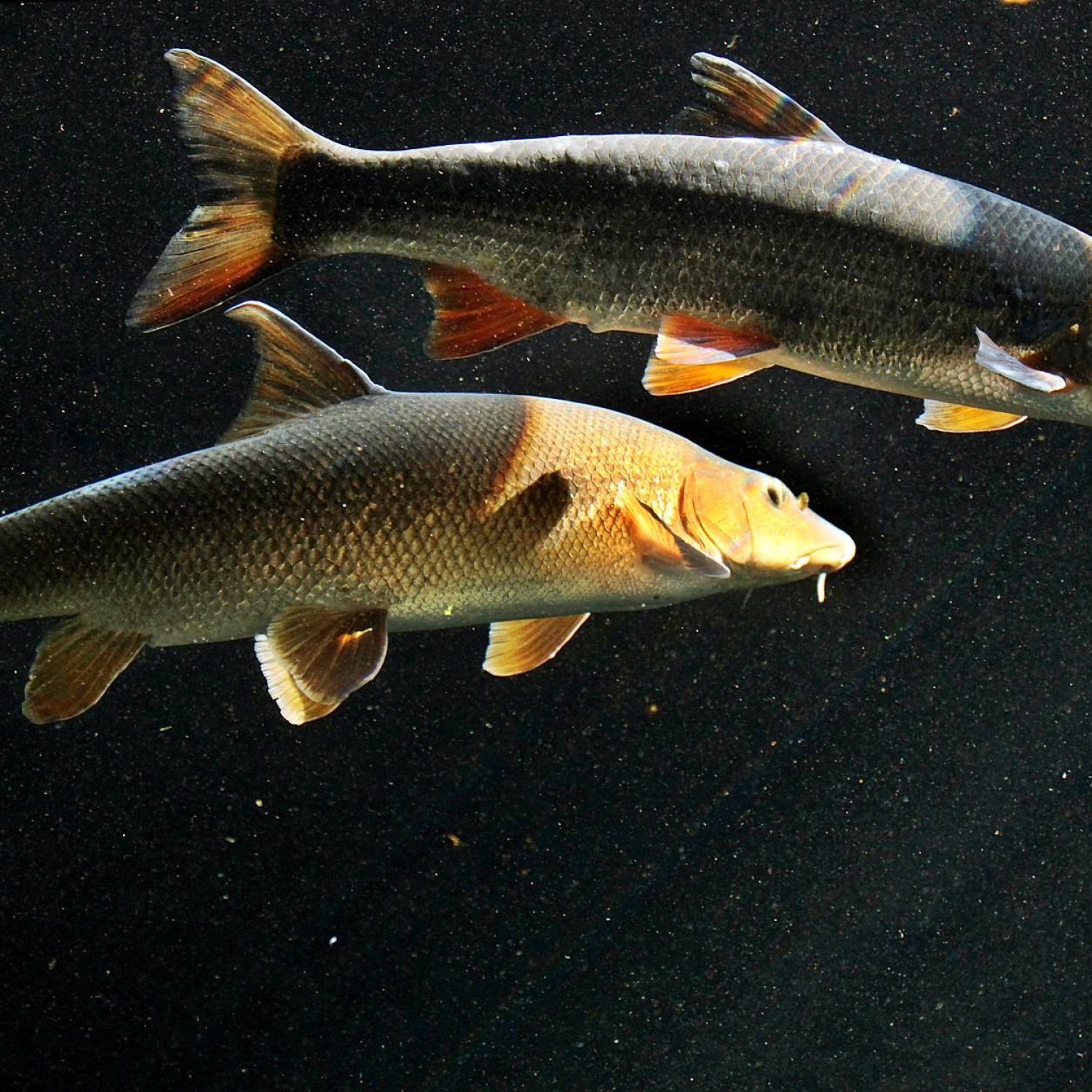
Nase
No specific migration pattern
The Nase fish, found in various European countries, can live up to 10-15 years. With no set migration pattern, these fish reproduce through spawning. A popular and peaceful addition to any aquarium, this species is known for its distinctive snout. #Nasefish #Europeanfish #spawningfish #aquariumfish
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: Nase
Habitat: Rivers and streams
Color: Grayish-brown
The Mysterious Nase: A Unique and Fascinating Fish Found in the Waters of Europe
When it comes to the world of fish, there are many fascinating and diverse species that call the waters their home. Some may be brightly colored, others may have unique body shapes, but there is one fish that stands out for its mysterious aura - the Nase.Scientifically known as Chondrostoma nasus, the Nase is a fish that can be found in the rivers and streams of Europe. It may not be the most well-known or popular fish, but it is definitely one that captures the interest of fish enthusiasts and researchers alike Nase. In this article, we will dive deep into the world of the Nase and uncover its unique features, behavior, and more.
The Habitat and Distribution of the Nase
The Nase is primarily found in the rivers and streams of Europe, making it a freshwater fish. It is a hardy species that can adapt well to different types of water bodies, as long as they have a strong current. This is why they are commonly found in fast-flowing rivers and streams with gravel or rocky bottoms.As for its geographic distribution, the Nase can be found in multiple European countries, including Germany, Austria, Switzerland, France, and Italy. They are most commonly found in the Danube, Elbe, and Rhine rivers, but they can also be found in smaller rivers and streams throughout Europe.
The Appearance of the Nase
The Nase may not be the most colorful fish, but its body shape is what makes it stand out. It has a slender and elongated body, similar to that of a carp or trout. Its color can vary between individuals, but it is commonly described as a grayish-brown color with a silvery sheen North American Darter.The Nase can grow up to 70 cm in length, with an average adult size also reaching up to 70 cm. Its size and appearance make it a formidable predator in the waters it inhabits.
Feeding Habits and Reproduction
The Nase is a bottom feeder, which means it mainly feeds on aquatic plants and small invertebrates found on the river or streambed. Its herbivorous diet also includes algae, which it grazes on using its specialized feeding apparatus known as pharyngeal teeth.When it comes to reproduction, the Nase follows a sexual mode of reproduction. The females lay their eggs on gravel beds, and the males fertilize them externally. This process is known as spawning, and it usually takes place during the spring and summer months. After the eggs are fertilized, they hatch within a few weeks, and the young Nase begin their lives in the safety of the riverbed.
Migration and Behavior
Unlike other fish species that have specific migration patterns, the Nase does not follow a particular route. It is known as a resident fish, which means it stays in the same area throughout its life. However, during the spawning season, they may travel upstream to find suitable spawning grounds.As for its behavior, the Nase is known to be a shy and elusive fish. They are mostly active during the day and hide under rocks or crevices to protect themselves from predators. They are also a very social species and can often be found in shoals, especially during feeding times.
The Mystique of the Nase
The Nase may not be the flashiest or most glamorous fish out there, but its mysterious aura and unique features make it a highly sought after species by fish enthusiasts and researchers alike. In addition, its long lifespan of 10-15 years adds to its mystique, as there is still much to learn about this elusive species.One of the most intriguing aspects of the Nase is its specialized feeding apparatus, which allows it to feed on a variety of plant and animal matter. This adaptation makes it a vital species in maintaining the balance of its freshwater ecosystem, as it helps control the growth of aquatic plants and small invertebrates.
The Nase has also played a role in the cultural and spiritual practices of the countries where it is found. In German mythology, this fish is believed to have healing powers, and it has been used in traditional medicine for centuries.
Conservation Efforts for the Nase
Like many other fish species, the Nase is facing threats from habitat destruction, pollution, and overfishing. In several European countries, there are efforts to protect and restore the populations of this fish, as it is a vital component of the freshwater ecosystem.Some of the conservation measures include establishing protected areas, implementing fishing quotas, and reducing pollution in rivers and streams. These efforts have shown some positive results, with the Nase populations slowly increasing in certain areas.
In Conclusion
The Nase may not be as well-known as other popular fish species, but it is undoubtedly a unique and fascinating fish with many interesting features. From its mysterious appearance to its specialized feeding habits and long lifespan, this fish continues to captivate the minds of researchers and enthusiasts.Through conservation efforts and continued research and study, we hope to unravel more of the mysteries surrounding this elusive fish and work towards preserving its populations for generations to come. So next time you take a stroll by a river or stream in Europe, keep an eye out for the Nase and appreciate its beauty and contribution to the freshwater ecosystem.
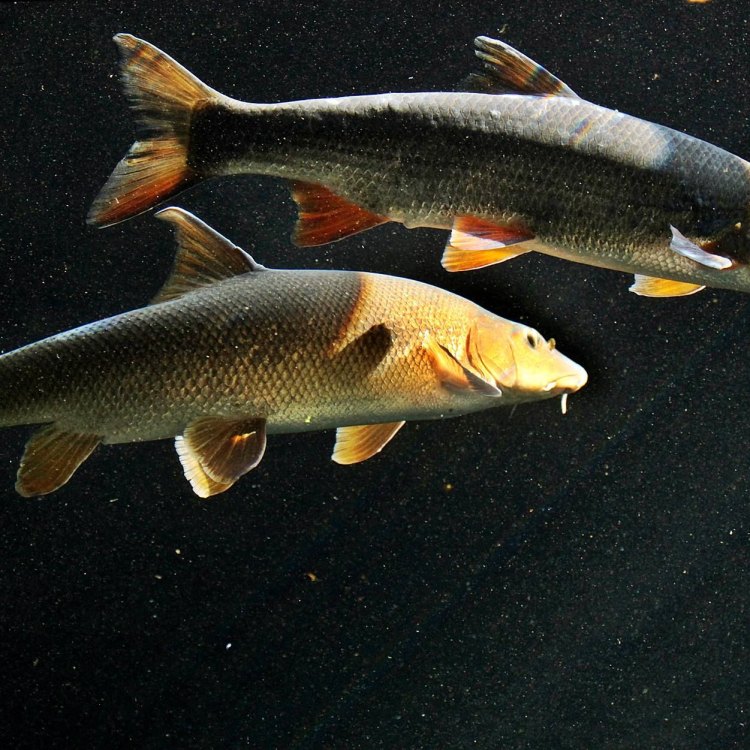

Nase
Fish Details Nase - Scientific Name: Chondrostoma nasus
- Category: Fish N
- Scientific Name: Chondrostoma nasus
- Common Name: Nase
- Habitat: Rivers and streams
- Feeding Habitat: Bottom feeder
- Feeding Method: Herbivorous
- Geographic Distribution: Europe
- Country Of Origin: Multiple European countries
- Color: Grayish-brown
- Body Shape: Slender and elongated
- Length: Up to 70 cm
- Adult Size: Up to 70 cm
- Age: 10-15 years
- Reproduction: Sexual
- Reproduction Behavior: Spawning
- Migration Pattern: No specific migration pattern
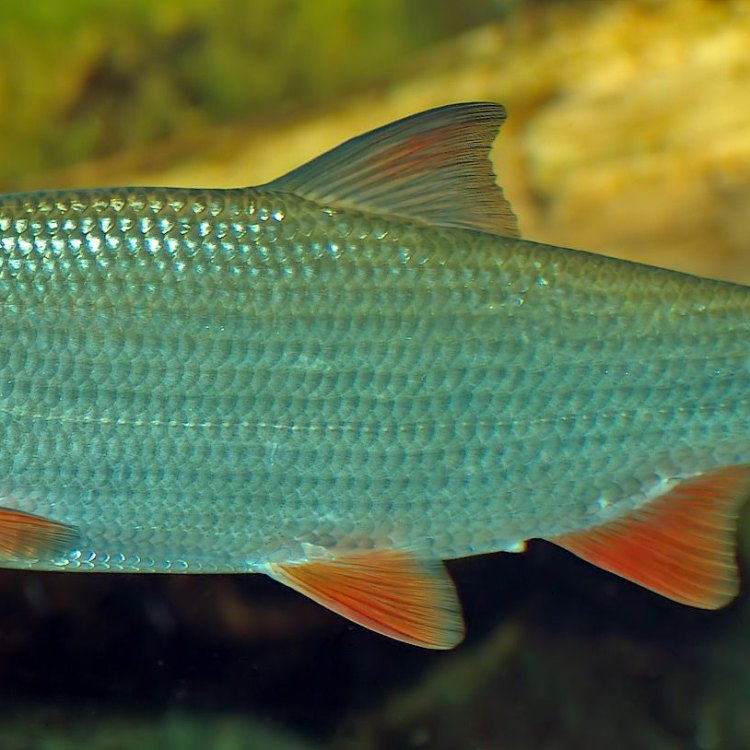

Nase
- Social Group: Schools
- Behavior: Solitary or in small groups
- Diet: Mainly algae and aquatic plants
- Predators: Birds, large fish
- Prey: Algae, aquatic plants
- Environmental Threats: Loss of habitat, pollution
- Conservation Status: Least Concern
- Special Features: Prominent snout, small mouth
- Interesting Facts: The nase is known for its ability to jump out of the water
- Reproduction Period: Spring
- Nesting Habit: Gravel or rocky substrate
- Lifespan: Up to 15 years
- Habitat Threats: Dams, pollution, habitat degradation
- Population Trends: Stable
- Habitats Affected: Rivers and streams
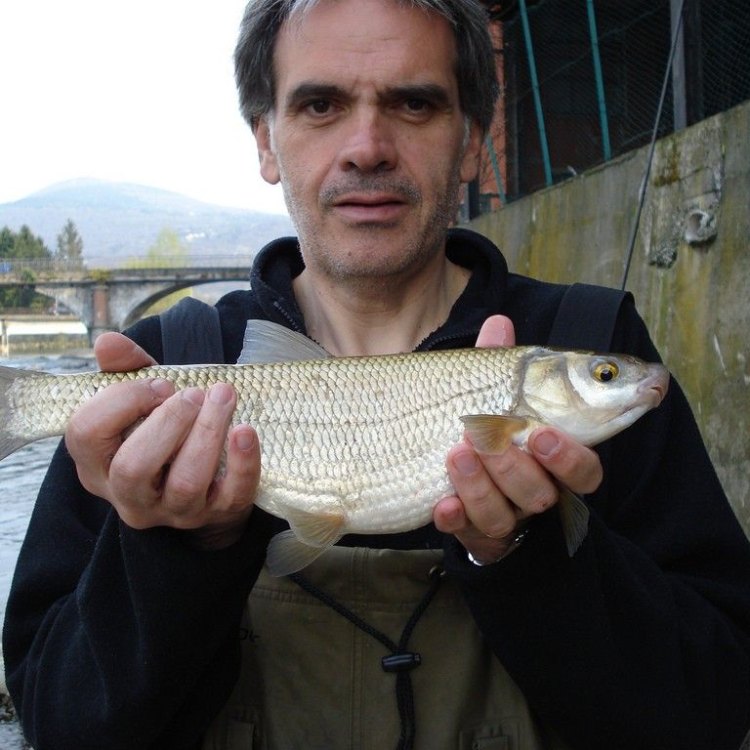

Chondrostoma nasus
The Unique Features of Nase: The Solitary Social Group Fish of Schools
In the world of fish, there are countless species that inhabit various bodies of water. Some are known for their bright colors, while others are admired for their swift swimming abilities. But one fish that stands out for its unique features is the nase, also known as Chondrostoma nasus.Found in the rivers and streams of Europe, the nase is a member of the carp family RadioDouRosul.com. While it may not have the same flashy appearance as some of its relatives, it has its own special qualities that make it an interesting and important species in its habitat.
Let’s dive deeper into the world of nase and explore its solitary social group behavior, diet, predators, environmental threats, and more.
Solitary or in Small Groups
One of the most fascinating aspects of nase is its social behavior. Unlike many fish species, nase are known to be solitary or in small groups. This means that they are not typically found in large schools like other fish. Instead, they prefer to live and feed independently or with a few other individuals.This unique behavior could be attributed to the nase’s natural habitat. They are native to fast-flowing rivers and streams, and in these environments, it is more advantageous for them to be solitary or in small groups. They can navigate the currents more easily and have better access to food sources Northern Pike.
Mainly Algae and Aquatic Plants
When it comes to diet, nase are primarily herbivores. They mainly feed on algae and aquatic plants found in their habitat. Their small mouth and prominent snout are adapted to suck and scrape food off rocks and other surfaces, making them perfectly suited for their diet.Interestingly, nase have specialized pharyngeal teeth that allow them to crush and digest hard plant materials. This is an important adaptation that allows them to digest their main source of food effectively.
Predators and Prey
Like any other species, nase are not without their predators. Large birds and fish, such as pike and catfish, are known to prey on them. However, their solitary behavior and the sharp spines on their dorsal and pectoral fins help protect them from being an easy target.On the other hand, nase are also known to consume their predators’ prey. This is because they feed on algae and plants, which are often found on the surface of larger fish. This unique behavior is an example of the interconnectedness of ecosystems and how each species plays a role in maintaining balance.
Environmental Threats
Unfortunately, like many other species, nase face environmental threats that endanger their survival. Loss of habitat, pollution, and overfishing are some of the main threats to this species.Dams and other water regulation structures disrupt the natural flow of rivers and streams, which can have a negative impact on the nase’s ability to thrive in its habitat. Pollution, such as agricultural runoff, can also be harmful to nase as it can affect the quality of their food and water.
Conservation Status
Despite these threats, the nase is currently listed as “Least Concern” by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This is due to the fact that they have a wide distribution, and their population trends are stable.But that doesn’t mean we should ignore the threats that they face. It is important to take steps to protect their habitat and educate others about the importance of this unique species.
Reproduction, Nesting Habits, and Lifespan
The nase reproductive period takes place in the spring, usually between March and May. During this time, the males will develop bright red coloration on their fins to attract females. Once they have bred, the females will lay their eggs in gravel or rocky substrates.The eggs will hatch within a few days, and the fry will then attach themselves to the substrate with a sticky adhesive. They will remain in this stage for about two weeks before becoming free-swimming. The young nase will reach sexual maturity at around two to three years, and they can live up to 15 years in the wild.
Habitat Threats and Population Trends
As mentioned earlier, nase face various habitat threats that could potentially harm their population. Dams, pollution, and habitat degradation are among the main concerns.But thanks to conservation efforts, the population trends of nase are currently stable. However, continued monitoring and conservation efforts are crucial to ensure that their population remains at a healthy level.
In Conclusion
Overall, the nase is a unique and fascinating fish with a variety of interesting features. From its solitary social behavior to its ability to jump out of the water, it is clear that this species is an important part of its natural habitat.It is up to us to protect and preserve this species for generations to come. By understanding and appreciating its unique features, we can work towards creating a safer environment for the nase and other species like it. After all, every species plays a role in maintaining the delicate balance of our ecosystems, and the nase is no exception.

The Mysterious Nase: A Unique and Fascinating Fish Found in the Waters of Europe
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.