
Scaly Dragonfish
There is limited information available about the migration patterns of the Scaly Dragonfish.
The Scaly Dragonfish, a stunning species found along the Atlantic coast, has limited information on its migration patterns. These fish can live up to 12 years and are known for their elaborate courtship displays during mating season. Found in countries like the United States, Bermuda, and Brazil, they use their pectoral fins to attract females.
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: Scaly Dragonfish
Habitat: The Scaly Dragonfish is found in tropical and subtropical waters of the Atlantic Ocean, from the United States to Brazil. It inhabits shallow reefs, rocky areas, and seagrass beds.
Color: The Scaly Dragonfish has a dark brown body with a mottled pattern of lighter and darker spots. It also has prominent, large scales that resemble armor.
The Mystical and Fierce Scaly Dragonfish: A Hidden Gem of the Atlantic Ocean
Have you ever heard of a fish that resembles a mythical creature with its dragon-like appearance and scale-covered body? If not, let us introduce you to the Scaly Dragonfish, a fascinating creature found in the Atlantic Ocean. Although they may not breathe fire, these remarkable creatures have captured the attention of marine enthusiasts and researchers alike with their distinct features and behaviors. In this article, we will explore the extraordinary world of the Scaly Dragonfish, from its habitat and feeding habits to its reproduction behavior and migration patterns.A Deep Dive into the Habitat of the Scaly Dragonfish
The Scaly Dragonfish, scientifically known as Dactylopterus volitans, is found in tropical and subtropical waters of the Atlantic Ocean, spanning from the eastern coast of the United States to Brazil Scaly Dragonfish. They are commonly found in shallow reefs, rocky areas, and seagrass beds, and can also be spotted near open water. These fish prefer warm and well-oxygenated waters, making the Atlantic Ocean a perfect home for them.The Scaly Dragonfish is a solitary fish and is usually found resting on the sandy bottom, camouflaging itself with its mottled brown body adorned with lighter and darker spots. The large scales on their body act as armor, offering protection against predators and other external elements. These unique features not only make them visually striking but also help them thrive in their chosen habitat.
Satiate Their Appetite: The Feeding Habits of the Scaly Dragonfish
The Scaly Dragonfish is a carnivorous fish and has a diverse diet. They primarily feed on small fish like grunts, gobies, and drums, but also consume crustaceans like shrimp and crabs. They are opportunistic feeders and can be found scavenging on dead animals or preying on other smaller fish. Their diet is primarily determined by their habitat, and they are known to adjust their feeding habits according to their surroundings Stingray.The Scaly Dragonfish is not a picky eater and can usually be found feeding around reefs and rocky areas, or in open water close to the seafloor. They are also excellent hunters and use their sharp teeth to capture prey with precision. Their unique feeding habits have helped maintain a balance in the marine ecosystem by regulating the population of their prey species.
Uncovering the Mysterious Geographical Distribution of the Scaly Dragonfish
The Scaly Dragonfish has a wide geographical distribution and can be found in the western Atlantic Ocean, ranging from the United States to Brazil. These fish have been spotted in various countries along the Atlantic coast, including the United States, Bermuda, the Bahamas, and Brazil. However, there is limited information available on their exact population and distribution, which adds to their elusive aura.Their ability to adapt to different habitats and environments has allowed them to thrive in various areas, making them accessible to researchers and marine enthusiasts from different parts of the world. Their widespread distribution has also sparked interest in studying their migratory patterns, which remains a mystery even today.
The Beautiful Color and Shape of the Scaly Dragonfish
One of the most distinctive features of the Scaly Dragonfish is its coloration and body shape. They have a dark brown body with a unique mottled pattern of lighter and darker spots, which adds to their camouflage in their habitat. Their prominent, large scales, resembling armor, make them a sight to behold.In addition to the scales, their body shape also adds to their dragon-like appearance. These fish have a flattened body with a wide, triangular-shaped head. They have large pectoral fins and a long caudal fin, which give them incredible maneuverability and agility in the water. These features, combined with their unique coloration, make them a standout among other marine creatures.
A Look into the Size, Age, and Reproduction of the Scaly Dragonfish
The Scaly Dragonfish can grow up to 14 inches in length and reach a maximum adult size of 12-14 inches. These fish are known to live up to 12 years, but there is limited information available on their exact lifespan. The Scaly Dragonfish is an oviparous species, meaning they lay eggs to reproduce. However, the reproduction behavior of these fish is still being researched.During the mating season, male Scaly Dragonfish perform elaborate courtship displays to attract females. They display their pectoral fins and swim in circular patterns, showcasing their agility and strength. This behavior is not only a spectacle to witness but also an essential part of their reproductive cycle.
The Curious Case of Migration Patterns of the Scaly Dragonfish
Despite being a widely distributed species, there is limited information available on the migration patterns of the Scaly Dragonfish. Researchers have observed that these fish have a diverse diet and can adapt to different environments, which may lead to limited or no seasonal migration for food. Another factor contributing to the lack of information could be the elusive nature of these creatures, making it challenging to track their movements.Conclusion:
The Scaly Dragonfish may not be as well-known as other marine creatures, but they have distinct features and behaviors that make them a valuable addition to the ocean's ecosystem. From their unique coloration and appearance to their elusive migration patterns, these fish continue to intrigue researchers and marine enthusiasts. With more studies and research, we can uncover more secrets about this mystical and fierce creature of the Atlantic Ocean - the Scaly Dragonfish.
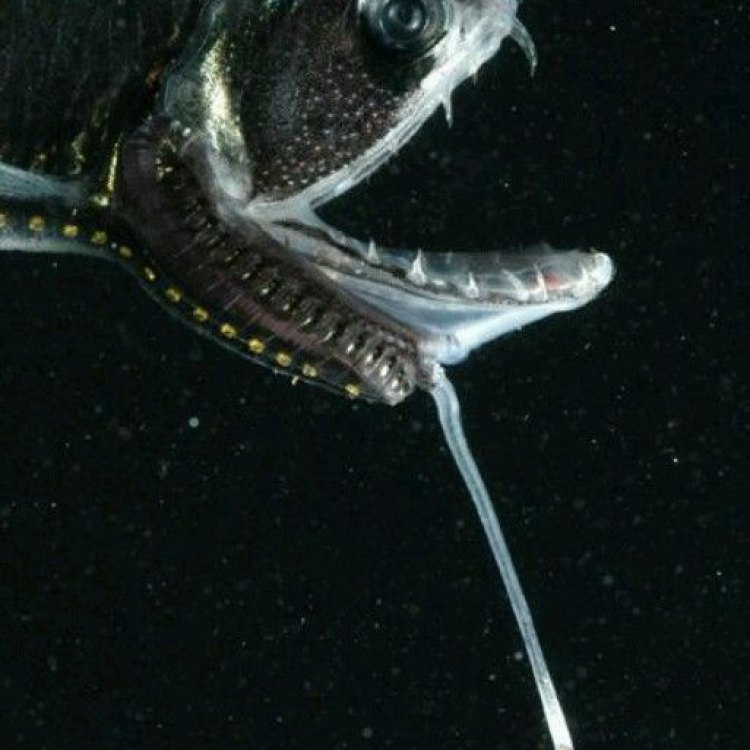
Scaly Dragonfish
Fish Details Scaly Dragonfish - Scientific Name: Dactylopterus volitans
- Category: Fish S
- Scientific Name: Dactylopterus volitans
- Common Name: Scaly Dragonfish
- Habitat: The Scaly Dragonfish is found in tropical and subtropical waters of the Atlantic Ocean, from the United States to Brazil. It inhabits shallow reefs, rocky areas, and seagrass beds.
- Feeding Habitat: The Scaly Dragonfish feeds in open water, often near the bottom, and around reefs and rocky areas.
- Feeding Method: It is a carnivorous fish that primarily feeds on small fish such as grunts, gobies, and drums. It also consumes shrimp, crabs, and other crustaceans.
- Geographic Distribution: The Scaly Dragonfish has a wide geographic distribution and is found in the western Atlantic Ocean, ranging from the eastern coast of the United States to Brazil.
- Country Of Origin: Various countries along the Atlantic coast, including the United States, Bermuda, the Bahamas, and Brazil.
- Color: The Scaly Dragonfish has a dark brown body with a mottled pattern of lighter and darker spots. It also has prominent, large scales that resemble armor.
- Body Shape: The Scaly Dragonfish has a flattened body with a wide, triangular-shaped head. It has large pectoral fins and a long caudal fin, which give it a dragon-like appearance.
- Length: The Scaly Dragonfish can grow up to 14 inches in length.
- Adult Size: The adult size of the Scaly Dragonfish is around 12-14 inches.
- Age: The maximum reported age of the Scaly Dragonfish is around 12 years.
- Reproduction: The Scaly Dragonfish is oviparous, meaning it lays eggs.
- Reproduction Behavior: During the mating season, male Scaly Dragonfishes perform elaborate courtship displays to attract females. They display their pectoral fins and swim in circular patterns.
- Migration Pattern: There is limited information available about the migration patterns of the Scaly Dragonfish.
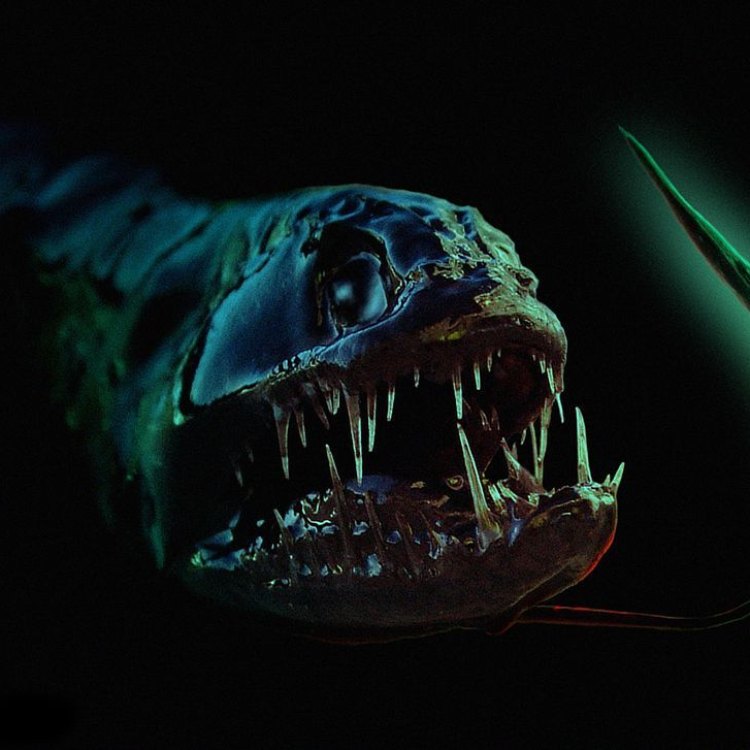
Scaly Dragonfish
- Social Group: The Scaly Dragonfish is a solitary species and is typically found alone or in small groups.
- Behavior: The Scaly Dragonfish is a nocturnal species and is most active during the night. It spends its days hiding in crevices and caves.
- Diet: The Scaly Dragonfish primarily feeds on small fish such as grunts, gobies, and drums. It also consumes shrimp, crabs, and other crustaceans.
- Predators: The main predators of the Scaly Dragonfish include larger fish and marine mammals such as dolphins.
- Prey: The Scaly Dragonfish preys on small fish such as grunts, gobies, and drums. It also consumes shrimp, crabs, and other crustaceans.
- Environmental Threats: The Scaly Dragonfish faces threats from habitat destruction, pollution, overfishing, and climate change.
- Conservation Status: The conservation status of the Scaly Dragonfish is currently unknown.
- Special Features: The Scaly Dragonfish has large, fan-like pectoral fins that it uses to glide through the water. It also has a large mouth with sharp teeth for capturing its prey.
- Interesting Facts: 1. The Scaly Dragonfish gets its name from its dragon-like appearance and the large, scaly armor-like plates on its body. 2. It is capable of producing sound by grinding its pharyngeal teeth together, which may be used for communication. 3. The Scaly Dragonfish is not commonly kept in aquariums due to its specialized care requirements and large adult size.
- Reproduction Period: The Scaly Dragonfish reproduces during the summer months.
- Nesting Habit: The Scaly Dragonfish does not build nests.
- Lifespan: The maximum reported lifespan of the Scaly Dragonfish is around 12 years.
- Habitat Threats: The Scaly Dragonfish faces threats from habitat destruction, pollution, overfishing, and climate change.
- Population Trends: There is limited information available about the population trends of the Scaly Dragonfish.
- Habitats Affected: The Scaly Dragonfish primarily inhabits shallow reefs, rocky areas, and seagrass beds.
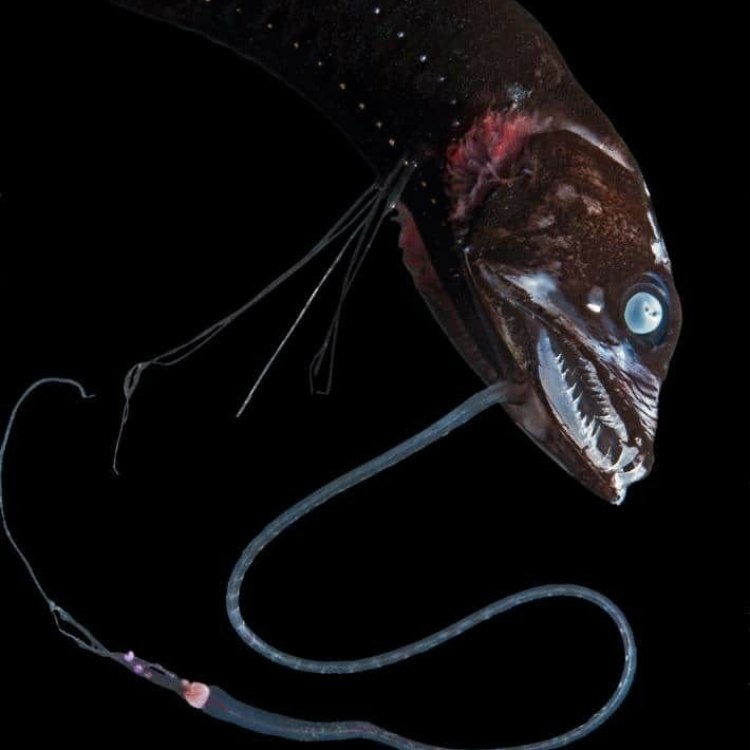

Dactylopterus volitans
Discover the Mysterious World of the Scaly Dragonfish: A Solitary and Fascinating Species
Deep in the depths of the sea, there is a creature that looks like it came straight out of a fantasy book. With its dragon-like appearance, armored scales, and large pectoral fins, the Scaly Dragonfish is a unique and fascinating species that has captured the attention of marine enthusiasts and scientists alike. Despite its intimidating looks, this mysterious species is a solitary creature that spends most of its time hidden in the shadows of the ocean.In this article, we will take a deep dive into the world of the Scaly Dragonfish, exploring its behavior, social groups, diet, predators, prey, environmental threats, conservation status, and special features RadioDouRosul.com. We will also uncover some interesting facts about this elusive species and touch upon its nesting habits, lifespan, population trends, and preferred habitats. So, get ready to embark on a journey to discover the secrets of the Scaly Dragonfish.
Social Group and Behavior
Unlike many other fish species, the Scaly Dragonfish is a solitary creature and is typically found alone or in small groups. It spends its days hiding in crevices and caves, usually in shallow reefs, rocky areas, and seagrass beds. This nocturnal species is most active during the night, making it quite challenging to observe in its natural habitat.
The Scaly Dragonfish is a stealthy predator, using its camouflage and sharp senses to hunt for food. It is also known to be a fast swimmer, thanks to its large pectoral fins that resemble a fan. These fins allow it to glide gracefully through the water, making it look like a mythical creature from another world.
Diet and Prey
As mentioned, the Scaly Dragonfish is a fierce predator, and its diet consists primarily of small fish such as grunts, gobies, and drums Sandbar Shark. It also feeds on shrimp, crabs, and other crustaceans. With its sharp teeth and agile hunting skills, the Scaly Dragonfish is a formidable predator to smaller marine species.
Interestingly, the Scaly Dragonfish is also known to produce sound by grinding its pharyngeal teeth together. Though the exact purpose of this sound is unknown, it is believed that it could be used for communication with other members of its species.
Predators and Environmental Threats
Despite its fierce nature, the Scaly Dragonfish is not entirely safe in the ocean. Its main predators include larger fish, such as groupers and snappers, and marine mammals, such as dolphins. These predators are always on the lookout for their next meal, and the Scaly Dragonfish makes for an easy target due to its slow movement and large size.
Moreover, like many other marine species, the Scaly Dragonfish is also facing significant threats from human activities. Habitat destruction, pollution, overfishing, and climate change are all posing risks to this unique species. As a result, its population is declining, and its conservation status is currently unknown.
Special Features and Interesting Facts
The Scaly Dragonfish gets its name from its dragon-like appearance and the large, scaly armor plates on its body. These plates are actually modified scales that protect the fish from potential predators. They also give it a unique and intimidating appearance, making it stand out among other marine species.
Another fascinating feature of the Scaly Dragonfish is its large mouth and sharp, pointed teeth. This helps the fish to capture its prey quickly and effectively. Its mouth is also capable of extending, allowing it to swallow larger prey whole.
Did you know that the Scaly Dragonfish is not commonly kept in aquariums? Despite its popularity among marine enthusiasts, this fish has very specialized care requirements and can grow up to 3 feet in length when fully mature. As a result, it is not a practical option for most home aquariums.
Reproduction and Nesting Habits
The Scaly Dragonfish reproduces during the summer months, with little known about its reproductive biology. However, it is believed that the females release eggs into the water, which are then fertilized by the male. These eggs are likely to be pelagic, meaning they float freely in the water column until they hatch.
Unlike other fish species, the Scaly Dragonfish does not build nests to lay its eggs. Instead, it relies on its camouflage and hiding abilities to protect its offspring. The female may also choose a more secluded spot to lay her eggs to increase the chances of survival for her young.
Lifespan and Population Trends
The maximum reported lifespan for the Scaly Dragonfish is around 12 years, though there is limited information available on its longevity in the wild. Like many other marine species, the exact population trends of the Scaly Dragonfish are also not well-documented. However, given the increasing threats it faces, it is likely that its numbers are decreasing.
Preferred Habitats
As mentioned earlier, the Scaly Dragonfish is most commonly found in shallow reefs, rocky areas, and seagrass beds. These habitats provide it with ample food sources and hiding places to stay safe from predators. They also allow it to use its pectoral fins to glide through the water effortlessly, making it easier for the fish to hunt.
In today's rapidly changing world, these habitats are also at risk due to human activities. The destruction of coral reefs, pollution, and climate change are all causing harm to the Scaly Dragonfish's preferred habitats, further threatening its survival.
In Conclusion
The Scaly Dragonfish is undoubtedly a unique and fascinating species, with its dragon-like appearance and impressive abilities. However, as we continue to explore and exploit the ocean's depths, we are also putting this amazing creature at risk. It is essential to understand the impact of our actions on marine life and take steps to conserve and protect species like the Scaly Dragonfish for future generations to marvel at.
Who knows what other mysterious and enchanting creatures are waiting to be discovered in the depths of the ocean? As we continue to learn more about the Scaly Dragonfish and other marine species, we are sure to uncover more surprises and wonders that will only add to our appreciation for the vast and diverse life that exists in our oceans.
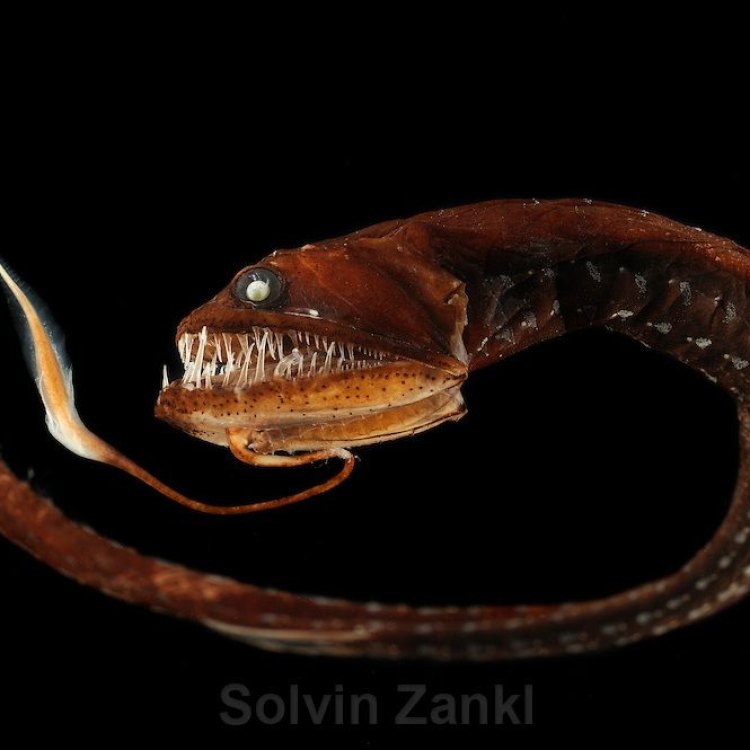

The Mystical and Fierce Scaly Dragonfish: A Hidden Gem of the Atlantic Ocean
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.












