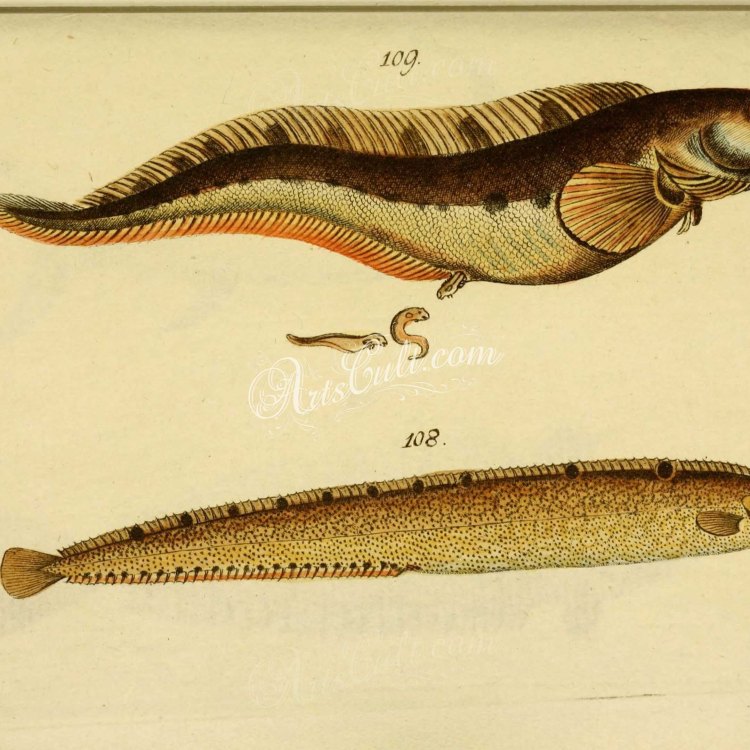
Eelpout
Eelpouts do not undertake long-distance migrations, but they may move within their local habitats in search of food and suitable breeding sites.
Discover the fascinating world of eelpouts - a native fish species found in Canada and the United States. These bottom-dwellers have a maximum lifespan of 7 years and exhibit unique reproductive behavior. Learn more about their migration patterns and breeding habits, all while exploring the rich biodiversity of Indonesia's aquatic life. #eelpouts #Indonesiafish #marinebiodiversity
Summary of Fish Details:
Common Name: Eelpout
Habitat: Eelpouts are found in coastal waters and estuaries along the Atlantic coast of North America. They prefer rocky and sandy bottoms, often hiding among rocks or in burrows.
Color: Eelpouts are typically brown or olive in color, with mottled patterns that help them blend in with their surroundings.
Meet the Eelpout: A Fascinating and Misunderstood Fish of North America
When you hear the word "eelpout," you may imagine a slimy, unattractive fish that spends its days lurking in the depths of the ocean. However, this perception couldn't be further from the truth. In fact, eelpouts are fascinating creatures that play a vital role in marine ecosystems and have captured the intrigue of scientists and fish enthusiasts alike.The scientific name for eelpout is Zoarces americanus, and they are commonly known by that name as well as "eel pout" or "slime eel Eelpout." They are found in coastal waters and estuaries along the Atlantic coast of North America, from Canada to the United States. Let's delve deeper into their habitat, feeding habits, and other interesting facts about this unique fish.
Habitat of the Eelpout
Eelpouts are mostly found in the Atlantic coast of North America, specifically in waters off the coast of Canada and the United States. They prefer living in shallow waters, in areas with rocky or sandy bottoms. You may also find them hiding among rocks or in burrows created by other marine creatures.Their preference for shallow waters makes eelpouts easily accessible to humans, as they can often be found in tidal pools or shallow waterways. However, eelpouts are considered a demersal species, meaning they are mostly found near the ocean floor.
Feeding Habits of the Eelpout
Eelpouts are benthic feeders, which means they feed on organisms that live on or near the ocean floor. Their diet consists of small fish, crustaceans, mollusks, and worms Eagle Ray. They use their sharp teeth to capture and consume their prey, and their ability to blend in with their surroundings makes them skilled hunters.Their varied diet and feeding habits make eelpouts important members of the marine food chain. They not only keep the population of their prey in check but also serve as a food source for larger predators.
The Color and Body Shape of the Eelpout
Eelpouts are typically brown or olive in color, with mottled patterns that help them blend in with the surrounding rocks and sand. This coloration also serves as a form of camouflage, making it easier for them to ambush their prey.In terms of body shape, eelpouts have elongated bodies with a long dorsal fin that runs along their back. Their cylindrical bodies taper towards the tail, giving them a snake-like appearance. However, unlike eels, eelpouts have pectoral fins that allow them to swim and maneuver in the water.
Length and Size of the Eelpout
Eelpouts can reach lengths of up to 18 inches (45 cm), although they are typically found in the 8 to 18 inch (20 to 45 cm) range. As for their weight, eelpouts can weigh anywhere between 1 to 2 pounds (0.5 to 1 kg).Although they may not seem like a substantial size, eelpouts play an essential role in their ecosystem, making them an important species to study and protect.
Reproduction and Behavior of the Eelpout
Eelpouts are oviparous, which means they reproduce by laying eggs. During the breeding season, which usually takes place in late winter or early spring, male eelpouts create nests in rocky crevices or burrows using algae and debris.Female eelpouts then deposit their eggs in these nests, and the males guard and aerate the eggs until they hatch. This behavior is essential for the survival of the eggs, as it ensures they receive enough oxygen and stay free from predators until they are ready to hatch.
Geographic Distribution and Country of Origin
Eelpouts are found along the Atlantic coast of North America, from Labrador in Canada to Massachusetts in the United States. They are native to this region and have been living here for thousands of years.Canada and the United States share a vast coastline, and this makes both countries the natural habitat for eelpouts. Due to their widespread distribution in this area, eelpouts are an essential species for the local marine ecosystems.
Age and Migration Patterns of the Eelpout
Eelpouts are relatively short-lived, with a maximum reported age of around 7 years. While they do not undertake long-distance migrations, they may move within their local habitats in search of food and suitable breeding sites.During the colder months, eelpouts prefer to stay close to their burrows or hide among rocks, waiting for warmer temperatures to return. As the water warms up, they may move towards shallower waters where food is more abundant.
In Conclusion
Despite their unassuming appearance, eelpouts are incredibly interesting and vital members of the marine ecosystem. Their unique hunting tactics, reproduction behavior, and crucial role in marine food webs make them a fascinating species to study.However, eelpouts are facing threats such as habitat destruction, pollution, and overfishing. It is crucial for us to understand and protect this species to ensure a healthy and balanced ocean for future generations. The next time you come across an eelpout, take a moment to appreciate its resilience and importance in the underwater world around us.
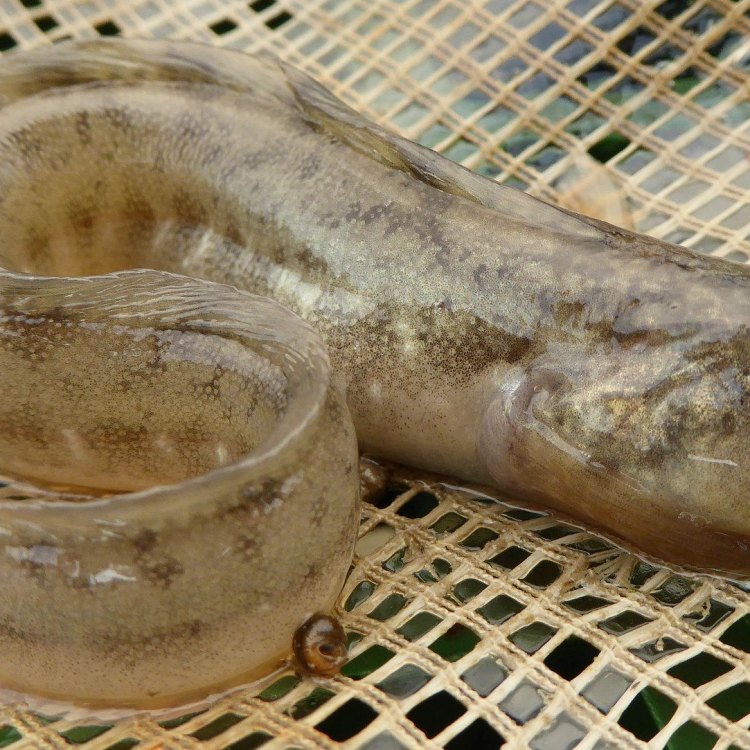

Eelpout
Fish Details Eelpout - Scientific Name: Zoarces americanus
- Category: Fish E
- Scientific Name: Zoarces americanus
- Common Name: Eelpout
- Habitat: Eelpouts are found in coastal waters and estuaries along the Atlantic coast of North America. They prefer rocky and sandy bottoms, often hiding among rocks or in burrows.
- Feeding Habitat: Eelpouts are benthic feeders, meaning they feed on organisms that live on or near the ocean floor.
- Feeding Method: They have a varied diet that includes small fish, crustaceans, mollusks, and worms. They use their sharp teeth to capture and consume their prey.
- Geographic Distribution: Eelpouts are found along the Atlantic coast of North America, from Labrador in Canada to Massachusetts in the United States.
- Country Of Origin: Canada and United States
- Color: Eelpouts are typically brown or olive in color, with mottled patterns that help them blend in with their surroundings.
- Body Shape: They have elongated bodies with a long dorsal fin that runs along their back. Their bodies are cylindrical and taper towards the tail.
- Length: Eelpouts can reach lengths of up to 18 inches (45 cm).
- Adult Size: Adult eelpouts usually range in size from 8 to 18 inches (20 to 45 cm).
- Age: The maximum reported age for eelpouts is around 7 years.
- Reproduction: Eelpouts are oviparous, which means they reproduce by laying eggs.
- Reproduction Behavior: During the breeding season, male eelpouts create nests in rocky crevices or burrows using algae and debris. Females deposit their eggs in the nests, and the males guard and aerate the eggs until they hatch.
- Migration Pattern: Eelpouts do not undertake long-distance migrations, but they may move within their local habitats in search of food and suitable breeding sites.
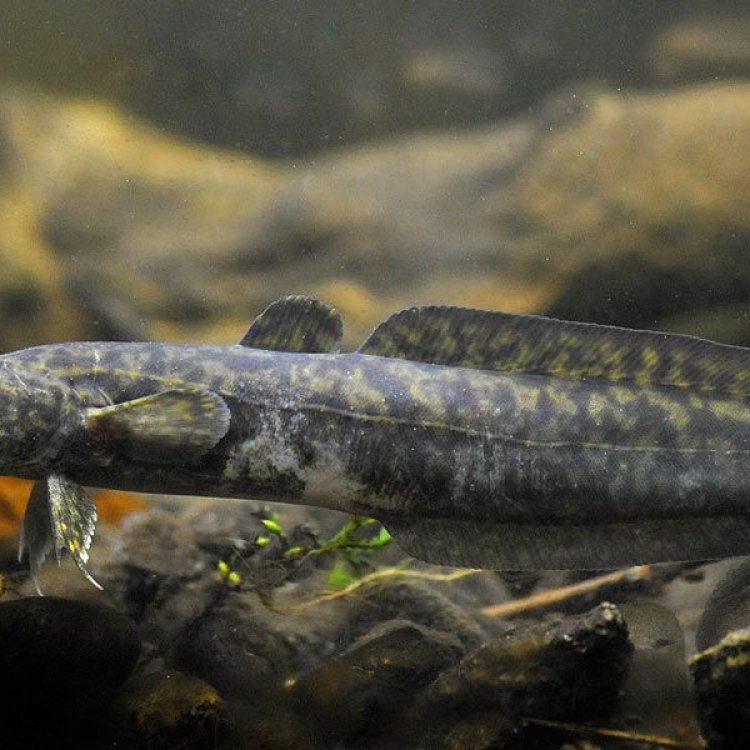

Eelpout
- Social Group: Eelpouts are generally solitary animals, but they may gather in small groups during the breeding season.
- Behavior: Eelpouts are nocturnal animals and are most active at night. They are bottom-dwelling fish and spend much of their time hiding in rock crevices or burrows.
- Diet: They are carnivorous and feed on small fish, crustaceans, mollusks, and worms.
- Predators: Predators of eelpouts include larger fish species and seabirds.
- Prey: Prey of eelpouts include small fish, crustaceans, mollusks, and worms.
- Environmental Threats: The main environmental threats to eelpouts include habitat destruction, pollution, and overfishing.
- Conservation Status: The conservation status of eelpouts is currently unknown.
- Special Features: Eelpouts have a unique ability to produce antifreeze proteins, which allows them to survive in cold waters.
- Interesting Facts: Eelpouts are also known as 'fish doctors' because their slime contains enzymes that have antibacterial properties.
- Reproduction Period: The breeding season for eelpouts typically occurs from late winter to early spring.
- Nesting Habit: Male eelpouts create nests in rocky crevices or burrows using algae and debris.
- Lifespan: The maximum reported lifespan for eelpouts is around 7 years.
- Habitat Threats: The main threats to the habitat of eelpouts include coastal development, pollution, and climate change.
- Population Trends: There is limited information on the population trends of eelpouts.
- Habitats Affected: Eelpouts are primarily found in coastal habitats, which are vulnerable to habitat destruction and pollution.
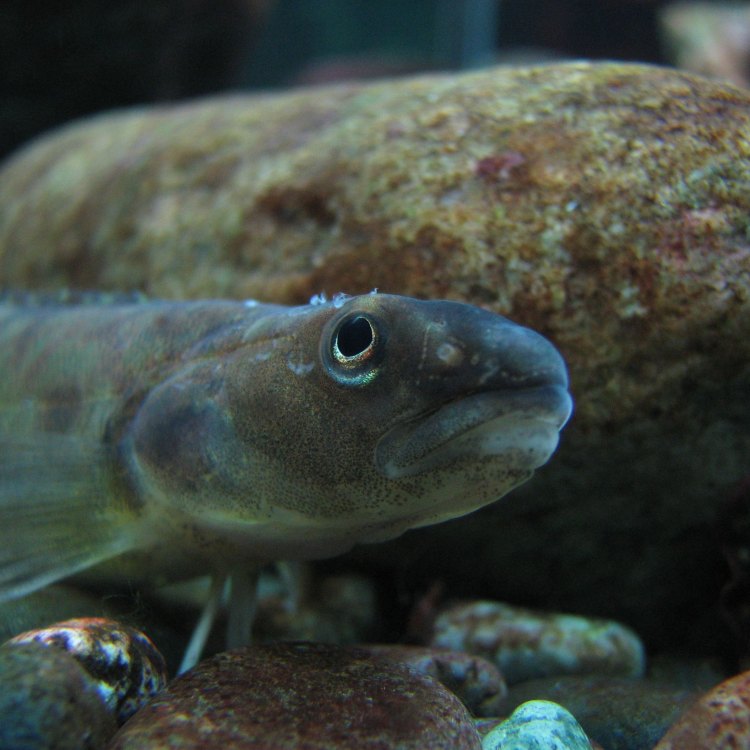

Zoarces americanus
The Fascinating World of Eelpouts: Surviving in the Depths of the Ocean
Deep in the cold and dark depths of the ocean, lives a fascinating creature that has captured the curiosity of many. With its unusual features and unique behaviors, the eelpout is a mysterious and elusive fish that is not often talked about. In this article, we will delve deep into the unique world of eelpouts, learning about their social habits, behaviors, diet, predators, and their struggle to survive in today's changing environment.Eelpouts belong to the family Zoarcidae, and there are over 300 known species found in oceans around the world RadioDouRosul.com. Despite their name, eelpouts are not true eels, but they have an elongated body and slender appearance, making them look similar. They are also commonly known as "eel-like fish" due to their snake-like appearance and behavior.
Social Group and Behavior
Eelpouts are generally solitary creatures, living and hunting alone. However, they may gather in small groups during the breeding season. During this time, males will create nests in rocky crevices or burrows using algae and debris, where females will lay their eggs. After fertilization, the male will guard the nest until the eggs hatch, declining to eat during this period.These nocturnal animals are most active at night, making them elusive to researchers and hard to observe in their natural habitat. They are bottom-dwelling fish, spending much of their time hiding in rock crevices or burrows. Eelpouts are also known to camouflage themselves by changing color to match their surroundings, making them even more difficult to spot European Eel.
Diet and Predators
Eelpouts are carnivorous and have a varied diet. They mainly feed on small fish, crustaceans, mollusks, and worms. Due to their ambush-style hunting, eelpouts have a unique feeding strategy. They use their elongated bodies to their advantage, wriggling into crevices and dragging their prey out, surprising them with their quick movements.As with any other species in the food chain, eelpouts are not exempt from predators. Larger fish species and seabirds are known to feed on eelpouts, making them a vital part of the ocean ecosystem.
Environmental Threats and Conservation Status
Like many other marine creatures, eelpouts face numerous environmental threats, making their survival precarious. Habitat destruction, pollution, and overfishing pose significant threats to these unique animals. As bottom-dwelling fish, they are vulnerable to habitat destruction caused by coastal development and pollution. Overfishing also poses a significant threat, as eelpouts are often caught as bycatch, caught unintentionally while fishing for other species.Interestingly, the conservation status of eelpouts is currently unknown, as there is limited information on their population trends. However, with the increasing threat to their habitat and overfishing, there is a growing concern for their survival.
Special Features and Interesting Facts
Eelpouts have a unique survival mechanism in cold waters. They can produce antifreeze proteins, which prevent their body fluids from freezing and help them survive in freezing temperatures. This adaptation gives them the ability to thrive in the cold, deep waters where other fish cannot survive.Another interesting fact about eelpouts is their slimy coating. They are also known as "fish doctors" because their slime contains enzymes that have antibacterial properties. This slime helps to protect them from harmful bacteria and parasites, keeping them healthy in their harsh environment.
Reproduction Period and Nesting Habit
The breeding season for eelpouts typically occurs from late winter to early spring. During this time, males will create nests in rocky crevices or burrows using algae and debris. They then work tirelessly to attract a female and allow her to lay fertilized eggs before guarding the nest until the eggs hatch. This unique reproductive strategy is essential for successful breeding and ensuring the survival of the species.Habitat Threats and Population Trends
As mentioned earlier, habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change are significant threats to eelpouts and their habitat. Coastal development and pollution pose a direct threat to their underwater homes, making it difficult for eelpouts to find suitable shelter and food. The warming temperatures due to climate change also have an adverse impact on their survival, affecting their cold-water habitat.As there is limited information on their population trends, it is challenging to determine the exact impact these threats have on eelpouts. However, it is clear that their habitat and population are under threat, and conservation efforts must be made to protect this unique species.
Habitats Affected by Eelpouts
Eelpouts are primarily found in coastal habitats, making them essential to the health of these ecosystems. However, these habitats are vulnerable to habitat destruction and pollution, making the survival of eelpouts and other marine creatures dependent on the health of these habitats. With their unique ability to thrive in cold waters, eelpouts play a vital role in maintaining the balance of these habitats.The Importance of Protecting Eelpouts
Eelpouts may not be as well-known as dolphins or sharks, but they play a crucial role in the ocean ecosystem. As bottom-dwelling fish, they help to keep the sea floor clean and healthy. They also serve as an important source of food for larger fish and seabirds, contributing to the food chain. Furthermore, their unique ability to produce antifreeze proteins and their antibacterial slime make them valuable for scientific research.Protecting eelpouts and their habitat is crucial not only for their survival but also for the overall health of the ocean. This can be achieved through stricter regulations on fishing and coastal development, as well as reducing pollution in our oceans. By protecting these unique creatures, we are also preserving the delicate balance of our marine ecosystems.
In Conclusion
Despite their elusive nature, eelpouts are fascinating creatures with unique features and behaviors. From their ability to produce antifreeze proteins to their unusual reproductive strategy, they have captured the interest of researchers and ocean enthusiasts alike. However, with the increasing threats to their habitat and population, it is crucial that we take action to protect these incredible creatures and their underwater homes. Only through conservation efforts can we ensure that eelpouts continue to thrive and survive in the depths of the ocean.
Meet the Eelpout: A Fascinating and Misunderstood Fish of North America
Disclaimer: The content provided is for informational purposes only. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information on this page 100%. All information provided here may change without prior notice.