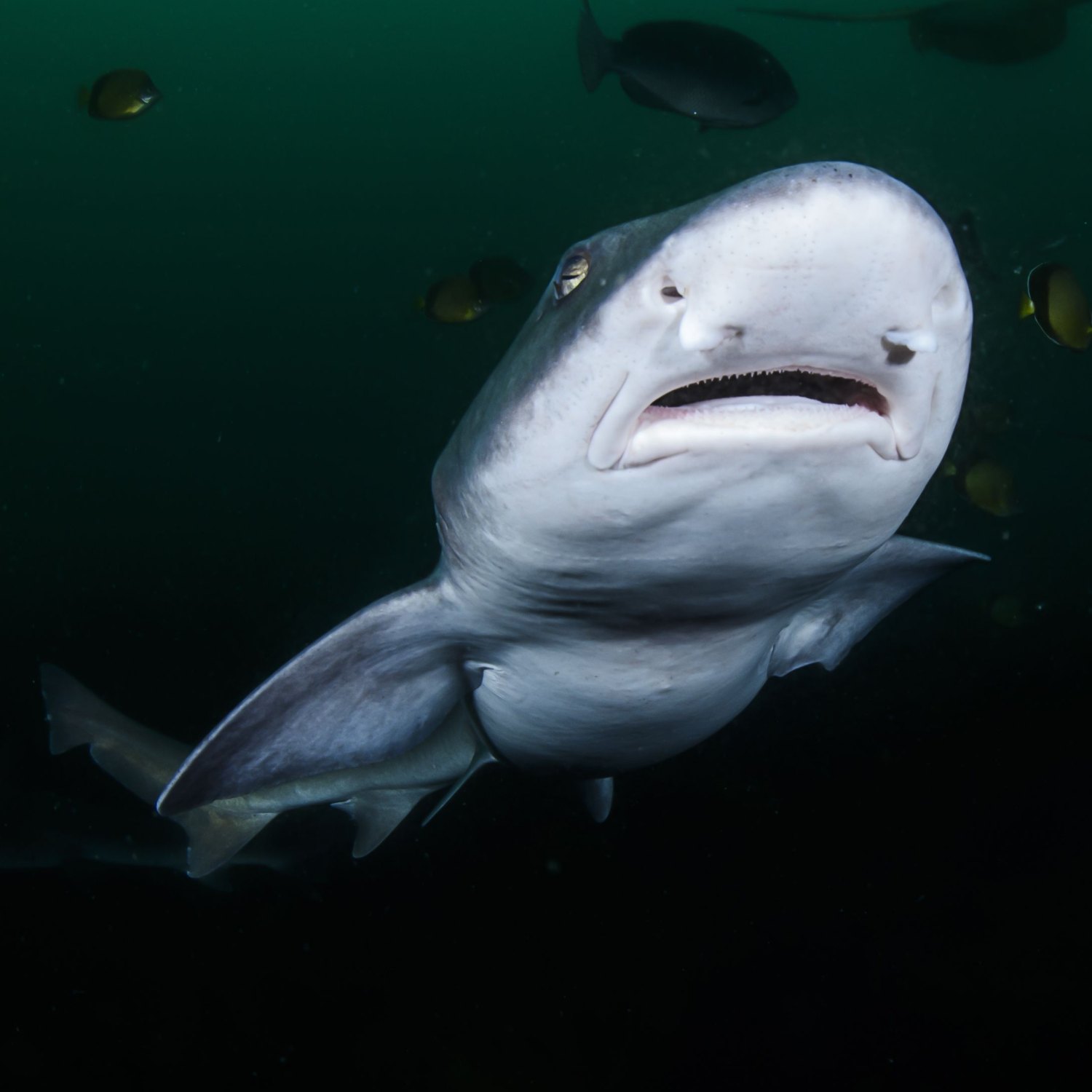
Houndshark
Houndsharks do not have a specific migration pattern and are relatively sedentary.
Houndsharks, also known as grey nurse sharks, are fascinating creatures found in the North Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea. With a lifespan of 20 to 30 years, these sedentary sharks reproduce through a unique behavior where the male bites the female's pectoral fin. Learn more about this mesmerizing fish in our article! #FishFacts #Houndsharks #OceanWonders
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: Houndshark
Habitat: Houndsharks can be found in the coastal waters of the North Atlantic Ocean, from Norway to Morocco, and the Mediterranean Sea.
Color: Houndsharks have a brownish-grey or grey color on the upper body, fading to a lighter and white color on the underside.
The Fascinating Houndshark: An Elusive Predator of the North Atlantic and Mediterranean Sea
The ocean is a vast and mysterious world, home to a diverse array of creatures. Among these creatures is the Houndshark, a fascinating and elusive predator found in the coastal waters of the North Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. With a scientific name of Triakis scyllium, this unique shark has captured the attention of scientists and ocean enthusiasts alike.Meet the Houndshark
The Houndshark, also known as the Gulf Smooth Hound or European Smooth Hound, is a species of shark in the Triakidae family Houndshark. It is easily recognizable by its slender and elongated body, with a distinct, high and wide dorsal fin. This feature gives it a hound-like appearance, hence its common name. With a length reaching up to 5 feet (1.5 meters), the Houndshark is considered a medium-sized shark.
Habitat and Geographic Distribution
The Houndshark can be found in the coastal waters of the North Atlantic Ocean, from Norway to Morocco, and in the Mediterranean Sea. It primarily inhabits sandy or rocky bottoms, near reefs or in kelp forests. These sharks are typically found in shallow waters, up to depths of 330 feet (100 meters).
Feeding Habits
The Houndshark is an opportunistic predator, meaning it will feed on a variety of prey depending on what is available. They are known to feed on a wide range of fish, including herring, mackerel, and cod, as well as crustaceans such as crabs and lobsters, and cephalopods like squid and octopus Hoki.
Reproduction and Behavior
Houndsharks are ovoviviparous, which means the embryos develop inside eggs inside the female's body. The gestation period for these sharks is approximately 9 to 10 months, with the female giving birth to around 4 to 10 pups. Interestingly, the pups are born fully developed, unlike other shark species that hatch from eggs.
During mating, the male bites the pectoral fin of the female, and copulation occurs with the male clamping onto the female's body. This behavior is believed to help the males keep their balance during the mating process.
Appearance and Coloration
Houndsharks have a distinct coloration that makes them stand out. Their upper body has a brownish-grey or grey color, while their underside fades to a lighter and white color. This coloration helps them blend in with the sandy bottom, making it easier for them to sneak up on prey.
Long Lifespan
The lifespan of Houndsharks is estimated to be around 20 to 30 years. Like many other shark species, the Houndshark has a slow growth rate and takes several years to reach maturity. This long lifespan allows them to be apex predators in their habitat and helps maintain balance in the marine ecosystem.
Threats and Conservation Status
The Houndshark is not currently listed as endangered or vulnerable by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). However, it is still facing threats that could potentially impact its population. These threats include overfishing, accidental capture in fishing gear, and habitat destruction.
With the depletion of fish stocks due to intensive fishing practices, Houndsharks are facing competition for food resources. Additionally, they are often caught as bycatch in fisheries targeting other species. This accidental capture can significantly impact the population, especially if the sharks are discarded back into the ocean instead of being released alive.
A Lesson from the Houndshark
The Houndshark may not be as well-known as other shark species, but it holds a vital role in the marine ecosystem. Its elusive nature makes it a challenging species to study, and there is still much to be learned about its behavior and biology.
But perhaps the most important lesson we can learn from the Houndshark is the need for conservation. As apex predators, they play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the marine ecosystem. It is our responsibility to protect and preserve these magnificent creatures for present and future generations to enjoy.
In Conclusion
The Houndshark may not be the most popular or well-known shark, but it is undoubtedly an intriguing and unique species. From its hound-like appearance to its elusive nature, there is no doubt that this shark has captured the curiosity and interest of many. With its important role in the marine ecosystem, it is crucial that we continue to learn about and protect the Houndshark for generations to come.
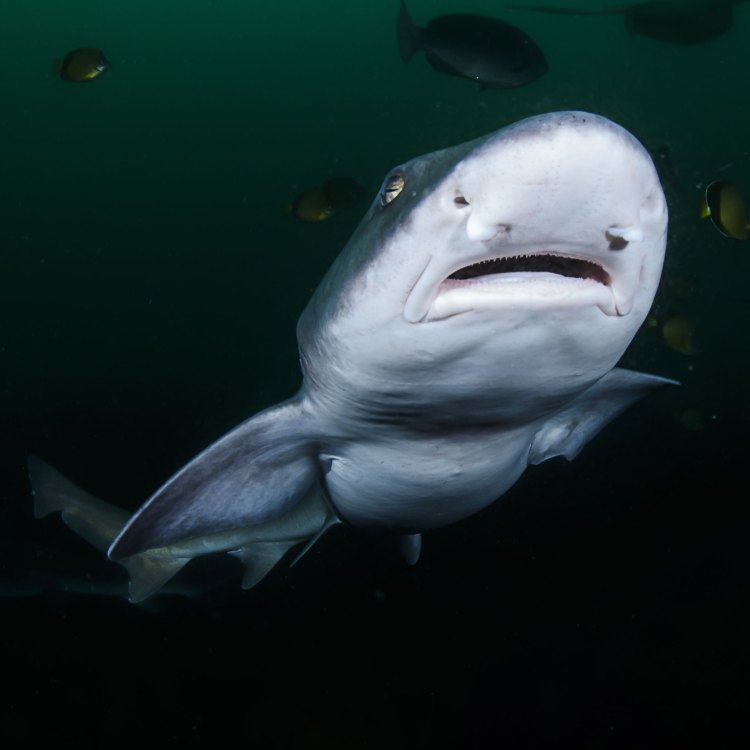

Houndshark
Fish Details Houndshark - Scientific Name: Triakis scyllium
- Category: Fish H
- Scientific Name: Triakis scyllium
- Common Name: Houndshark
- Habitat: Houndsharks can be found in the coastal waters of the North Atlantic Ocean, from Norway to Morocco, and the Mediterranean Sea.
- Feeding Habitat: They primarily inhabit sandy or rocky bottoms, near reefs or in kelp forests.
- Feeding Method: Houndsharks are opportunistic predators, feeding on a variety of fish, crustaceans, and cephalopods.
- Geographic Distribution: North Atlantic Ocean, Mediterranean Sea
- Country Of Origin: Multiple countries along the North Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea
- Color: Houndsharks have a brownish-grey or grey color on the upper body, fading to a lighter and white color on the underside.
- Body Shape: They have a slender and elongated body with a distinct, high and wide dorsal fin.
- Length: Houndsharks can reach lengths of up to 5 feet (1.5 meters).
- Adult Size: Adult Houndsharks typically measure around 3.9 to 4.9 feet (1.2 to 1.5 meters) in length.
- Age: The lifespan of Houndsharks is estimated to be around 20 to 30 years.
- Reproduction: Houndsharks are ovoviviparous, which means the embryos develop inside eggs inside the female's body.
- Reproduction Behavior: During mating, the male bites the pectoral fin of the female, and copulation occurs with the male clamping onto the female's body.
- Migration Pattern: Houndsharks do not have a specific migration pattern and are relatively sedentary.
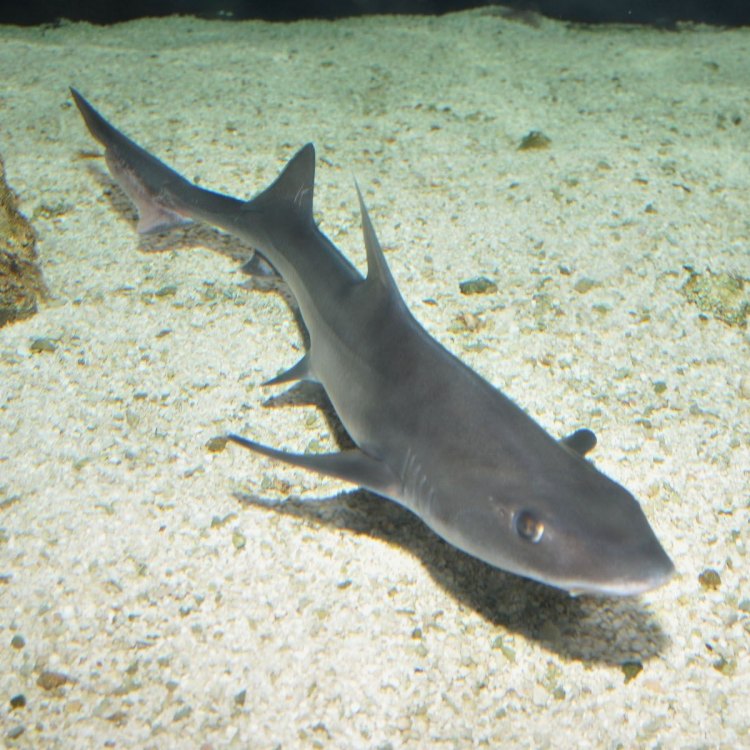

Houndshark
- Social Group: They are primarily solitary animals, although they may gather in small groups.
- Behavior: Houndsharks are generally nocturnal and more active at night.
- Diet: They are opportunistic predators, feeding on a variety of fish, crustaceans, and cephalopods.
- Predators: Larger sharks and marine mammals, such as dolphins, may prey on Houndsharks.
- Prey: They feed on small fish, crustaceans, and cephalopods.
- Environmental Threats: Overfishing is a significant threat to Houndshark populations.
- Conservation Status: The conservation status of Houndsharks is currently of least concern, although certain populations may be at risk.
- Special Features: Houndsharks have a long, slender body with large pectoral fins and a distinct, high and wide dorsal fin.
- Interesting Facts: Interestingly, the liver of Houndsharks is relatively large and contains a high concentration of oil, which aids in buoyancy.
- Reproduction Period: The mating and reproduction period for Houndsharks typically occurs during spring and early summer.
- Nesting Habit: Houndsharks do not build nests. The embryos develop inside eggs inside the female's body.
- Lifespan: The lifespan of Houndsharks is estimated to be around 20 to 30 years.
- Habitat Threats: Houndsharks are threatened by habitat destruction, pollution, and overfishing.
- Population Trends: The population trends of Houndsharks are currently stable, but certain populations may be declining.
- Habitats Affected: Houndsharks primarily inhabit sandy or rocky bottoms near reefs or in kelp forests.
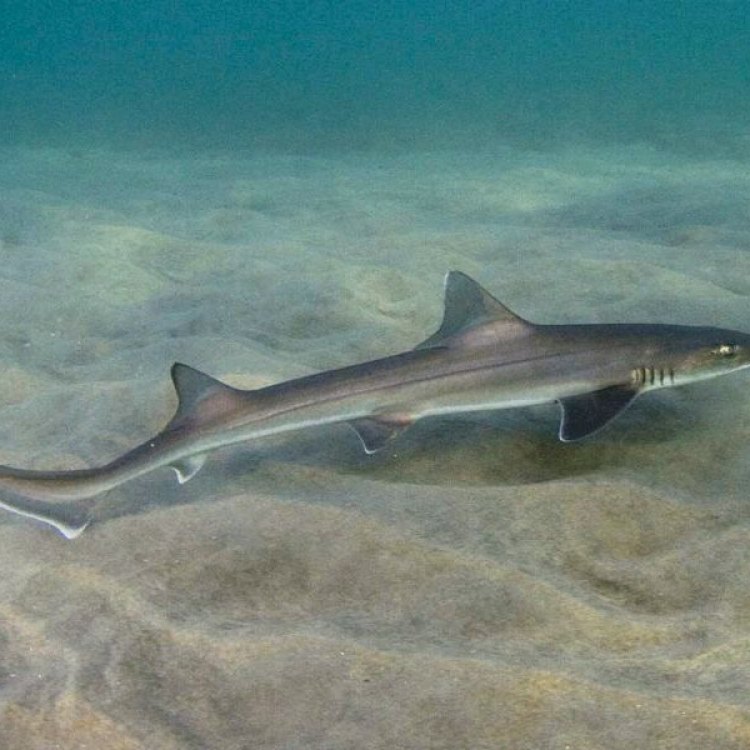

Triakis scyllium
The Fascinating World of Houndsharks: Exploring Their Unique Features and Threats
Deep in the vast and mysterious oceans, a group of animals roam that are both fascinating and elusive. These creatures are known as houndsharks, and they have captivated the minds of marine biologists and ocean enthusiasts alike with their unique features and behaviors. In this article, we will dive into the world of houndsharks, exploring their social groups, behavior, diet, predators, prey, environmental threats, conservation status, special features, interesting facts, reproduction period, nesting habits, lifespan, habitat threats, population trends, and affected habitats.The Social Group of Houndsharks
Houndsharks are primarily solitary animals, with a tendency to roam and hunt alone RadioDouRosul.com. However, they may occasionally gather in small groups, which could consist of a few individuals or up to twenty or more. These gatherings are usually temporary and often occur during breeding or in areas abundant in food sources.The Behavior of Houndsharks
Houndsharks are generally nocturnal and more active at night. During the day, they tend to rest on the ocean floor, buried in sand or hidden in crevices. At night, they become more active, using their excellent sense of smell to hunt for food. This behavior allows them to avoid larger predators and increase their chances of survival.The Diet of Houndsharks
Unlike some shark species that have a specialized diet, houndsharks are opportunistic predators, meaning they will eat whatever is available to them. They have a diverse diet that includes small fish, crustaceans, and cephalopods. Their sharp teeth and powerful jaws allow them to hunt and devour their prey efficiently Horsefish.The Predators and Prey of Houndsharks
Houndsharks are apex predators, meaning they are at the top of their food chain. However, they are not invincible, and larger sharks, as well as marine mammals such as dolphins, may prey on them. On the other hand, houndsharks themselves are an important part of their ecosystem and regulate the populations of their prey species.Environmental Threats to Houndsharks
Despite being apex predators, houndsharks are not immune to environmental threats. One of the most significant threats to their populations is overfishing. Houndsharks are often caught as bycatch in commercial fisheries, and their slow reproductive rate means that they cannot replenish their populations as quickly as they are being depleted.The Conservation Status of Houndsharks
Currently, the conservation status of houndsharks is listed as least concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This means that their populations are stable, and they are not at immediate risk of extinction. However, this status may change in certain regions or populations that face more severe threats.The Special Features of Houndsharks
Houndsharks are known for their distinct, long, and slender body shape. They have large pectoral fins that help them glide gracefully through the water and a prominent, high and wide dorsal fin that gives them their unique appearance. Another special feature of houndsharks is their liver, which is relatively large and contains a high concentration of oil, aiding in buoyancy and providing a reserve of energy.Interesting Facts about Houndsharks
Aside from their unique features, houndsharks also have some interesting facts that may surprise you. For instance, their genus name, Triakis, comes from the Greek word for three points, referring to the three prominent fins on their back. Additionally, houndsharks are known to produce a buzzing sound when threatened, hence their name "houndshark," resembling the sound of a dog's bark.The Mating and Reproduction Period of Houndsharks
The mating and reproduction period for houndsharks typically occurs during spring and early summer. During this time, females produce eggs that are fertilized by males, and the embryos develop inside the eggs inside the female's body. The gestation period can last up to a year, depending on the species, and females may give birth to anywhere from two to twenty pups.The Nesting Habit of Houndsharks
Unlike some shark species that build nests, houndsharks do not engage in this behavior. Instead, the embryos develop inside the female's body until they are ready to hatch. After giving birth, the mother offers no further care to her offspring, and the pups are left to fend for themselves.The Lifespan of Houndsharks
Studies suggest that houndsharks have a lifespan of around 20 to 30 years in the wild. However, this can vary depending on the species and environmental conditions. With the threat of overfishing and habitat destruction, this lifespan may also be shortened.Habitat Threats to Houndsharks
Houndsharks primarily inhabit sandy or rocky bottoms near reefs or in kelp forests. These habitats are vital to their survival, as they provide them with shelter and a diverse food source. However, these habitats are also threatened by human activities, such as pollution and destructive fishing practices, which can harm the delicate marine ecosystem and impact houndshark populations.The Population Trends of Houndsharks
Currently, the population trends of houndsharks are stable. However, certain populations may be declining due to various threats, as mentioned earlier. This highlights the importance of monitoring and conserving these sharks to ensure their populations remain stable and healthy.The Affected Habitats of Houndsharks
Houndsharks inhabit coastal areas and shallow waters, making them vulnerable to threats like pollution, habitat destruction, and overfishing. These threats not only impact their survival but also have a ripple effect on their habitat and the entire marine ecosystem. By protecting houndsharks, we can also help conserve their habitats and the species that rely on them.In conclusion, houndsharks are truly unique creatures with a lot to offer in terms of their biology, behavior, and importance in their ecosystem. As with many species, they face a range of environmental threats that can impact their survival and, in turn, the health of our oceans. By understanding and appreciating these fascinating animals, we can take the necessary steps to protect and conserve them for future generations to come. As ocean lovers, it is our responsibility to ensure these magnificent creatures continue to swim and thrive in the vast blue waters of our planet.
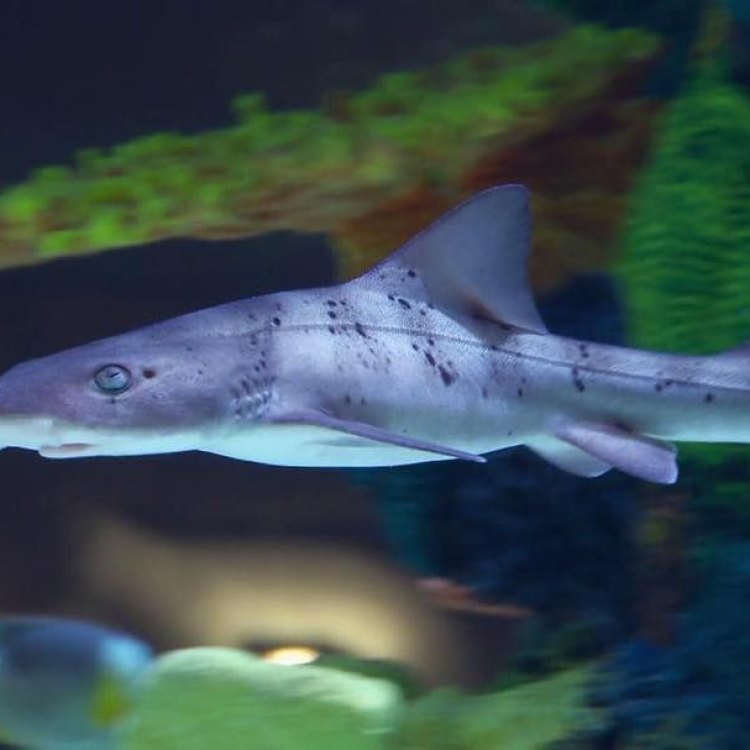

The Fascinating Houndshark: An Elusive Predator of the North Atlantic and Mediterranean Sea
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.