coral reefs, seagrass beds, and mangroves can be affected by the depletion of horsefish populations, leading to an overabundance of prey species and the disruption of the natural ecosystem.
In conclusion, the horsefish is a fascinating and unique creature that can easily captivate anyone with its striking appearance and intriguing features. However, their survival is threatened by various environmental factors, making it essential to protect and conserve their populations. As humans, it is our responsibility to understand and preserve these beautiful and elusive creatures to maintain the balance and health of our marine ecosystems.

The Majestic Horsefish: A Unique Creature of the Atlantic Ocean
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.