Northern Pike
Northern pike do not have a significant migration pattern.
Discover the fascinating world of Northern Pike, a species of Fish N found in North America, Europe, and Asia. Did you know they can live up to 25 years and lay between 5,000-30,000 eggs during spawning? Learn more about their unique nesting and reproduction behavior. #NorthernPike #FishN #Wildlife #FishingFacts
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: Northern Pike
Habitat: Northern pike inhabit lakes, ponds, rivers, and other freshwater bodies.
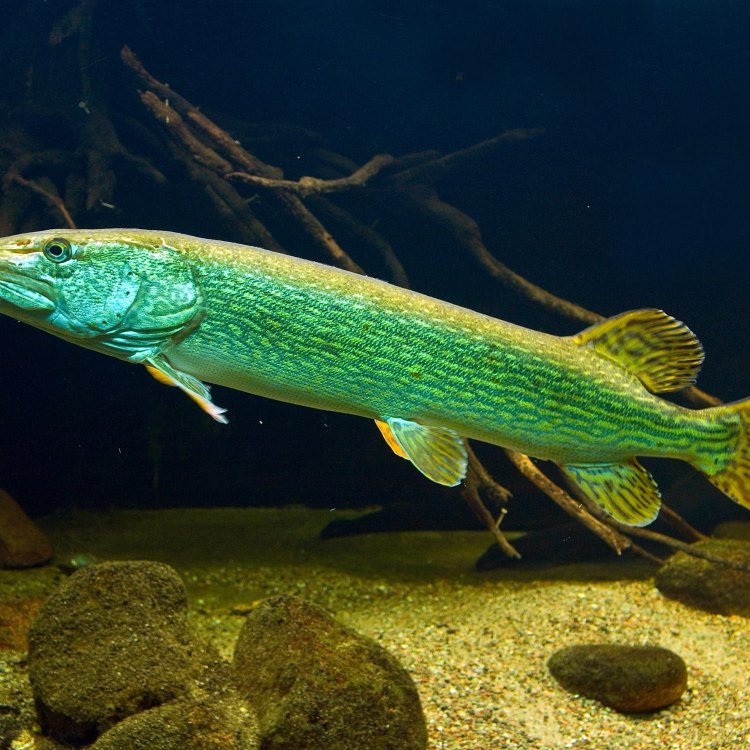
Color: They have a dark greenish-brown color on their back, lighter sides with rows of light-colored oval spots, and a white or yellow belly.
The Notorious Northern Pike: The Ultimate Freshwater Predator
The Northern Pike, scientifically known as Esox lucius, is a fierce and fascinating fish that inhabits the northern parts of North America, Europe, and Asia. With its unique features, exceptional hunting skills, and widespread distribution, the Northern Pike has become a popular subject among fishermen, biologists, and nature enthusiasts alike.But what exactly makes the Northern Pike stand out? And why has it earned its reputation as the ultimate freshwater predator? Let's discover the outstanding features of this species and delve into the world of this notorious fish.
The Habits and Habitat of the Northern Pike
The Northern Pike is a cold-water fish that inhabits lakes, ponds, rivers, and other freshwater bodies Northern Pike. They prefer areas with vegetation or structures where they can hide and ambush their prey. Due to their preference for cold water, they are often found in the cooler northern regions of North America, Europe, and Asia.Northern Pike are also known to be solitary creatures. They prefer to hunt alone and only come together during the spawning season. They are territorial and tend to stay in one area unless they need to move due to changes in water temperature or food availability.
Fierce Feeders: The Feeding Habits of the Northern Pike
One of the most intriguing traits of the Northern Pike is their feeding behavior. These fish are ambush predators, meaning they lie in wait for their prey and then strike with incredible speed and strength. They primarily feed on other fish, but they also have a diverse diet that includes amphibians, crustaceans, and small mammals.With their sharp teeth and streamlined body, the Northern Pike is built for hunting Northern Clingfish. They can reach impressive speeds of up to 10 mph in short bursts, making them one of the fastest predators in the freshwater ecosystem. They also have keen eyesight and are skilled at camouflaging themselves in their surroundings, making them even more effective at catching their prey.
The Geographic Distribution of the Northern Pike
As mentioned earlier, the Northern Pike can be found in the northern parts of North America, Europe, and Asia. They have a widespread distribution and can adapt to different environments, making them a versatile and resilient species. They are also commonly found in colder regions, such as Canada, Alaska, and northern Europe.Appearance and Physical Characteristics
Another aspect that makes the Northern Pike an interesting species is its unique appearance. They have a dark greenish-brown color on their back, lighter sides with rows of light-colored oval spots, and a white or yellow belly. This distinct coloration allows them to blend in with their surroundings, making them even more effective at ambushing their prey.In terms of their body shape, Northern Pike have a long body with a large head and a pointed snout. Their body is also elongated and streamlined, giving them the ability to move quickly through the water. They also have a robust jaw filled with sharp teeth, perfectly evolved for catching and holding onto their prey.
Size, Age, and Reproduction
Northern Pike can grow to impressive sizes, reaching up to 1.5 meters (4.9 feet) in length. The average adult size, however, is around 0.8 to 1.5 meters (2.6 to 4.9 feet). As for their age, Northern Pike can live up to 25 years in the wild, making them one of the longest-living freshwater fish species.When it comes to reproduction, Northern Pike use external fertilization, where the female deposits her eggs and the male releases his sperm to fertilize them. During spawning, female Northern Pike create a nest by thrashing their tails in shallow water. They can lay between 5,000 and 30,000 eggs, which are then fertilized by the male. The eggs hatch within a few weeks, and the juvenile fish grow rapidly before reaching maturity in 3-4 years.
Migration Patterns and Behavior
Unlike other fish species, Northern Pike do not have a significant migration pattern. They are not known to travel long distances, and they tend to stay in one area unless forced to move due to environmental changes. However, they may swim to different areas within their habitat in search of food or to find a suitable nesting site during the spawning season.In Conclusion
The Northern Pike is a fascinating and formidable fish that has captured the interest of many people. Its unique features, hunting skills, and widespread distribution make it a significant species in the freshwater ecosystem. However, as with all wildlife, it is essential to understand and respect the natural behaviors and habitats of the Northern Pike to ensure their survival and the balance of the ecosystem they inhabit. So next time you see a Northern Pike gliding through the water, remember the remarkable traits that make this fish a true predator, and appreciate the beauty and complexity of nature.

Northern Pike
Fish Details Northern Pike - Scientific Name: Esox lucius
- Category: Fish N
- Scientific Name: Esox lucius
- Common Name: Northern Pike
- Habitat: Northern pike inhabit lakes, ponds, rivers, and other freshwater bodies.
- Feeding Habitat: They prefer areas with vegetation or structures where they can ambush their prey.
- Feeding Method: Northern pike are ambush predators and they primarily feed on other fish, but they also eat amphibians, crustaceans, and small mammals.
- Geographic Distribution: Northern pike are found in the northern parts of North America, Europe, and Asia.
- Country Of Origin: They are native to the northern regions of North America, Europe, and Asia.
- Color: They have a dark greenish-brown color on their back, lighter sides with rows of light-colored oval spots, and a white or yellow belly.
- Body Shape: Northern pike have a long body with a large head, sharp teeth, and a streamlined shape.
- Length: They can grow up to 1.5 meters (4.9 feet) in length.
- Adult Size: Adult northern pike can reach a size of 0.8 to 1.5 meters (2.6 to 4.9 feet).
- Age: They can live up to 25 years in the wild.
- Reproduction: Northern pike reproduce through external fertilization, where the female deposits her eggs and the male releases his sperm to fertilize them.
- Reproduction Behavior: During spawning, female northern pike create a nest by thrashing their tails in shallow water. They can lay between 5,000 and 30,000 eggs.
- Migration Pattern: Northern pike do not have a significant migration pattern.

Northern Pike
- Social Group: They are solitary fish and do not form social groups.
- Behavior: Northern pike are known for their aggressive behavior and voracious appetite. They are ambush predators and use their sharp teeth to capture and devour their prey.
- Diet: Their diet primarily consists of other fish, but they also eat amphibians, crustaceans, and small mammals.
- Predators: Northern pike have few natural predators, but larger pike, muskellunge, and humans may prey on them.
- Prey: They prey on smaller fish, frogs, mice, and other small aquatic animals.
- Environmental Threats: Habitat destruction, pollution, overfishing, and climate change are environmental threats to northern pike.
- Conservation Status: The conservation status of northern pike is of least concern.
- Special Features: Northern pike have sharp teeth, a slimy coating on their scales that allows them to move quickly through water, and a long and slender body shape.
- Interesting Facts: Northern pike are known for their voracious appetite and aggressive behavior. They can grow rapidly and reach impressive sizes. They are also highly adaptable to different environments.
- Reproduction Period: They reproduce in the spring or early summer.
- Nesting Habit: Female northern pike create a nest by thrashing their tails in shallow water, usually in areas with vegetation.
- Lifespan: They can live up to 25 years in the wild.
- Habitat Threats: Habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change are threats to the habitat of northern pike.
- Population Trends: Population trends of northern pike vary in different regions.
- Habitats Affected: Northern pike can affect the habitats they inhabit by preying on other fish and controlling their populations.

Esox lucius
The Mighty Northern Pike: A Predator of the Aquatic World
The northern pike, also known as the "water wolf", is a fierce and powerful predator inhabiting freshwater bodies in the Northern Hemisphere. This fish, with its sleek body and sharp teeth, is not only a formidable hunter but also an essential part of its ecosystem.Let's dive deeper into the fascinating world of the northern pike and uncover its unique features, behaviors, and threats.
Appearance and Habitat
Northern pike, found in Canada, Europe, and parts of Asia, have a distinct appearance that sets them apart from other fish RadioDouRosul.com. They have a slender and elongated body, covered in small scales with a greenish-brown color and blotches of yellow, orange, and white. This camouflage helps them blend in with their surroundings, making them hard to spot by their prey.One of the most striking features of the northern pike are its sharp teeth. These teeth, along with their slimy coating, allow them to move quickly through the water, making them efficient and deadly hunters.
They primarily inhabit freshwater bodies such as lakes, rivers, and streams, where they can find plenty of prey to sustain their large appetites. They are also highly adaptable and can survive in various water temperatures and conditions.
Solitary Creatures with Aggressive Behavior
Unlike other fish, northern pike are solitary creatures and do not form social groups. They prefer to swim and hunt alone, using their well-developed senses to navigate their surroundings and locate potential prey.These fish are known for their aggressive behavior and voracious appetite Nase. They are ambush predators and use their sharp teeth to capture and devour their prey. Their swift and precise attacks make them a formidable opponent for any aquatic species.
Varied Diet
Northern pike are opportunistic predators and have a broad and varied diet. Their main source of food is other fish, but they also consume amphibians, crustaceans, and even small mammals. They have been known to prey on smaller fish, frogs, mice, and other small aquatic animals.This diverse diet enables them to thrive in different environments and adapt to changes in their food supply. However, their preferred food sources remain fish, and they play a vital role in controlling fish populations in their habitat.
Natural Predators and Threats
Northern pike have a few natural predators, including larger pike, muskellunge, and humans. However, their biggest threats come from environmental factors.Habitat destruction, pollution, overfishing, and climate change are significant environmental threats to northern pike populations. These fish are highly sensitive to water pollution, and any changes in their habitat can have a severe impact on their populations.
Conservation Status
According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the conservation status of northern pike is of least concern. This means that their populations are stable, and they are not at immediate risk of extinction.However, it is crucial to monitor their populations and protect their habitats to ensure their continued survival.
Reproduction and Nesting Habits
Northern pike reproduce in the spring or early summer, depending on the water temperature and conditions. The female pike lay thousands of eggs, which are then fertilized by the male during spawning. These eggs are released in shallow, weedy areas, providing the ideal environment for the eggs to hatch.Female northern pike are also responsible for creating a nest for their eggs. They do this by thrashing their tails in shallow water, usually in areas with vegetation, such as reeds and water lilies. This process helps to clear the area and create a spot for the eggs to develop safely.
Long Lifespan and Varied Population Trends
Northern pike can live up to 25 years in the wild, depending on their habitat's quality and food supply. They have an impressive growth rate and can reach lengths of up to 6 feet and weights of over 50 pounds.Population trends of northern pike vary in different regions. In some areas, they are abundant, while in others, their populations have declined due to overfishing and habitat destruction. However, these fish have shown resilience and can bounce back quickly if given the chance.
Impact on Habitats
Northern pike can affect the habitats they inhabit. As top predators, they play a crucial role in controlling the population of other fish species. Their presence can also regulate the number of aquatic plants, providing a balance within the ecosystem.However, overfishing and human interference can lead to imbalances in these habitats, affecting not only the northern pike but also other species relying on them for survival.
In Conclusion
In summary, the northern pike is a formidable and fascinating creature that has adapted to survive in various habitats. Their aggressive behavior and impressive hunting abilities make them an essential part of their ecosystem, ensuring a stable and balanced environment.However, their populations face threats from human activities, which can have severe consequences for both the fish and their habitat. It is our responsibility to protect and preserve these magnificent creatures to maintain the delicate balance of our aquatic world.

The Notorious Northern Pike: The Ultimate Freshwater Predator
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.