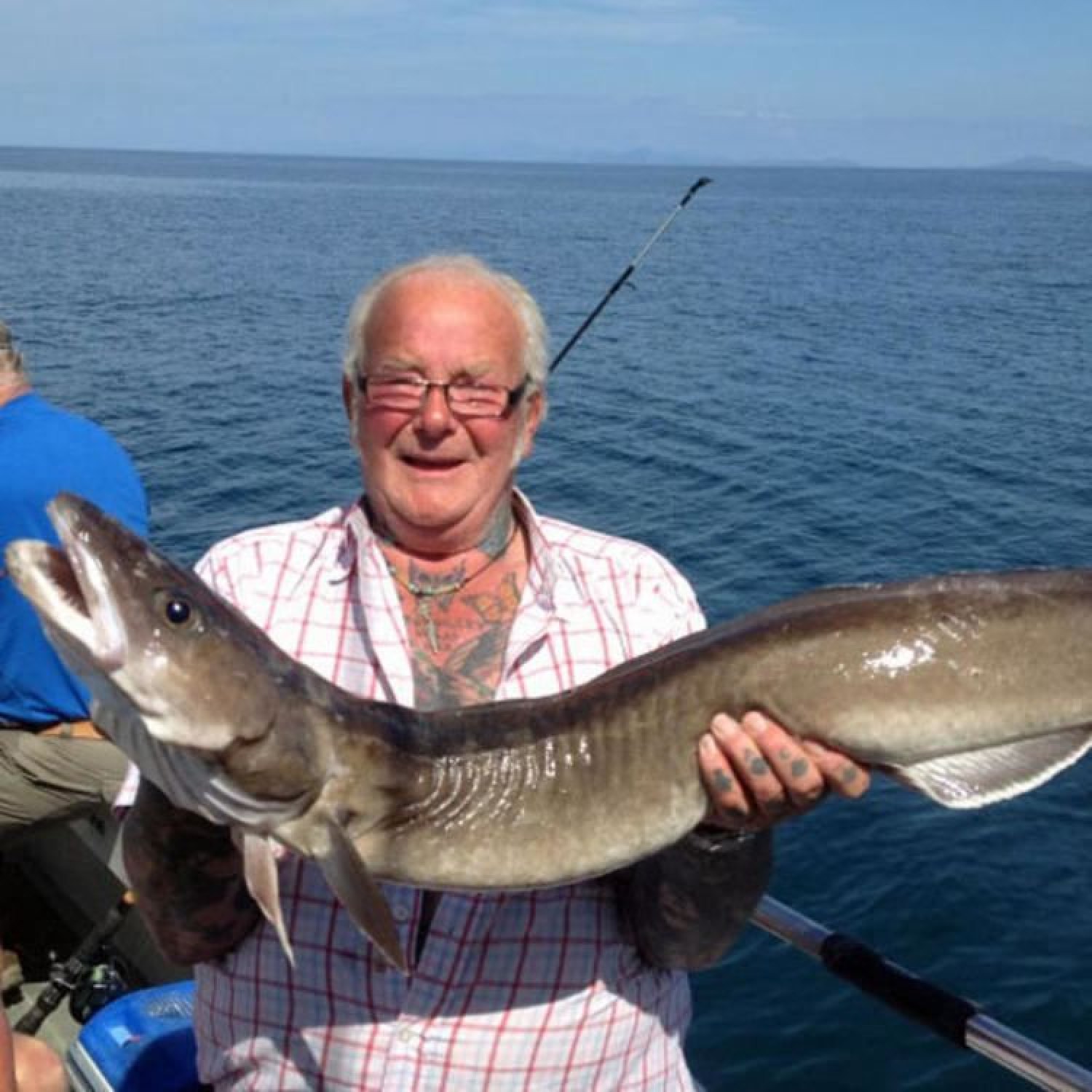
Ling
They have a diel vertical migration pattern, moving to deeper waters during the day and returning to shallower waters at night.
Discover the fascinating Ling fish- known for its diel vertical migration in Indonesia! This mighty fish can live up to 20 years and spawns in Norway. Don't miss out on learning more about its unique lifestyle! #Ling #FishFacts #Indonesia #Norway #Migration.
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: Ling
Habitat: Ling can be found in deep water habitats, especially along the continental shelf and slope.
Color: The color of Ling can vary, but they are usually brown or gray with a lighter underbelly.
The Ling Fish: A Fearless Predator of the Deep Sea
The vast and mysterious depths of the ocean hold many secrets and creatures waiting to be discovered. One such creature is the ling fish, also known as Molva molva. With its unique features and behaviors, this fish has captured the attention of researchers and fishermen alike. In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of the ling fish and uncover its outstanding features Ling.Habitat and Geographic Distribution
The ling fish is found in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean, from the coast of Norway to the Bay of Biscay. These deep-sea dwellers prefer to inhabit waters in the continental slope and shelf, which can reach depths of up to 600 meters (1968 feet). Such habitats provide them with plenty of prey and shelter from potential predators.Feeding near the seafloor, the ling fish is an ambush predator, lying in wait and pouncing on their unsuspecting prey. This unique hunting method is one of the many traits that make the ling fish stand out from other deep-sea species.
Appearance and Body Shape
The ling fish has a distinctive and elongated body with a pointed head and large mouth, perfectly adapted for its hunting abilities. They can grow to an average length of 100-130 centimeters (39-51 inches) but have been known to reach a maximum size of up to 200 centimeters (78 inches).Their color can vary, but they are usually a shade of brown or gray with a lighter underbelly, allowing them to blend in with their surroundings. This camouflage plays an essential role in their survival, as it helps them to hide from larger predators Ladyfish.
Life Span and Reproduction
The ling fish can live for up to 20 years, making them one of the longest-living deep-sea species. They reach sexual maturity at the age of four, and their reproductive behavior is fascinating. During the spawning season, which usually takes place between February and April, the ling fish migrate to their preferred spawning grounds.While little is known about their courtship rituals, it is believed that males and females engage in a courtship dance before the female releases her eggs and the males fertilize them. This process results in a massive release of eggs, with each female producing up to 2 million eggs. From these eggs, small larval ling fish will hatch and start their journey into adulthood.
Migration Pattern
The ling fish has a diel vertical migration pattern, which means they move to deeper waters during the day and return to shallower waters at night. This behavior is believed to be connected to their feeding habits, as they usually feed near the seafloor.The ling fish's migration pattern also changes depending on the season, with a more substantial vertical migration occurring in the winter when they are looking for warmer waters. This pattern helps them to adapt to changes in water temperature and find the best feeding and spawning grounds.
The Ling Fish and Humans
For centuries, the ling fish has been an essential part of human culture and livelihoods, especially in Norway, where it is known as "Lange." The Norwegians have been fishing for ling for generations, with some traditional fishing boats still in use today. The fish is not only highly prized for its culinary value, but it also has a unique place in Norwegian folklore.Apart from its cultural significance, the ling fish is also essential to the fishing industry. Due to its long lifespan, the ling fish can accumulate high levels of toxins, making it an excellent indicator for the health of the ocean. As such, it plays a crucial role in monitoring and conservation efforts.
Threats to the Ling Fish
Despite its many outstanding features, the ling fish is facing several threats that are putting its survival at risk. The high demand for this fish has led to overfishing, especially in the Northeast Atlantic, where it is the most targeted species. Furthermore, its slow reproductive rate and long lifespan make the ling fish vulnerable to changes in the ecosystem.Pollution and habitat destruction also pose a significant threat to the ling fish, with constant development and industrialization in coastal areas affecting their feeding and spawning grounds. Without proper management and conservation efforts, this fearless predator could be at risk of extinction.
Conservation Efforts
Thankfully, there are ongoing efforts to protect and preserve the ling fish and its environment. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has listed the ling fish as "Near Threatened" on the Red List of Threatened Species, raising awareness and calling for action to ensure its survival.Several measures are being taken to reduce overfishing of the ling fish, including tighter fishing regulations and the implementation of sustainable fishing practices. The Norwegian government has also designated offshore areas as protected marine zones, giving the ling fish a safe haven to thrive.
Conclusion
In the depths of the ocean, a fearless and fascinating predator roams, undisturbed by the mysteries that surround it. With its unique features, behaviors, and vital role in its ecosystem, the ling fish continues to captivate and intrigue researchers and fishermen alike.As we continue to learn more about this incredible species, it is imperative that we take action to protect and preserve its natural habitat. With proper management and conservation efforts, we can ensure that the ling fish will continue to thrive and inspire for generations to come.
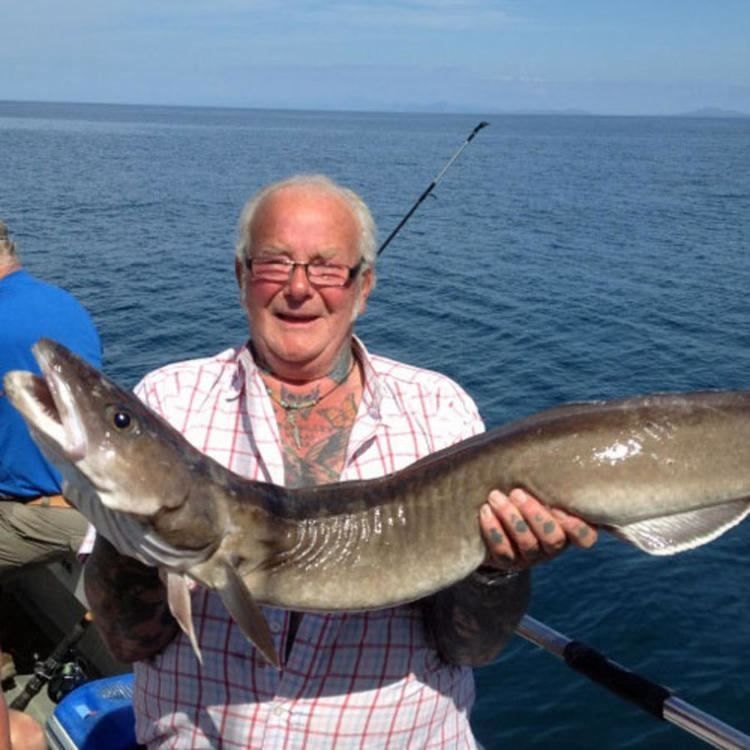

Ling
Fish Details Ling - Scientific Name: Molva molva
- Category: Fish L
- Scientific Name: Molva molva
- Common Name: Ling
- Habitat: Ling can be found in deep water habitats, especially along the continental shelf and slope.
- Feeding Habitat: Ling feeds near the seafloor.
- Feeding Method: They are ambush predators, lying in wait and pouncing on their prey.
- Geographic Distribution: They are found in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean, from the coast of Norway to the Bay of Biscay.
- Country Of Origin: Norway
- Color: The color of Ling can vary, but they are usually brown or gray with a lighter underbelly.
- Body Shape: Ling have a long, slender body with a pointed head and a large mouth.
- Length: The average length of Ling is around 100-130 cm (39-51 inches).
- Adult Size: Ling can reach a maximum size of up to 200 cm (78 inches) in length.
- Age: Ling can live for up to 20 years.
- Reproduction: Ling reproduce through sexual reproduction.
- Reproduction Behavior: During the spawning season, Ling migrate to their spawning grounds.
- Migration Pattern: They have a diel vertical migration pattern, moving to deeper waters during the day and returning to shallower waters at night.

Ling
- Social Group: Ling are solitary fish and do not form social groups.
- Behavior: Ling are known to be voracious predators and will eat a variety of prey items.
- Diet: Their diet consists mainly of fish, but they also feed on squid and crustaceans.
- Predators: Adult Ling have few natural predators, but they may be preyed upon by larger fish, sharks, and marine mammals.
- Prey: Ling prey on smaller fish, such as haddock, whiting, and sand eels.
- Environmental Threats: Overfishing is a major threat to Ling populations.
- Conservation Status: The conservation status of Ling is currently listed as Least Concern.
- Special Features: Ling have a long, tapering body and a large, toothed mouth.
- Interesting Facts: Ling is highly valued as a food fish and is often exported to other countries.
- Reproduction Period: Ling spawn during the winter months, usually from January to April.
- Nesting Habit: Ling do not build nests, as they release their eggs into the water column.
- Lifespan: Ling can live for up to 20 years.
- Habitat Threats: Habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change are potential threats to Ling habitat.
- Population Trends: Ling populations have declined in some areas due to overfishing.
- Habitats Affected: Ling are primarily found in deep water habitats, so their populations are affected by changes in these habitats.

Molva molva
Ling Fish: A Voracious Predator of the Deep Sea
When we think of marine life, we often imagine schools of colorful fish swimming together in a social group. However, there is a type of fish that prefers to live a solitary life, hunting and surviving on its own - the Ling fish. Despite its independent nature, the Ling is a fascinating species that has many unique features and interesting behaviors. In this article, we will explore the life of the solitary Ling fish and shed light on some lesser-known facts about this ocean dweller RadioDouRosul.com.The Ling fish, also known as "Molanus molanotus," is a member of the Cusk family, found in the North Atlantic Ocean, from Norway to the Mediterranean Sea and up to the coast of South Africa. It is a relatively large fish, reaching up to 4 feet in length and weighing up to 40 pounds. Its body is long and slender, tapering towards the tail, which gives it a distinct appearance. However, the most striking feature of the Ling fish is its large, toothed mouth, perfect for capturing and devouring its prey.
While most fish form social groups for survival and reproduction, the Ling stands out as a solitary species. It prefers to live alone, roaming the deep sea in search of food. This behavior may also be due to the fact that the Ling is an aggressive predator, known for its voracious appetite. It will feed on a wide variety of prey, including fish, squid, and crustaceans. Its strong jaw and sharp teeth make it difficult for prey to escape from its grip, making the Ling a top predator in its habitat Longnose Sucker.
Speaking of habitat, the Ling is primarily found in deep waters, usually at depths of 200 to 1,000 meters. However, they can also be found in shallower waters, close to cliffs and rocky bottoms. This fish is highly adaptable and can thrive in a range of conditions, from cold and temperate waters to warmer, tropical regions.
Like many other fish, Ling also has its predators. Adult Ling are not as vulnerable, but larger fish, sharks, and marine mammals may occasionally prey on them. However, the greatest threat to Ling populations is not from predators but from human activities, specifically overfishing. The Ling is a highly valued food fish and is often exported to other countries, making it a lucrative target for fishing industries. As a result, Ling populations have significantly declined, raising concerns about its conservation status.
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) currently lists the Ling as a species of Least Concern. This means that while its populations have been affected by overfishing, they are not at a critical level. However, this does not mean we should overlook the potential threat to the Ling. It is important to monitor and regulate fishing activities to maintain healthy populations of this vital species in the ocean's delicate ecosystem.
One of the reasons for the Ling's high commercial value is its delicious taste. Its flesh is firm, flaky, and mild in flavor, making it a popular choice for seafood lovers. Its meat is also rich in omega-3 fatty acids, making it a nutritious option as well. In fact, Ling has been a popular food fish for centuries, with records dating back to the 16th century showing its significance in European markets.
As a species, the Ling also has some fascinating behaviors when it comes to reproduction. They typically spawn during the winter months, from January to April, with peaks in February and March. During this time, male and female Lings release their eggs and sperm into the water column, where the eggs are fertilized. While other fish may build nests or provide some form of care for their eggs, Ling do not exhibit any such behavior. Once the eggs hatch, the young Lings are left to fend for themselves.
Despite its solitary and independent nature, Ling can live for up to 20 years in the wild, making it a relatively long-lived fish. However, its lifespan may be threatened by habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change. As a deep-water species, any changes in its habitat can have a significant impact on Ling populations. This further emphasizes the importance of conservation efforts to ensure the sustainability of this species.
In conclusion, the Ling fish is a unique, solitary predator of the deep sea. Its physical features, interesting behaviors, and valuable commercial use make it an important species in the ocean. However, its populations face significant threats from human activities, specifically overfishing, which must be properly managed to prevent a decline in its population. As we continue to explore and exploit the ocean's resources, it is important to remember the delicate balance of its ecosystem and work towards its preservation.

The Ling Fish: A Fearless Predator of the Deep Sea
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.